
2002-03 Australian bushfire season
Encyclopedia
The 2002–03 Australian bushfire season was a particularly extensive bushfire season in Australia
. It ran predominantly from December 2002 to March 2003 and involved over 3,000 separate fires in Victoria
alone. The 2003 Canberra bushfires
were also particularly severe.
The developing drought
in Australia and well below-average rainfall through winter and spring of 2002 established conditions conducive to above-average bushfire potential. During the 2002-03 season, there were 5,999 bushfires attended by the relevant agency Australia wide, 21,241,000 ha burnt and 7 fatalities.
Perhaps the most well known fire of the season was the Great Divide Fire Complex
that burnt in north-eastern Victoria
, the Victorian Alps
and Gippsland. This fire was ignited in several locations by multiple lightning
strikes and burnt 1.12 million hectares of land over the course of 2 months. Over 15,000 personnel were directly engaged with this fire complex.
hi

. Ongoing drought and lack of spring rain led to the Bureau of Meteorology predicting conditions comparable to that of the 1983 Ash Wednesday fires
and Fire Authorities were subsequently placed on high alert.
. The Big Desert Fire was, at the time, the biggest fire in Victoria in 20 years, affecting 181,400 hectares of predominantly public land and requiring significant resources to contain.
in East Gippsland
. The fire was seen as posing a major threat and required significant firefighting resources. At the time the main fires started on 8 January, a total of 180 DSE firefighters were allocated to the Yambulla fire, supported by bulldozers and firebombing aircraft. The fire was contained within a few days. The level of resourcing did, however, impact on the local resources available to fight the multiple outbreaks that followed.
On 7 January, multiple lightning strikes in north-east Victoria
and Gippsland
started hundreds of fires in Victoria that would remain uncontained until 7 March, a full 2 months later. In early February, at the peak of the fires, around 3,760 people were involved in the fire effort, excluding local CFA brigades. This figure includes 160 Defence Force staff, over 300 interstate firefighters, 33 alpine firefighting specialists from New Zealand and 35 personnel from the United States. In total, 15,725 personnel were directly engaged on the 2003 Great Divide Fire Complex.
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
. It ran predominantly from December 2002 to March 2003 and involved over 3,000 separate fires in Victoria
Victoria (Australia)
Victoria is the second most populous state in Australia. Geographically the smallest mainland state, Victoria is bordered by New South Wales, South Australia, and Tasmania on Boundary Islet to the north, west and south respectively....
alone. The 2003 Canberra bushfires
2003 Canberra bushfires
The Canberra bushfires of 2003 caused severe damage to the outskirts of Canberra, the Australian capital city. Almost 70% of the Australian Capital Territory’s pasture, forests and nature parks were severely damaged, and most of the renowned Mount Stromlo Observatory was destroyed...
were also particularly severe.
The developing drought
Drought
A drought is an extended period of months or years when a region notes a deficiency in its water supply. Generally, this occurs when a region receives consistently below average precipitation. It can have a substantial impact on the ecosystem and agriculture of the affected region...
in Australia and well below-average rainfall through winter and spring of 2002 established conditions conducive to above-average bushfire potential. During the 2002-03 season, there were 5,999 bushfires attended by the relevant agency Australia wide, 21,241,000 ha burnt and 7 fatalities.
Perhaps the most well known fire of the season was the Great Divide Fire Complex
2003 Eastern Victorian alpine bushfires
The Eastern Victorian alpine bushfires, also known as the Great Divide Fire Complex, started with eighty seven fires that were started by lightning in the north east of Victoria on 8 January 2003...
that burnt in north-eastern Victoria
Victoria (Australia)
Victoria is the second most populous state in Australia. Geographically the smallest mainland state, Victoria is bordered by New South Wales, South Australia, and Tasmania on Boundary Islet to the north, west and south respectively....
, the Victorian Alps
Australian Alps
The Australian Alps are the highest mountain ranges of mainland Australia. They are located in southeastern Australia and straddle the Australian Capital Territory, south-eastern New South Wales and eastern Victoria...
and Gippsland. This fire was ignited in several locations by multiple lightning
Lightning
Lightning is an atmospheric electrostatic discharge accompanied by thunder, which typically occurs during thunderstorms, and sometimes during volcanic eruptions or dust storms...
strikes and burnt 1.12 million hectares of land over the course of 2 months. Over 15,000 personnel were directly engaged with this fire complex.
Overview
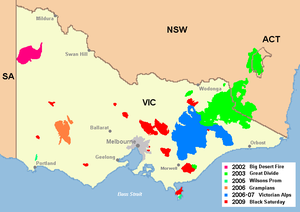
While hundreds or thousands of individual fires burn in any given bushfire season, areas of large fires that join and split are referred to as 'fire complexes'. The major fire complexes included:- Big Desert Fire (17–25 December)
- Yambulla Fire (6–11 January)
- Great Divide Fire Complex2003 Eastern Victorian alpine bushfiresThe Eastern Victorian alpine bushfires, also known as the Great Divide Fire Complex, started with eighty seven fires that were started by lightning in the north east of Victoria on 8 January 2003...
(7 January – 7 March) - Canberra bushfires2003 Canberra bushfiresThe Canberra bushfires of 2003 caused severe damage to the outskirts of Canberra, the Australian capital city. Almost 70% of the Australian Capital Territory’s pasture, forests and nature parks were severely damaged, and most of the renowned Mount Stromlo Observatory was destroyed...
(8 January – 14 February)
hi
Timeline

September-November 2002
The first fires of the 2002–03 season were reported in September 2002 in VictoriaVictoria (Australia)
Victoria is the second most populous state in Australia. Geographically the smallest mainland state, Victoria is bordered by New South Wales, South Australia, and Tasmania on Boundary Islet to the north, west and south respectively....
. Ongoing drought and lack of spring rain led to the Bureau of Meteorology predicting conditions comparable to that of the 1983 Ash Wednesday fires
Ash Wednesday fires
The Ash Wednesday bushfires, known in South Australia as Ash Wednesday II, were a series of bushfires that occurred in south-eastern Australia on 16 February 1983. Within twelve hours, more than 180 fires fanned by winds of up to 110 km per hour caused widespread destruction across the states...
and Fire Authorities were subsequently placed on high alert.
December 2002
From 17–25 December, multiple lightning strikes in the Big Desert Wilderness Park ignited vegetation creating a fire complex within the park south of MurrayvilleMurrayville, Victoria
Murrayville is a town on the section of the Mallee Highway between Ouyen and the South Australian border. It is about east of the South Australian border and north west of the state capital Melbourne, but east of Adelaide...
. The Big Desert Fire was, at the time, the biggest fire in Victoria in 20 years, affecting 181,400 hectares of predominantly public land and requiring significant resources to contain.
January-March 2003
On 6 January lightning ignited a fire near Yambulla, north west of GenoaGenoa, Victoria
Genoa is a town in Eastern Gippsland, Victoria, Australia. It is close to the New South Wales border where the Princes Highway crosses the Genoa river. The town is an important access point to the Croajingolong National Park...
in East Gippsland
East Gippsland
East Gippsland is the eastern region of Gippsland, Australia covering 31,740 square kilometres of Victoria. It has a population of 80,114....
. The fire was seen as posing a major threat and required significant firefighting resources. At the time the main fires started on 8 January, a total of 180 DSE firefighters were allocated to the Yambulla fire, supported by bulldozers and firebombing aircraft. The fire was contained within a few days. The level of resourcing did, however, impact on the local resources available to fight the multiple outbreaks that followed.
On 7 January, multiple lightning strikes in north-east Victoria
Victoria (Australia)
Victoria is the second most populous state in Australia. Geographically the smallest mainland state, Victoria is bordered by New South Wales, South Australia, and Tasmania on Boundary Islet to the north, west and south respectively....
and Gippsland
Gippsland
Gippsland is a large rural region in Victoria, Australia. It begins immediately east of the suburbs of Melbourne and stretches to the New South Wales border, lying between the Great Dividing Range to the north and Bass Strait to the south...
started hundreds of fires in Victoria that would remain uncontained until 7 March, a full 2 months later. In early February, at the peak of the fires, around 3,760 people were involved in the fire effort, excluding local CFA brigades. This figure includes 160 Defence Force staff, over 300 interstate firefighters, 33 alpine firefighting specialists from New Zealand and 35 personnel from the United States. In total, 15,725 personnel were directly engaged on the 2003 Great Divide Fire Complex.
Aftermath
In October 2003, the DSE published a report on the 2002–03 fires, which was considered a formidable task as it had to document over 3,000 separate fires and all the effects and personnel involved. The report concluded that the responses and containment of the fires was commendable. No lives were lost, and stock losses and property damage was kept to a minimum considering the area of land affected by the fires.Statistics

Victoria
- General:
- Over 3,000 fires burned from December to March.
- Firefighters worked on the ground for over 70 days.
- Over 1.12 million hectares were affected in Victoria's North East and Gippsland.
- Over 181,400 hectares were affected in the Big Desert.
- A total of 1.3 million hectares burnt throughout the season.
- No lives were lost as a direct result of these fires.
- Over 35 agencies were involved in fighting the fires and support roles, as well as interstate, New Zealand and US firefighters.
- The total personnel directly engaged on the North East and Gippsland fires was 15,725. A peak of over 3,760 personnel were involved at any one time. 8,595 were volunteers, more than half.
- 8,500 people attended over 250 community briefings.
- Structures:
- 41 houses were lost
- 1,000 houses were protected within the perimeter of the fires
- 7,000 houses were at risk within 5km from the fire perimeter
- 12,000 houses were at risk within 10km of the fire perimeter

