
10BASE2
Encyclopedia





Ethernet
Ethernet is a family of computer networking technologies for local area networks commercially introduced in 1980. Standardized in IEEE 802.3, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies....
that uses thin coaxial cable
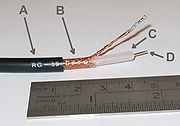
Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable, or coax, has an inner conductor surrounded by a flexible, tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing the same geometric axis...
(RG-58A/U
RG-58
RG-58/U is a type of coaxial cable often used for low-power signal and RF connections. The cable has a characteristic impedance of either 50 or 52 Ω. "RG" was originally a unit indicator for bulk RF cable in the U.S. military's Joint Electronics Type Designation System...
or similar, as opposed to the thicker RG-8 cable used in 10BASE5
10BASE5
10BASE5 was the original commercially available variant of Ethernet.For its physical layer it used cable similar to RG-8/U coaxial cable but with extra braided shielding. This is a stiff, diameter cable with an impedance of 50 ohms , a solid center conductor, a foam insulating filler, a shielding...
networks), terminated with BNC connector
BNC connector
The BNC connector ' is a common type of RF connector used for coaxial cable. It is used with radio, television, and other radio-frequency electronic equipment, test instruments, video signals, and was once a popular computer network connector. BNC connectors are made to match the characteristic...
s. During the mid to late 1980s this was the dominant 10 Mbit/s Ethernet standard, but due to the immense demand for high speed networking, the low cost of Category 5
Category 5 cable
Category 5 cable is a twisted pair cable for carrying signals. This type of cable is used in structured cabling for computer networks such as Ethernet. It is also used to carry other signals such as telephony and video. The cable is commonly connected using punch down blocks and modular connectors...
Ethernet cable, and the popularity of 802.11 wireless networks, both 10BASE2 and 10BASE5
10BASE5
10BASE5 was the original commercially available variant of Ethernet.For its physical layer it used cable similar to RG-8/U coaxial cable but with extra braided shielding. This is a stiff, diameter cable with an impedance of 50 ohms , a solid center conductor, a foam insulating filler, a shielding...
have become increasingly obsolete, but still exist in many locations.
Name origination
The name 10BASE2 is derived from several characteristics of the physical medium. The 10 comes from the maximum transmission speed of 10 Mbit/s (millions of bitBit
A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states...
s per second
Second
The second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
). The BASE stands for baseband
Baseband
In telecommunications and signal processing, baseband is an adjective that describes signals and systems whose range of frequencies is measured from close to 0 hertz to a cut-off frequency, a maximum bandwidth or highest signal frequency; it is sometimes used as a noun for a band of frequencies...
signalling, and the 2 supposedly represents the maximum segment length of 200 meters, but as a matter of fact, it can only run up to 185 meters. (The IEEE rounded 185 up to 200 to come up with the name 10Base2, to fit with the general standard).
Network design
10BASE2 coax cables had a maximum length of 185 meters (607 ft). The maximum practical number of nodes that can be connected to a 10BASE2 segment is limited to 30. In a 10BASE2 network, each segment of cable is connected to the transceiverMedium Attachment Unit
A Medium Attachment Unit is a transceiver which converts signals on an Ethernet cable to and from Attachment Unit Interface signals.On original 10BASE5 Ethernet, the MAU was typically clamped to the Ethernet cable...
(which is usually built into the network adaptor) using a BNC T-connector, with one segment connected to each female connector of the T.
As was the case with most other high-speed buses, Ethernet segments had to be terminated
Electrical termination
Electrical termination of a signal involves providing a terminator at the end of a wire or cable to prevent an RF signal from being reflected back from the end, causing interference...
with a resistor
Resistor
A linear resistor is a linear, passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.The current through a resistor is in direct proportion to the voltage across the resistor's terminals. Thus, the ratio of the voltage applied across a resistor's...
at each end. Each end of the cable had a 50 ohm (Ω) resistor attached. Typically this resistor was built into a male BNC
BNC connector
The BNC connector ' is a common type of RF connector used for coaxial cable. It is used with radio, television, and other radio-frequency electronic equipment, test instruments, video signals, and was once a popular computer network connector. BNC connectors are made to match the characteristic...
and attached to the last device on the bus. This is most commonly connected directly to the T-connector on a workstation though it does not technically have to be. A few devices such as Digital's DEMPR and DESPR had a built-in terminator and so could only be used at one physical end of the cable run. If termination was missing, or if there was a break in the cable, the AC
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
signal on the bus was reflected, rather than dissipated, when it reached the end. This reflected signal was indistinguishable from a collision, and so no communication would be able to take place.
Terminators had a metallic chain attached to them for grounding purposes, however many people never understood how to properly ground cabling and thus grounded the terminators at both ends rather than just one end. This caused many of the grounding loop problems during that era which caused network outages and/or data corruption when swells of electricity traversed the coaxial cabling's outer shield on its path to the ground with the least resistance.
When wiring a 10BASE2 network, special care has to be taken to ensure that cables are properly connected to all T-connectors, and appropriate terminators are installed. One, and only one, terminator must be connected to ground
Ground (electricity)
In electrical engineering, ground or earth may be the reference point in an electrical circuit from which other voltages are measured, or a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth....
via a ground wire. Bad contacts or shorts are especially difficult to diagnose, though a time-domain reflectometer
Time-domain reflectometer
A time-domain reflectometer is an electronic instrument used to characterize and locate faults in metallic cables . It can also be used to locate discontinuities in a connector, printed circuit board, or any other electrical path...
will find most problems quickly. A failure at any point of the network cabling tends to prevent all communications. For this reason, 10BASE2 networks could be difficult to maintain and were often replaced by 10BASE-T
Ethernet over twisted pair
Ethernet over twisted pair technologies use twisted-pair cables for the physical layer of an Ethernet computer network. Other Ethernet cable standards employ coaxial cable or optical fiber. Early versions developed in the 1980s included StarLAN followed by 10BASE-T. By the 1990s, fast, inexpensive...
networks, which (provided category 5 cable
Category 5 cable
Category 5 cable is a twisted pair cable for carrying signals. This type of cable is used in structured cabling for computer networks such as Ethernet. It is also used to carry other signals such as telephony and video. The cable is commonly connected using punch down blocks and modular connectors...
or better was used) also provided a good upgrade path to 100BASE-TX
Ethernet over twisted pair
Ethernet over twisted pair technologies use twisted-pair cables for the physical layer of an Ethernet computer network. Other Ethernet cable standards employ coaxial cable or optical fiber. Early versions developed in the 1980s included StarLAN followed by 10BASE-T. By the 1990s, fast, inexpensive...
. An alternative reliable connection has been established by the introduction of EAD-socket
EAD-socket
EAD is an abbreviation for German Ethernet-Anschlussdose. The EAD standard defines wall mounted Ethernet connection outlets that enjoy a higher reliability than standard BNC T-connectors....
s.
Comparisons to 10BASE-T
10BASE2 networks cannot generally be extended without breaking service temporarily for existing users and the presence of many joints in the cable also makes them very vulnerable to accidental or malicious disruption. There were proprietary wallport/cable systems that claimed to avoid these problems (e.g. SaferTap) but these never became widespread, possibly due to a lack of standardization.10BASE2 systems do have a number of advantages over 10BASE-T. They do not need the 10BASE-T hub, so the hardware cost is very low, and wiring can be particularly easy since only a single wire run is needed, which can be sourced from the nearest computer. These characteristics mean that 10BASE2 is ideal for a small network of two or three machines, perhaps in a home where easily concealed wiring may be an advantage. For a larger complex office network the difficulties of tracing poor connections make it impractical. Unfortunately for 10BASE2, by the time multiple home computer networks became common, the format had already been practically superseded. As a matter of fact, it is becoming very difficult to find 10BASE2-compatible network cards as distinct pieces of equipment, and integrated LAN controllers on motherboards don't have the connector, although the underlying logic may still be present.
See also
- 10BASE510BASE510BASE5 was the original commercially available variant of Ethernet.For its physical layer it used cable similar to RG-8/U coaxial cable but with extra braided shielding. This is a stiff, diameter cable with an impedance of 50 ohms , a solid center conductor, a foam insulating filler, a shielding...
(thicknet) - 10BASE-T10BASE-TEthernet over twisted pair technologies use twisted-pair cables for the physical layer of an Ethernet computer network. Other Ethernet cable standards employ coaxial cable or optical fiber. Early versions developed in the 1980s included StarLAN followed by 10BASE-T. By the 1990s, fast, inexpensive...
- Local area networkLocal area networkA local area network is a computer network that interconnects computers in a limited area such as a home, school, computer laboratory, or office building...
- Electrical terminationElectrical terminationElectrical termination of a signal involves providing a terminator at the end of a wire or cable to prevent an RF signal from being reflected back from the end, causing interference...
- Computer networkComputer networkA computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information....
- EAD-socketEAD-socketEAD is an abbreviation for German Ethernet-Anschlussdose. The EAD standard defines wall mounted Ethernet connection outlets that enjoy a higher reliability than standard BNC T-connectors....
- EthernetEthernetEthernet is a family of computer networking technologies for local area networks commercially introduced in 1980. Standardized in IEEE 802.3, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies....
- Bus networkBus networkA bus network topology is a network architecture in which a set of clients are connected via a shared communications line, called a bus. There are several common instances of the bus architecture, including one in the motherboard of most computers, and those in some versions of Ethernet...
- Coaxial CableCoaxial cableCoaxial cable, or coax, has an inner conductor surrounded by a flexible, tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing the same geometric axis...
- List of network buses

