
17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency
Encyclopedia
17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase III deficiency is a rare disorder of sexual development affecting testosterone
biosynthesis, which can produce impaired virilization
(traditionally termed male pseudohermaphroditism) of genetically male infants and children and excessive virilization of female adults.
It is an autosomal recessive
condition and is one of the few disorders of sexual development that can affect the primary and/or secondary sex characteristic
s of both males and females
.
(often complete absence of male sexual differentiation) can lead to development of female external genitalia. These children are raised as female, and their diagnosis is often discovered when there is absence of menarche (first menstruation) and when they begin to virilize during puberty (slowly become more like a man; deepening of the voice, acne, male musculature etc). At careful examination, testis can often be found in the inguinal channel.
 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase III deficiency is caused by mutation
17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase III deficiency is caused by mutation
s found in the 17Beta Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
(17BHSD3) gene. 17BHSD3 deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder.
Testosterone
Testosterone is a steroid hormone from the androgen group and is found in mammals, reptiles, birds, and other vertebrates. In mammals, testosterone is primarily secreted in the testes of males and the ovaries of females, although small amounts are also secreted by the adrenal glands...
biosynthesis, which can produce impaired virilization
Virilization
In biology and medicine, virilization refers to the biological development of sex differences, changes that make a male body different from a female body. Most of the changes of virilization are produced by androgens...
(traditionally termed male pseudohermaphroditism) of genetically male infants and children and excessive virilization of female adults.
It is an autosomal recessive
Recessive
In genetics, the term "recessive gene" refers to an allele that causes a phenotype that is only seen in a homozygous genotype and never in a heterozygous genotype. Every person has two copies of every gene on autosomal chromosomes, one from mother and one from father...
condition and is one of the few disorders of sexual development that can affect the primary and/or secondary sex characteristic
Secondary sex characteristic
Secondary sex characteristics are features that distinguish the two sexes of a species, but that are not directly part of the reproductive system. They are believed to be the product of sexual selection for traits which give an individual an advantage over its rivals in courtship and aggressive...
s of both males and females
XY sex-determination system
The XY sex-determination system is the sex-determination system found in humans, most other mammals, some insects and some plants . In this system, females have two of the same kind of sex chromosome , and are called the homogametic sex. Males have two distinct sex chromosomes , and are called...
.
Prevalence
In the Netherlands, 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase III deficiency is estimated to occur in 1:147,000 newborns.Clinical characteristics
17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase III deficiency is clinically characterized by either ambiguous external genitalia or complete female external genitalia at birth; as a consequence of impaired male sexual differentiation in 46,XY individuals. Further investigations on ambiguous genitalia will eventually lead to findings of intersexuality. Severely impaired virilizationVirilization
In biology and medicine, virilization refers to the biological development of sex differences, changes that make a male body different from a female body. Most of the changes of virilization are produced by androgens...
(often complete absence of male sexual differentiation) can lead to development of female external genitalia. These children are raised as female, and their diagnosis is often discovered when there is absence of menarche (first menstruation) and when they begin to virilize during puberty (slowly become more like a man; deepening of the voice, acne, male musculature etc). At careful examination, testis can often be found in the inguinal channel.
Biochemistry
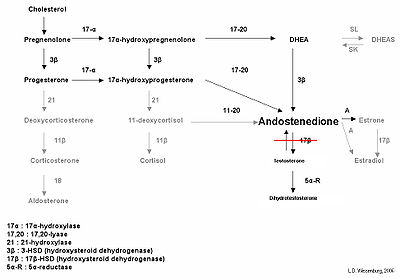
17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase III deficiency is characterized biochemically by decreased levels of testosterone and increased levels of androstenedione as a result of the defect in conversion of androstenedione into testosterone. This leads to clinically important higher ratio of androstenedione to testosterone (A'dion/T) (see figure).
Genetics

Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
s found in the 17Beta Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
17Beta Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
The 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases are a group of alcohol oxidoreductases which catalyse the dehydrogenation of 17-hydroxysteroids in steroidogenesis.Note that the major reactions catalysed by 17β-HSD The 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (17β-HSD enzymes) are a group of alcohol oxidoreductases...
(17BHSD3) gene. 17BHSD3 deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder.

