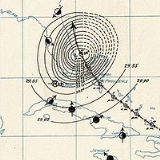
1899 Hurricane San Ciriaco
Encyclopedia
1899 San Ciriaco hurricane, also known as the 1899 Puerto Rico Hurricane, was the longest-lived Atlantic hurricane and the eleventh deadliest tropical cyclone
in the basin. It was an intense and long-lived Atlantic Cape Verde-type hurricane
which crossed Puerto Rico
over the two day period August 8 to August 9, 1899. Many deaths occurred as a result, due to flooding. The cyclone kept tropical storm strength or higher for 28 days, which makes it the longest duration Atlantic hurricane on record and the second-longest anywhere in the world (behind Hurricane John
in 1994). The estimated ACE
of 73.57 is the highest ever recorded in the Atlantic basin
.
of the tropical cyclone
are unknown, but it was first observed on August 3 to the west-southwest of Cape Verde
. That day, a ship reported tropical storm force winds and an atmospheric pressure
of 995 mbar
. For a few days, its exact path was unknown due to lack of observations, although it is estimated that the storm continued west-northwestward and attained hurricane status on August 5. On August 7, as it approached the northern Lesser Antilles
, the hurricane began to be tracked continuously by ship and land observations. By that date, it was quickly intensifying into a powerful storm, and a station on Montserrat
reported a pressure of 930 mbar. This suggested sustained winds of 150 mph (240 km/h), which would be the peak intensity of the hurricane.
Late on August 7, the hurricane moved through the northern Lesser Antilles, passing directly over Guadeloupe
and a short distance to the south of Saint Kitts
; in the latter island, a station reported winds of 120 mph (193 km/h). Continuing west-northwestward, the hurricane weakened slightly before making landfall
on August 8 along the southeastern coast of Puerto Rico
. The city of Guayama
recorded a pressure of 940 mbar, suggesting a landfall intensity of 140 mph (225 km/h).
August 8 was the namesday of Saint Cyriacus
. It crossed the island in an east-southeast to west-northwest direction, causing maximum wind speeds between 110 and 140 mph (177 and 225.3 km/h) throughout.
After it passed Puerto Rico, it brushed northern Dominican Republic
as a Category 3 hurricane, but passed north enough to not cause major damage. It passed through the Bahamas, retaining its strength as it moved slowly northward. After drifting northeastward, the hurricane turned northwestward, hitting the Outer Banks
on August 17. It drifted northeast ward over the state, re-emerging into the Atlantic on the 19th. It continued eastward, where it became extratropical on the 22nd.
The extratropical cyclone turned southeastward where, on August 26, it became a tropical storm again. Like most of the rest of its lifetime, it drifted, first to the northwest then to the east. It strengthened as it moved eastward, and on September 3, as it was moving through the Azores
, it again became a hurricane. The intensification didn't last long, and the hurricane became extratropical for the final time on the 4th. It dissipated that day while racing across the northeastern Atlantic.
reported a change in wind from the northeast to the northwest, the United States Weather Bureau ordered hurricane signals
at Roseau
, Dominica
, Basseterre
, Saint Kitts
, and San Juan, Puerto Rico
; later, a hurricane signal was raised at Santo Domingo
, Dominican Republic
. Information on the hurricane was also sent to other locations throughout the Caribbean.
Estimates of storm-related fatalities range from 3,100 to 3,400, with millions of dollars in crop damage in Puerto Rico. North Carolina had considerable tobacco
and corn
damage from the longevity of the strong winds and rain.
Overall, the island was swamped by 28 days of rain, contributing to the overall disaster (see History of Puerto Rico
).
, it was the deadliest hurricane to hit the island and the strongest at the time, until 30 years later when the island was hit by the Hurricane San Felipe Segundo
, a Category 5 hurricane, in 1928. It was also the tenth deadliest Atlantic hurricane ever recorded.
Also, with an Accumulated cyclone energy
of 73.57, it has the highest ACE of any Atlantic hurricane in history. In 2004, Hurricane Ivan
became the second Atlantic hurricane to surpass an ACE value of 70, but did not surpass the San Ciriaco hurricane.
San Ciriaco is also the longest lasting Atlantic hurricane in recorded history, lasting for 28 days (31 including subtropical time).
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
in the basin. It was an intense and long-lived Atlantic Cape Verde-type hurricane
Cape Verde-type hurricane
A Cape Verde-type hurricane is an Atlantic hurricane that develops near the Cape Verde islands, off the west coast of Africa. The average hurricane season has about two Cape Verde-type hurricanes, which are usually the largest and most intense storms of the season because they often have plenty of...
which crossed Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico , officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico , is an unincorporated territory of the United States, located in the northeastern Caribbean, east of the Dominican Republic and west of both the United States Virgin Islands and the British Virgin Islands.Puerto Rico comprises an...
over the two day period August 8 to August 9, 1899. Many deaths occurred as a result, due to flooding. The cyclone kept tropical storm strength or higher for 28 days, which makes it the longest duration Atlantic hurricane on record and the second-longest anywhere in the world (behind Hurricane John
Hurricane John (1994)
Hurricane John formed during the 1994 Pacific hurricane season and became both the longest-lasting and the farthest-traveling tropical cyclone ever observed...
in 1994). The estimated ACE
Accumulated cyclone energy
Accumulated cyclone energy is a measure used by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration to express the activity of individual tropical cyclones and entire tropical cyclone seasons, particularly the North Atlantic hurricane season. It uses an approximation of the energy used by a...
of 73.57 is the highest ever recorded in the Atlantic basin
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
.
Meteorological history
The exact originsTropical cyclogenesis
Tropical cyclogenesis is the term that describes the development and strengthening of a tropical cyclone in the atmosphere. The mechanisms through which tropical cyclogenesis occurs are distinctly different from those through which mid-latitude cyclogenesis occurs...
of the tropical cyclone
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
are unknown, but it was first observed on August 3 to the west-southwest of Cape Verde
Cape Verde
The Republic of Cape Verde is an island country, spanning an archipelago of 10 islands located in the central Atlantic Ocean, 570 kilometres off the coast of Western Africa...
. That day, a ship reported tropical storm force winds and an atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the force per unit area exerted into a surface by the weight of air above that surface in the atmosphere of Earth . In most circumstances atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point...
of 995 mbar
Bar (unit)
The bar is a unit of pressure equal to 100 kilopascals, and roughly equal to the atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level. Other units derived from the bar are the megabar , kilobar , decibar , centibar , and millibar...
. For a few days, its exact path was unknown due to lack of observations, although it is estimated that the storm continued west-northwestward and attained hurricane status on August 5. On August 7, as it approached the northern Lesser Antilles
Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles are a long, partly volcanic island arc in the Western Hemisphere. Most of its islands form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea with the Atlantic Ocean, with the remainder located in the southern Caribbean just north of South America...
, the hurricane began to be tracked continuously by ship and land observations. By that date, it was quickly intensifying into a powerful storm, and a station on Montserrat
Montserrat
Montserrat is a British overseas territory located in the Leeward Islands, part of the chain of islands called the Lesser Antilles in the West Indies. This island measures approximately long and wide, giving of coastline...
reported a pressure of 930 mbar. This suggested sustained winds of 150 mph (240 km/h), which would be the peak intensity of the hurricane.
Late on August 7, the hurricane moved through the northern Lesser Antilles, passing directly over Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe is an archipelago located in the Leeward Islands, in the Lesser Antilles, with a land area of 1,628 square kilometres and a population of 400,000. It is the first overseas region of France, consisting of a single overseas department. As with the other overseas departments, Guadeloupe...
and a short distance to the south of Saint Kitts
Saint Kitts
Saint Kitts Saint Kitts Saint Kitts (also known more formally as Saint Christopher Island (Saint-Christophe in French) is an island in the West Indies. The west side of the island borders the Caribbean Sea, and the eastern coast faces the Atlantic Ocean...
; in the latter island, a station reported winds of 120 mph (193 km/h). Continuing west-northwestward, the hurricane weakened slightly before making landfall
Landfall (meteorology)
Landfall is the event of a tropical cyclone or a waterspout coming onto land after being over water. When a waterspout makes landfall it is reclassified as a tornado, which can then cause damage inland...
on August 8 along the southeastern coast of Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico , officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico , is an unincorporated territory of the United States, located in the northeastern Caribbean, east of the Dominican Republic and west of both the United States Virgin Islands and the British Virgin Islands.Puerto Rico comprises an...
. The city of Guayama
Guayama, Puerto Rico
Guayama is a municipality of Puerto Rico founded on January 29, 1736 and located on the Southern Coastal Valley region, bordering the Caribbean, south of Cayey; east of Salinas; and west of Patillas and Arroyo. Guayama is spread over 9 wards and Guayama Pueblo...
recorded a pressure of 940 mbar, suggesting a landfall intensity of 140 mph (225 km/h).
August 8 was the namesday of Saint Cyriacus
Saint Cyriacus
Cyriacus, or Cyriac, is a Christian martyr who was killed in the persecution of Diocletian. He is one of twenty-seven saints, most of them martyrs, who bear this name, of whom only seven are honoured by a specific mention of their names in the Roman Martyrology.-Life:Of the Saint Cyriacus who,...
. It crossed the island in an east-southeast to west-northwest direction, causing maximum wind speeds between 110 and 140 mph (177 and 225.3 km/h) throughout.
After it passed Puerto Rico, it brushed northern Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic is a nation on the island of La Hispaniola, part of the Greater Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean region. The western third of the island is occupied by the nation of Haiti, making Hispaniola one of two Caribbean islands that are shared by two countries...
as a Category 3 hurricane, but passed north enough to not cause major damage. It passed through the Bahamas, retaining its strength as it moved slowly northward. After drifting northeastward, the hurricane turned northwestward, hitting the Outer Banks
Outer Banks
The Outer Banks is a 200-mile long string of narrow barrier islands off the coast of North Carolina, beginning in the southeastern corner of Virginia Beach on the east coast of the United States....
on August 17. It drifted northeast ward over the state, re-emerging into the Atlantic on the 19th. It continued eastward, where it became extratropical on the 22nd.
The extratropical cyclone turned southeastward where, on August 26, it became a tropical storm again. Like most of the rest of its lifetime, it drifted, first to the northwest then to the east. It strengthened as it moved eastward, and on September 3, as it was moving through the Azores
Azores
The Archipelago of the Azores is composed of nine volcanic islands situated in the middle of the North Atlantic Ocean, and is located about west from Lisbon and about east from the east coast of North America. The islands, and their economic exclusion zone, form the Autonomous Region of the...
, it again became a hurricane. The intensification didn't last long, and the hurricane became extratropical for the final time on the 4th. It dissipated that day while racing across the northeastern Atlantic.
Impact
On August 7, after stations in the Lesser AntillesLesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles are a long, partly volcanic island arc in the Western Hemisphere. Most of its islands form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea with the Atlantic Ocean, with the remainder located in the southern Caribbean just north of South America...
reported a change in wind from the northeast to the northwest, the United States Weather Bureau ordered hurricane signals
Tropical cyclone warnings and watches
Warnings and watches are two levels of alert issued by national weather forecasting bodies to coastal areas threatened by the imminent approach of a tropical cyclone of tropical storm or hurricane intensity. They are notices to the local population and civil authorities to make appropriate...
at Roseau
Roseau
-Architecture:The central district of Roseau is tightly packed with small and large houses and even larger modern concrete structures. There is little green or open space situated within the city, and this is even more so today, as many of the courtyards which was once commonplace within the city...
, Dominica
Dominica
Dominica , officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island nation in the Lesser Antilles region of the Caribbean Sea, south-southeast of Guadeloupe and northwest of Martinique. Its size is and the highest point in the country is Morne Diablotins, which has an elevation of . The Commonwealth...
, Basseterre
Basseterre
Basseterre , estimated population 15,500 in 2000, is the capital of the Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis in the West Indies. Geographically, the Basseterre port is located at , on the south western coast of Saint Kitts Island, and it is one of the chief commercial depots of the Leeward Islands...
, Saint Kitts
Saint Kitts
Saint Kitts Saint Kitts Saint Kitts (also known more formally as Saint Christopher Island (Saint-Christophe in French) is an island in the West Indies. The west side of the island borders the Caribbean Sea, and the eastern coast faces the Atlantic Ocean...
, and San Juan, Puerto Rico
San Juan, Puerto Rico
San Juan , officially Municipio de la Ciudad Capital San Juan Bautista , is the capital and most populous municipality in Puerto Rico, an unincorporated territory of the United States. As of the 2010 census, it had a population of 395,326 making it the 46th-largest city under the jurisdiction of...
; later, a hurricane signal was raised at Santo Domingo
Santo Domingo
Santo Domingo, known officially as Santo Domingo de Guzmán, is the capital and largest city in the Dominican Republic. Its metropolitan population was 2,084,852 in 2003, and estimated at 3,294,385 in 2010. The city is located on the Caribbean Sea, at the mouth of the Ozama River...
, Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic is a nation on the island of La Hispaniola, part of the Greater Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean region. The western third of the island is occupied by the nation of Haiti, making Hispaniola one of two Caribbean islands that are shared by two countries...
. Information on the hurricane was also sent to other locations throughout the Caribbean.
Estimates of storm-related fatalities range from 3,100 to 3,400, with millions of dollars in crop damage in Puerto Rico. North Carolina had considerable tobacco
Tobacco
Tobacco is an agricultural product processed from the leaves of plants in the genus Nicotiana. It can be consumed, used as a pesticide and, in the form of nicotine tartrate, used in some medicines...
and corn
Maize
Maize known in many English-speaking countries as corn or mielie/mealie, is a grain domesticated by indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica in prehistoric times. The leafy stalk produces ears which contain seeds called kernels. Though technically a grain, maize kernels are used in cooking as a vegetable...
damage from the longevity of the strong winds and rain.
Overall, the island was swamped by 28 days of rain, contributing to the overall disaster (see History of Puerto Rico
History of Puerto Rico
The history of Puerto Rico began with the settlement of the archipelago of Puerto Rico by the Ortoiroid people between 3000 and 2000 BC. Other tribes, such as the Saladoid and Arawak Indians, populated the island between 430 BC and 1000 AD. At the time of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New...
).
Records
Hurricane San Ciriaco set many records on its path. Killing nearly 3,500 people in Puerto RicoPuerto Rico
Puerto Rico , officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico , is an unincorporated territory of the United States, located in the northeastern Caribbean, east of the Dominican Republic and west of both the United States Virgin Islands and the British Virgin Islands.Puerto Rico comprises an...
, it was the deadliest hurricane to hit the island and the strongest at the time, until 30 years later when the island was hit by the Hurricane San Felipe Segundo
1928 Okeechobee Hurricane
The Okeechobee hurricane, or San Felipe Segundo hurricane, was a deadly hurricane that struck the Leeward Islands, Puerto Rico, the Bahamas, and Florida in September of the 1928 Atlantic hurricane season...
, a Category 5 hurricane, in 1928. It was also the tenth deadliest Atlantic hurricane ever recorded.
Also, with an Accumulated cyclone energy
Accumulated cyclone energy
Accumulated cyclone energy is a measure used by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration to express the activity of individual tropical cyclones and entire tropical cyclone seasons, particularly the North Atlantic hurricane season. It uses an approximation of the energy used by a...
of 73.57, it has the highest ACE of any Atlantic hurricane in history. In 2004, Hurricane Ivan
Hurricane Ivan
Hurricane Ivan was a large, long-lived, Cape Verde-type hurricane that caused widespread damage in the Caribbean and United States. The cyclone was the ninth named storm, the sixth hurricane and the fourth major hurricane of the active 2004 Atlantic hurricane season...
became the second Atlantic hurricane to surpass an ACE value of 70, but did not surpass the San Ciriaco hurricane.
San Ciriaco is also the longest lasting Atlantic hurricane in recorded history, lasting for 28 days (31 including subtropical time).
See also
- History of Puerto RicoHistory of Puerto RicoThe history of Puerto Rico began with the settlement of the archipelago of Puerto Rico by the Ortoiroid people between 3000 and 2000 BC. Other tribes, such as the Saladoid and Arawak Indians, populated the island between 430 BC and 1000 AD. At the time of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New...
- List of Atlantic hurricane records
- Puerto Rican immigration to HawaiiPuerto Rican immigration to HawaiiPuerto Rican immigration to Hawaii began when Puerto Rico's sugar industry was devastated by two hurricanes in 1899. The devastation caused a world wide shortage in sugar and a huge demand for the product from Hawaii...

