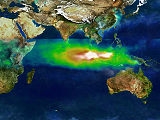
1997 Southeast Asian haze
Encyclopedia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
. The total costs of the Southeast Asian haze are estimated at US$9 billion due mainly to health care and disruption of air travel and business activities.
The influence of the 1997 fires in Kalimantan and Sumatra on ambient air quality was evident by July and peaked in September/October before weakening by November, when the delayed monsoonal rain
Monsoon
Monsoon is traditionally defined as a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation, but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with the asymmetric heating of land and sea...
extinguished the fires and improved air quality within the region. During the peak episode, satellite imagery (NASA/TOMS aerosol index maps) showed a haze layer which expanded over an area of more than 3 million km², covering large parts of Sumatra
Sumatra
Sumatra is an island in western Indonesia, westernmost of the Sunda Islands. It is the largest island entirely in Indonesia , and the sixth largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 with a population of 50,365,538...
and Kalimantan
Kalimantan
In English, the term Kalimantan refers to the Indonesian portion of the island of Borneo, while in Indonesian, the term "Kalimantan" refers to the whole island of Borneo....
. Its northward extension partially reached Malaysia, Singapore
Singapore
Singapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
, Brunei
Brunei
Brunei , officially the State of Brunei Darussalam or the Nation of Brunei, the Abode of Peace , is a sovereign state located on the north coast of the island of Borneo, in Southeast Asia...
and Thailand
Thailand
Thailand , officially the Kingdom of Thailand , formerly known as Siam , is a country located at the centre of the Indochina peninsula and Southeast Asia. It is bordered to the north by Burma and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the...
. During this period, particulate matter concentrations frequently exceeded national ambient air quality standards. Monthly mean horizontal visibility at most locations in Sumatra and Kalimantan in September was below 1 km and daily maximum visibility was frequently below 100 metres.
Causes
The 1997 Southeast Asian haze was caused mainly by slash and burnSlash and burn
Slash-and-burn is an agricultural technique which involves cutting and burning of forests or woodlands to create fields. It is subsistence agriculture that typically uses little technology or other tools. It is typically part of shifting cultivation agriculture, and of transhumance livestock...
techniques adopted by farmers in Indonesia. Slash and burn has been extensively used for many years as the cheapest and easiest means to clear the lands for traditional agriculture. Fire is also used during the long fallow rotation of the so-called jungle rubber in Sumatra and Kalimantan to remove most of the biomass
Biomass
Biomass, as a renewable energy source, is biological material from living, or recently living organisms. As an energy source, biomass can either be used directly, or converted into other energy products such as biofuel....
, including the woody parts before new plantations are re-established.
Fire may also be deliberately used as a weapon to claim property on the islands and provinces where land ownership is not clear, an action taken by both smallholders and large operators alike. After burning out its previous owner, the smallholder or large operator plants their own crops there, gaining de facto control over the disputed land .
During the fire season, dry fuels readily ignite and lead to large wild fires. These accidental fires may have the same underlying socio-economic and institutional problems. In cases like this, fire suppression can be very difficult and costly especially when they reach the highly flammable peat-swamp areas.
Effects
Particulate matter was the air pollutant that predominantly contributed to the haze and degradation in ambient air quality standards during this crisis. In all countries affected by the smoke hazeHaze
Haze is traditionally an atmospheric phenomenon where dust, smoke and other dry particles obscure the clarity of the sky. The World Meteorological Organization manual of codes includes a classification of horizontal obscuration into categories of fog, ice fog, steam fog, mist, haze, smoke, volcanic...
, an increase of acute health outcomes was observed. Health effects; included emergency room visits due to respiratory symptoms such as asthma
Asthma
Asthma is the common chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and bronchospasm. Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath...
, upper respiratory infection, decreased lung function as well as eye and skin irritation, were caused mainly by this particulate matter. In Singapore, for instance, health surveillance showed a 30% increase in hospital attendance due to air quality related symptoms. Generally, children and the elderly, as well as those with pre-existing respiratory and cardiac diseases were the most susceptible to adverse health outcomes from the haze
Haze
Haze is traditionally an atmospheric phenomenon where dust, smoke and other dry particles obscure the clarity of the sky. The World Meteorological Organization manual of codes includes a classification of horizontal obscuration into categories of fog, ice fog, steam fog, mist, haze, smoke, volcanic...
exposure. The smoke haze episode has added to the urban and industrial air pollution in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
, causing it to reach alarming levels in many metropolitan areas.
By scattering and absorbing light, the fire-related particulate also resulted in reduced visibility
Visibility
In meteorology, visibility is a measure of the distance at which an object or light can be clearly discerned. It is reported within surface weather observations and METAR code either in meters or statute miles, depending upon the country. Visibility affects all forms of traffic: roads, sailing...
; impairing transportation by air, land and water and seriously affecting the economies of Indonesia, Malaysia and Singapore. Among the economic sectors affected most were air, land and sea transportation, construction, tourism and agricultural industries. EEPSEA/WWF
World Wide Fund for Nature
The World Wide Fund for Nature is an international non-governmental organization working on issues regarding the conservation, research and restoration of the environment, formerly named the World Wildlife Fund, which remains its official name in Canada and the United States...
roughly estimated the economic value of the damages caused by the 1997 fires and haze. They estimated one billion US$ from haze-related damages for Indonesia only. The damages to Malaysia and Singapore are figured at 0.4 billion US$. Including the fire related damages, the total damages are estimated to amount to 4.5 billion US$. However, a variety of the damages such as decreased quality of life, loss of biodiversity and atmospheric impacts are difficult to establish.
Fire-related smoke haze episodes also reveal a social component: a large part of the population in Southeast Asia do not have the financial means to buy protective measures such as respiratory masks and air conditioning, nor are they able to refrain from outdoor work when air pollution is high.
Responses in the region
The 1997/98 smoke haze episode resulted in an intensification of regional measures towards cooperation in fire and smoke management which were initiated in the aftermath of similar episodes in 1991 and 1994. These measures include the establishment of ASEAN Haze Technical Task Force and the implementation of Regional and National Haze Action Plans. These plans define the ASEAN’s countries contributions to fire prevention, monitoring, fighting and other mitigation measures. Among others, it is also targeted to upgrade the national air quality and meteorological monitoring networks in order to strengthen the region’s early warning and monitoring system in respect to smoke haze.This incident made evident that in addition to sound fire management, a fundamental revision of the current land conversion and fire use policies is required to prevent the recurrence of similar episodes. Ground-based and airborne investigations of the smoke haze indicated that fires on peat swamp vegetation made a substantial contribution to the smoke haze development. However, this vegetation is estimated to have contributed only 30% of the total area burnt. Given this apparent particular relevance of peat swamp fires to the development of transboundary smoke haze, emission reduction and control strategies will have to focus on the prevention of fires in this type of vegetation as a matter of priority.
Future land use management will also have to consider 'air use' management. The health impacts and economic damages of the 1997/98 haze demonstrated that controlling future haze events represents an influencing factor for public and economic prosperity in the Southeast Asian region.
See also
- Air Quality IndexAir Quality IndexAir quality is defined as a measure of the condition of air relative to the requirements of one or more biotic species or to any human need or purpose. Air quality indices are numbers used by government agencies to characterize the quality of the air at a given location...
- Borneo peat swamp forestsBorneo peat swamp forestsThe Borneo peat swamp forests ecoregion, within the Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests Biome, are on the island of Borneo, which is divided between Brunei, Indonesia and Malaysia.-Location and description:...
- Pollutant Standards IndexPollutant Standards IndexThe Pollutant Standards Index, or PSI, provides a uniform system of measuring pollution levels for the major air pollutants. It is based on a scale devised by the United States Environmental Protection Agency to provide a way for broadcasts and newspapers to report air quality on a daily basis.The...
- HazeHazeHaze is traditionally an atmospheric phenomenon where dust, smoke and other dry particles obscure the clarity of the sky. The World Meteorological Organization manual of codes includes a classification of horizontal obscuration into categories of fog, ice fog, steam fog, mist, haze, smoke, volcanic...
- 2005 Malaysian haze2005 Malaysian hazeThe 2005 Malaysian haze was a week-long choking smog-like haze over Malaysia that almost brought the central part of Peninsular Malaysia to a standstill, prompted crisis talks with Indonesia and caused widespread inconvenience. The haze was at its worst on August 11, 2005...
- 2006 Southeast Asian haze
- Slash and burnSlash and burnSlash-and-burn is an agricultural technique which involves cutting and burning of forests or woodlands to create fields. It is subsistence agriculture that typically uses little technology or other tools. It is typically part of shifting cultivation agriculture, and of transhumance livestock...
- Asian brown cloudAsian brown cloudThe Asian brown cloud is a layer of air pollution that covers parts of South Asia, namely the northern Indian Ocean, India, and Pakistan. Viewed from satellite photos, the cloud appears as a giant brown stain hanging in the air over much of South Asia and the Indian Ocean every year between January...

