
U.S. Consumer Price Index
Encyclopedia
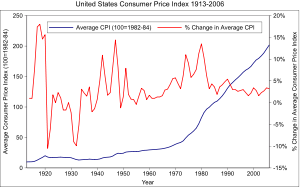
Consumer price index
A consumer price index measures changes in the price level of consumer goods and services purchased by households. The CPI, in the United States is defined by the Bureau of Labor Statistics as "a measure of the average change over time in the prices paid by urban consumers for a market basket of...
(CPI) is a time series
Time series
In statistics, signal processing, econometrics and mathematical finance, a time series is a sequence of data points, measured typically at successive times spaced at uniform time intervals. Examples of time series are the daily closing value of the Dow Jones index or the annual flow volume of the...
measure of the price level of consumer goods and services. The Bureau of Labor Statistics
Bureau of Labor Statistics
The Bureau of Labor Statistics is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics and statistics. The BLS is a governmental statistical agency that collects, processes, analyzes, and...
, which started the statistic in 1919, publishes the CPI on a monthly basis. The CPI is calculated by observing price changes among a wide array of products in urban areas and weighing these price changes by the share of income consumers spend purchasing them. The resulting statistic, measured as of the end of the month for which it is published, serves as one of the most popular measures of United States inflation
Inflation
In economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation also reflects an erosion in the purchasing power of money – a...
; however, the CPI focuses on approximating a cost-of-living index
Cost-of-living index
Cost of living is the cost of maintaining a certain standard of living. Changes in the cost of living over time are often operationalized in a cost of living index. Cost of living calculations are also used to compare the cost of maintaining a certain standard of living in different geographic areas...
not a general price index
Price index
A price index is a normalized average of prices for a given class of goods or services in a given region, during a given interval of time...
.
The CPI can be used to track changes in prices of all goods and services purchased for consumption by urban households, i.e., of the consumer basket. User fees (such as water and sewer service) and sales and excise taxes paid by the consumer are also included. Income taxes and investment items (like stocks, bonds, life insurance, and homes) are not included. The index measures inflation faced by consumers who live in urban areas designated by the U.S. Bureau of the Census.
The base period used for the current U.S. CPI is 1982-4.
Scope
BLS calculates the CPI for two population groups, one consisting only of wage earners and clerical workers and the other consisting of all urban consumers. In addition, a Core CPI, which excludes volatile food and energy prices and a Chained CPI are also widely used measures of consumer inflation.CPI for Urban Wage Earners and Clerical Workers (CPI-W)
The urban wage earner and clerical worker population consists of consumer units with clerical workers, sales workers, craft workers, operative, service workers, or laborers. (Excluded from this population are professional, managerial, and technical workers; the self-employed; short-term workers; the unemployed; and retirees and others not in the labor force.) More than one half of the consumer unit's income has to be earned from the above occupations, and at least one of the members must be employed for 37 weeks or more in an eligible occupation.The Consumer Price Index for Urban Wage Earners and Clerical Workers (CPI-W) is a continuation of the historical index that was introduced after World War I for use in wage negotiation. As new uses were developed for the CPI, the need for a broader and more representative index became apparent.CPI for All Urban Consumers (CPI-U)
The all-urban consumer population consists of all urban households in Metropolitan Statistical Areas (MSAs) and in urban places of 2,500 inhabitants or more. Non-farm consumers living in rural areas within MSAs are included, but the index excludes rural consumers and the military and institutional population. The Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers (CPI-U) introduced in 1978 is representative of the buying habits of approximately 80 percent of the non-institutional population of the United States, compared with 32 percent represented in the CPI-W. The methodology for producing the index is the same for both populations.Core CPI
The core CPI index excludes goods with high price volatility, such as food and energy. This measure of core inflation systematically excludes food and energy prices because, historically, they have been highly volatile and non-systemic. More specifically, food and energy prices are widely thought to be subject to large changes that often fail to persist and do not represent relative price changes. In many instances, large movements in food and energy prices arise because of supply disruptions such as drought or OPECOPEC
OPEC is an intergovernmental organization of twelve developing countries made up of Algeria, Angola, Ecuador, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela. OPEC has maintained its headquarters in Vienna since 1965, and hosts regular meetings...
-led cutbacks in production.
Chained CPI for All Urban Consumers (C-CPI-U)
This index applies to the same target population as the CPI-U. The same raw data are used, but a different formula is employed to calculate average prices. The chained CPI was developed to overcome a shortcoming of the CPI-U series, which does not account for the changes that people make in the composition of goods that they purchase over time, often in response to price changes. The alternative method of the C-CPI-U is intended to capture consumers' behavior as they respond to relative price changes.History
The Consumer Price Index was initiated during World War IWorld War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, when rapid increases in prices, particularly in shipbuilding centers, made an index essential for calculating cost-of-living adjustments in wages. To provide appropriate weighting patterns for the index, it reflected the relative importance of goods and services purchased in 92 different industrial centers in 1917-1919. Periodic collection of prices was started, and, in 1919, the Bureau of Labor Statistics began publication of separate indexes for 32 cities. Regular publication of a national index, the U.S. city average began in 1921, and indexes were estimated back to 1913 using records of food prices.
Because people's buying habits had changed substantially, a new study was made covering expenditures in the years 1934-1936, which provided the basis for a comprehensively revised index introduced in 1940. During World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, when many commodities were scarce and goods were rationed, the index weights were adjusted temporarily to reflect these shortages. In 1951, the BLS again made interim adjustments, based on surveys of consumer expenditures in seven cities between 1947 and 1949, to reflect the most important effects of immediate postwar changes in buying patterns. The index was again revised in 1953 and 1964.
In 1978, the index was revised to reflect the spending patterns based upon the surveys of consumer expenditures conducted in 1972-1974. A new and expanded 85-area sample was selected based on the 1970 Census of Population. The Point-of-Purchase Survey (POPS) was also introduced. POPS eliminated reliance on outdated secondary sources for screening samples of establishments or outlets where prices are collected. A second, more broadly based CPI for All Urban Consumers, the CPI-U was also introduced. The CPI-U took into account the buying patterns of professional and salaried workers, part-time workers, the self-employed, the unemployed, and retired people, in addition to wage earners and clerical workers.).
The hidden change in prices of housing
In January 1983 housing prices were replaced with owners' equivalent of rent because rents are more stable.Because house prices rose and fell more than rents during the housing bubble and crash, housing's effects on inflation and deflation are not reflected in the CPI.
Perceived overestimation of inflation
In 1995, the Senate Finance Committee appointed a commissionBoskin Commission
The Boskin Commission, formally called the "Advisory Commission to Study the Consumer Price Index", was appointed by the United States Senate in 1995 to study possible bias in the computation of the Consumer Price Index , which is used to measure inflation in the United States...
to study CPI's ability to estimate inflation. The CPI commission found in their study that the index overestimated the cost of living by a value between 0.8 to 1.6 percentage point
Percentage point
Percentage points are the unit for the arithmetic difference of two percentages.Consider the following hypothetical example: in 1980, 40 percent of the population smoked, and in 1990 only 30 percent smoked...
s.
If CPI overestimates inflation, then claims that real wage
Real wage
The term real wages refers to wages that have been adjusted for inflation. This term is used in contrast to nominal wages or unadjusted wages. Real wages provide a clearer representation of an individual's wages....
s have fallen over time could be unfounded. Additionally, real GDP growth, which is calculated using the CPI, would be severely underestimated. An overestimation of only a few tenths of a percentage point per annum compounds
Compound interest
Compound interest arises when interest is added to the principal, so that from that moment on, the interest that has been added also itself earns interest. This addition of interest to the principal is called compounding...
dramatically over time. In the 1970s and 80s the federal government
Federal government of the United States
The federal government of the United States is the national government of the constitutional republic of fifty states that is the United States of America. The federal government comprises three distinct branches of government: a legislative, an executive and a judiciary. These branches and...
began indexing several transfers and taxes including social security (see above Uses of the CPI). The overestimation of CPI would imply that the increases in these taxes and transfers have been greater than necessary, meaning the government and taxpayers have overpaid for them.
The Commission concluded that more than half of the overestimation was due to slow adjustments in the index to new products or changes in product quality. Because the index weights are only adjusted once every ten years, the CPI does not account for new technologies that are adopted by consumers quickly. For example, by 1996 there were over 47 million cellular phone users in the United States, but the weights for the CPI did not account for this new product until 1998. This new product lowered costs of communication when away from the home. The commission recommended that the BLS update weights more frequently than ten years to prevent new products from causing upward bias in the index.
Additional upward biases were said to come from several sources. Fixed weights do not accommodate consumer substitutions among commodities, such as buying more chicken when the price of beef increases. Because the CPI assumes that people continue to buy beef, it would increase even if people are buying chicken instead. However, this is by design: the CPI measures the change in expenses required for people to maintain the same standard of living. The Commission also found that 99% of all data were collected during the week, although an increasing amount of purchases happen during the weekend. Additional bias was said to stem from changes in retailing that were unaccounted for in the CPI.
Perceived underestimation of inflation
Some critics believe however, that because of changes to the way that the CPI is calculated, and because energy and food price changes are currently excluded from the Federal Reserve's calculation of "core inflationCore inflation
Core inflation is a measure of inflation which excludes certain items that face volatile price movements, notably food and energy.The preferred measure by the Federal Reserve of core inflation in the United States is the core Personal consumption expenditures price index...
," that inflation is being dramatically underestimated. The second argument is unrelated to the CPI, except insofar as the calculation of CPI is modified in response to a perceived overstatement of inflation.
The Federal Reserve's
Federal Reserve System
The Federal Reserve System is the central banking system of the United States. It was created on December 23, 1913 with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, largely in response to a series of financial panics, particularly a severe panic in 1907...
policy of ignoring food and energy prices when making interest rate decisions is often confused with the Bureau of Labor Statistics
Bureau of Labor Statistics
The Bureau of Labor Statistics is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics and statistics. The BLS is a governmental statistical agency that collects, processes, analyzes, and...
' measurement of the CPI. The BLS publishes both a headline CPI which counts food and energy prices, and also a CPI for All Items Less Food and Energy, or "Core" CPI. None of the prominent legislated uses of the CPI excludes food and energy. However, with regards to calculating inflation, the Federal Reserve no longer uses the CPI, preferring to use core PCE
Personal consumption expenditures price index
The PCE price index is a United States-wide indicator of the average increase in prices for all domestic personal...
instead.
Some critics believe that changes in CPI calculation due to the Boskin Commission
Boskin Commission
The Boskin Commission, formally called the "Advisory Commission to Study the Consumer Price Index", was appointed by the United States Senate in 1995 to study possible bias in the computation of the Consumer Price Index , which is used to measure inflation in the United States...
have led to dramatic cuts in inflation estimates. They believe that using pre-Boskin methods, which they also think are still used by most other countries, the current U.S. inflation is estimated to be around 7% per year. The BLS maintains that these beliefs are based on misunderstandings of the CPI. For example, the BLS has stated that changes made due to the introduction of the geometric mean formula to account for product substitution (one of the Boskin recommended changes) have lowered the measured rate of inflation by less than 0.3% per year, and the methods now used are commonly employed in the CPIs of developed nations.
Method of calculation
The calculation of the CPI involves a hybrid methodology consisting of two stages:In the first stage, elementary indices are created to show the price levels of very similar goods in the same area. For instance, there is an elementary index for "sports equipment in Seattle". As of June 2007, there are 8,018 of these elementary indices. (8,018 = 211 * 38, where 211 is the number of categories ("item strata") and 38 is the number of geographical areas considered.) All but a few of the elementary indices are based on geometric means formulas.
In the second stage, the elementary indices are combined to create a number of aggregate indices, including the CPI. (The CPI is an aggregate of all 8,018 basic indices. BLS also computes other aggregates computed uses smaller subsets of the basic indices. For instance, there is an all-items index for Boston, and an all-areas index for electricity.)
These aggregate indices (including the CPI) are calculated using a Laspeyres index computed as:

where:
 is the change in price level,
is the change in price level, is the price of each good
is the price of each good  in the first period,
in the first period, is the quantity of each good
is the quantity of each good  in the first period,
in the first period, is the price of each good
is the price of each good  in the second period.
in the second period.Weights of the CPI
The weight (or quantities, to use the above terminology) of an item in the CPI is derived from the expenditure on that item as estimated by the Consumer Expenditure SurveyConsumer Expenditure Survey
The Consumer Expenditure Survey is a Bureau of Labor Statistics survey that collects information on the buying habits of U.S. consumers. The program consists of two components — the Interview Survey and the Diary Survey — each with its own sample...
. This survey provides data on the average expenditure on selected items, such as white bread, gasoline and so on, that were purchased by the index population during the survey period. In a fixed-weight index such as the CPI, the implicit quantity of any item used in calculating the index remains the same from month to month.
A related concept is the relative importance of an item. The relative importance shows the share of total expenditure that would occur if quantities consumed were unaffected by changes in relative prices and actually remained constant. Although the implicit quantity weights remain fixed, the relative importance changes over time, reflecting average price changes. Items registering a greater than average price increase (or smaller decrease) become relatively more important.
Method evaluation
This two-stage method is relatively new. Before 1999, CPI used only Laspeyres indices, measures of the price changes in a fixed market basket of consumption goods and services of constant quantity and quality bought on average by urban consumers, either for all urban consumers (CPI-U) or for urban wage earners and clerical workers (CPI-W). It is argued that Laspeyres index systematically overstates inflation because it does not take into account changes in the quantities consumed that may occur as a response to price changes. The Laspeyres formula works under the assumption that consumers always buy the same amount of each good in the market basket, no matter what the price. The geometric mean price index formula used to calculate many of the elementary indices, in contrast, assumes that consumers will always spend the same amount of money on a good and shift the quantity they buy of that good based on the price. Critics argue that if due to price increases consumers shift from preferred goods to less preferred goods their standard of living has declined and therefore the geometric mean price formula understates inflation.Uses
- As an economic indicator. As the most widely used measure of inflation, the CPI is an indicator of the effectiveness of government fiscal and monetary policy. Especially for inflation targeting monetary policyMoney supplyIn economics, the money supply or money stock, is the total amount of money available in an economy at a specific time. There are several ways to define "money," but standard measures usually include currency in circulation and demand deposits .Money supply data are recorded and published, usually...
by the Federal Reserve; however, the Federal Reserve System has recently begun favoring the Personal consumption expenditures price indexPersonal consumption expenditures price indexThe PCE price index is a United States-wide indicator of the average increase in prices for all domestic personal...
(PCE) over the CPI as a measure of inflation. Business executives, labor leaders, and other private citizens also use the CPI as a guide in making economic decisions. - As a deflator of other economic series. The CPI and its components are used to adjust other economic series for price change and to translate these series into inflation-free dollars.
- As a means for indexationIndexationIndexation is a technique to adjust income payments by means of a price index, in order to maintain the purchasing power of the public after inflation....
(i.e. adjusting income payments). Over 2 million workers are covered by collective bargaining agreements which tie wages to the CPI. In the United States, the index affects the income of almost 80 million people as a result of statutory action: 47.8 million Social SecuritySocial securitySocial security is primarily a social insurance program providing social protection or protection against socially recognized conditions, including poverty, old age, disability, unemployment and others. Social security may refer to:...
beneficiaries, about 4.1 million militaryMilitaryA military is an organization authorized by its greater society to use lethal force, usually including use of weapons, in defending its country by combating actual or perceived threats. The military may have additional functions of use to its greater society, such as advancing a political agenda e.g...
and Federal Civil ServiceCivil serviceThe term civil service has two distinct meanings:* A branch of governmental service in which individuals are employed on the basis of professional merit as proven by competitive examinations....
retirees and survivors, and about 22.4 million food stamp recipients. Changes in the CPI also affect the cost of lunches for the 26.7 million children who eat lunch at school. Some private firms and individuals use the CPI to keep rents, royalties, alimony payments and child support payments in line with changing prices. Since 1985, the CPI has been used to adjust the Federal income taxIncome taxAn income tax is a tax levied on the income of individuals or businesses . Various income tax systems exist, with varying degrees of tax incidence. Income taxation can be progressive, proportional, or regressive. When the tax is levied on the income of companies, it is often called a corporate...
structure to prevent inflation-induced increases in taxes.
See also
- Consumer Price IndexConsumer price indexA consumer price index measures changes in the price level of consumer goods and services purchased by households. The CPI, in the United States is defined by the Bureau of Labor Statistics as "a measure of the average change over time in the prices paid by urban consumers for a market basket of...
- Cost of Living
- Boskin CommissionBoskin CommissionThe Boskin Commission, formally called the "Advisory Commission to Study the Consumer Price Index", was appointed by the United States Senate in 1995 to study possible bias in the computation of the Consumer Price Index , which is used to measure inflation in the United States...
- Stigler CommissionStigler CommissionFormally known as the Price Statistics Review Committee, the Stigler Commission was convened in 1961 to study the measurement of inflation in the United States. Headed by Nobel Prize winner George Stigler, its mandate was to conduct research into all types of price indices, including the Consumer...
- InflationInflationIn economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation also reflects an erosion in the purchasing power of money – a...
- Core inflationCore inflationCore inflation is a measure of inflation which excludes certain items that face volatile price movements, notably food and energy.The preferred measure by the Federal Reserve of core inflation in the United States is the core Personal consumption expenditures price index...
- Bureau of Labor StatisticsBureau of Labor StatisticsThe Bureau of Labor Statistics is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics and statistics. The BLS is a governmental statistical agency that collects, processes, analyzes, and...
- Producer Price IndexProducer price indexA Producer Price Index measures average changes in prices received by domestic producers for their output. It is one of several price indices.Its importance is being undermined by the steady decline in manufactured goods as a share of spending....
- GDP deflatorGDP deflatorIn economics, the GDP deflator is a measure of the level of prices of all new, domestically produced, final goods and services in an economy...
- Monetary PolicyMonetary policyMonetary policy is the process by which the monetary authority of a country controls the supply of money, often targeting a rate of interest for the purpose of promoting economic growth and stability. The official goals usually include relatively stable prices and low unemployment...
- Hedonic regressionHedonic regressionIn economics, hedonic regression or hedonic demand theory is a revealed preference method of estimating demand or value. It decomposes the item being researched into its constituent characteristics, and obtains estimates of the contributory value of each characteristic...
- Implicit price deflator (IPD)
- List of economics topics
External links
- U.S. Department of Labor, Bureau of Labor Statistics, CPI Home Page
- US Inflation Calculator & CPI US Inflation Calculator based on CPI data (1913-current).
- Note on a New, Supplemental Index of Consumer Price Change (Introduction to C-CPI-U)
- Consumer Price Index Chart Series Historical CPI data charted against other major economic indicators
- An Introductory look at the Chained Consumer Price Index
- Chained Consumer Price Index Top Picks at BLS

