
6-j symbol
Encyclopedia
Wigner's 6-j symbols were introduced by
Eugene Paul Wigner in 1940, and published in 1965.
They are related to Racah's W-coefficients
by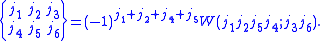
They have higher symmetry than Racah's W-coefficients.
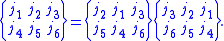
The 6-j symbol is also invariant if upper and lower arguments
are interchanged in any two columns: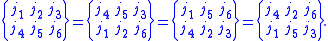
The 6-j symbol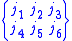
is zero unless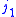 ,
, 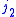 , and
, and 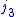 satisfy triangle conditions,
satisfy triangle conditions,
i.e.,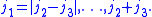
In combination with the symmetry relation for interchanging upper and lower arguments this
shows that triangle conditions must also be satisfied for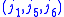 ,
,
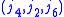 , and
, and 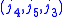 .
.
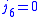 the expression for the 6-j symbol is:
the expression for the 6-j symbol is: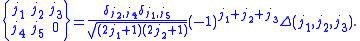
The function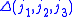 is equal to 1 when
is equal to 1 when 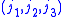 satisfy the triangle conditions,
satisfy the triangle conditions,
and zero otherwise. The symmetry relations can be used to find the expression when another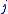 is equal
is equal
to zero.
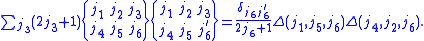
Eugene Paul Wigner in 1940, and published in 1965.
They are related to Racah's W-coefficients
Racah W-coefficient
Racah's W-coefficients were introduced by Giulio Racah in 1942. These coefficients have a purely mathematical definition. In physics they are used in calculations involving the quantum mechanical description of angular momentum, for example in atomic theory....
by
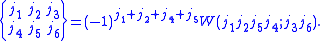
They have higher symmetry than Racah's W-coefficients.
Symmetry relations
The 6-j symbol is invariant under the permutation of any two columns: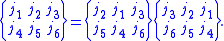
The 6-j symbol is also invariant if upper and lower arguments
are interchanged in any two columns:
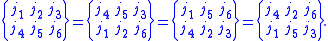
The 6-j symbol
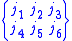
is zero unless
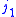 ,
, 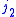 , and
, and 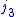 satisfy triangle conditions,
satisfy triangle conditions,i.e.,
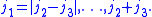
In combination with the symmetry relation for interchanging upper and lower arguments this
shows that triangle conditions must also be satisfied for
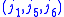 ,
,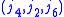 , and
, and 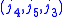 .
.Special case
When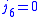 the expression for the 6-j symbol is:
the expression for the 6-j symbol is: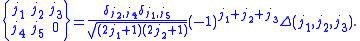
The function
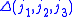 is equal to 1 when
is equal to 1 when 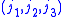 satisfy the triangle conditions,
satisfy the triangle conditions,and zero otherwise. The symmetry relations can be used to find the expression when another
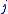 is equal
is equalto zero.
Orthogonality relation
The 6-j symbols satisfy this orthogonality relation: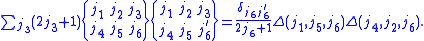
See also
- Clebsch–Gordan coefficients
- 3-jm symbol
- Racah W-coefficientRacah W-coefficientRacah's W-coefficients were introduced by Giulio Racah in 1942. These coefficients have a purely mathematical definition. In physics they are used in calculations involving the quantum mechanical description of angular momentum, for example in atomic theory....
- 9-j symbol
External links
(Gives exact answer)- Frederik J Simons: Matlab software archive, the code SIXJ.M Static table for j1 <= 11/2.

