
Abscissa
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, abscissa (plural abscissae or abscissæ) refers to that element of an ordered pair
which is plotted on the horizontal axis of a two-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system
, as opposed to the ordinate
. It is the first of the two terms (often labeled x and y) which define the location of a point in such a coordinate system.
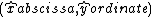
The usage of the word abscissa is first recorded in 1659 by Stefano degli Angeli, a mathematics professor in Rome
, according to Moritz Cantor
. Soon thereafter, Leibniz
used the term extensively in Latin
in his Mathematische Schriften (1692), after which it became a standardized mathematical term. Neither the terms abscissa nor ordinate were used by Descartes
, for whom the Cartesian coordinate system is most closely associated. The first occurrence of the term in English
is found in An Institution of Fluxions by the English mathematician Humphry Ditton
(1706), where he spells the word abscisse, possibly denoting the plural.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, abscissa (plural abscissae or abscissæ) refers to that element of an ordered pair
Ordered pair
In mathematics, an ordered pair is a pair of mathematical objects. In the ordered pair , the object a is called the first entry, and the object b the second entry of the pair...
which is plotted on the horizontal axis of a two-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system
Cartesian coordinate system
A Cartesian coordinate system specifies each point uniquely in a plane by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances from the point to two fixed perpendicular directed lines, measured in the same unit of length...
, as opposed to the ordinate
Ordinate
In mathematics, ordinate refers to that element of an ordered pair which is plotted on the vertical axis of a two-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system, as opposed to the abscissa...
. It is the first of the two terms (often labeled x and y) which define the location of a point in such a coordinate system.
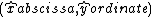
The usage of the word abscissa is first recorded in 1659 by Stefano degli Angeli, a mathematics professor in Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
, according to Moritz Cantor
Moritz Cantor
Moritz Benedikt Cantor was a German historian of mathematics.He was born at Mannheim, Germany. He came from a family that had emigrated to the Netherlands from Portugal, another branch of which had established itself in Russia, where Georg Cantor was born...
. Soon thereafter, Leibniz
Gottfried Leibniz
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz was a German philosopher and mathematician. He wrote in different languages, primarily in Latin , French and German ....
used the term extensively in Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
in his Mathematische Schriften (1692), after which it became a standardized mathematical term. Neither the terms abscissa nor ordinate were used by Descartes
René Descartes
René Descartes ; was a French philosopher and writer who spent most of his adult life in the Dutch Republic. He has been dubbed the 'Father of Modern Philosophy', and much subsequent Western philosophy is a response to his writings, which are studied closely to this day...
, for whom the Cartesian coordinate system is most closely associated. The first occurrence of the term in English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
is found in An Institution of Fluxions by the English mathematician Humphry Ditton
Humphry Ditton
Humphry Ditton was an English mathematician.-Life:Ditton was born at Salisbury. He studied theology, and was for some years a dissenting minister at Tonbridge, but on the death of his father he devoted himself to the congenial study of mathematics...
(1706), where he spells the word abscisse, possibly denoting the plural.
See also
- abscissa on Wiktionary
- Function (mathematics)Function (mathematics)In mathematics, a function associates one quantity, the argument of the function, also known as the input, with another quantity, the value of the function, also known as the output. A function assigns exactly one output to each input. The argument and the value may be real numbers, but they can...
- Relation (mathematics)Relation (mathematics)In set theory and logic, a relation is a property that assigns truth values to k-tuples of individuals. Typically, the property describes a possible connection between the components of a k-tuple...

