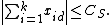±1-sequence
Encyclopedia
In mathematics, a ±1–sequence, (x1, x2, x3, ...), is a sequence
where each xi is one of {1, −1}.
Such sequences are commonly studied in discrepancy theory
.
, this problem is currently being studied by the Polymath project.
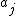 for j = 1, 2, …, N
for j = 1, 2, …, N
such that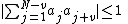
for all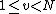 .
.
Barker codes of length 11 and 13 are used in direct-sequence spread spectrum
and pulse compression radar
systems because of their low autocorrelation
properties.
Sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an ordered list of objects . Like a set, it contains members , and the number of terms is called the length of the sequence. Unlike a set, order matters, and exactly the same elements can appear multiple times at different positions in the sequence...
where each xi is one of {1, −1}.
Such sequences are commonly studied in discrepancy theory
Discrepancy theory
In mathematics, discrepancy theory describes the deviation of a situation from the state one would like it to be. It is also called theory of irregularities of distribution. This refers to the theme of classical discrepancy theory, namely distributing points in some space such that they are evenly...
.
Erdős discrepancy problem
Let S=(x1, x2, x3,...) be a ±1–sequence, where xj denotes the jth term. The Erdős discrepancy problem asks whether there exists a sequence S and an integer CS, such that for any two positive integers d and k,, this problem is currently being studied by the Polymath project.
Barker Codes
A Barker code is a sequence of N values of +1 and −1,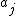 for j = 1, 2, …, N
for j = 1, 2, …, Nsuch that
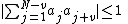
for all
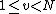 .
.Barker codes of length 11 and 13 are used in direct-sequence spread spectrum
Direct-sequence spread spectrum
In telecommunications, direct-sequence spread spectrum is a modulation technique. As with other spread spectrum technologies, the transmitted signal takes up more bandwidth than the information signal that is being modulated. The name 'spread spectrum' comes from the fact that the carrier signals...
and pulse compression radar
Pulse compression
Pulse compression is a signal processing technique mainly used in radar, sonar and echography to increase the range resolution as well as the signal to noise ratio...
systems because of their low autocorrelation
Autocorrelation
Autocorrelation is the cross-correlation of a signal with itself. Informally, it is the similarity between observations as a function of the time separation between them...
properties.
External links
- The Erdős discrepancy problem – Polymath Project