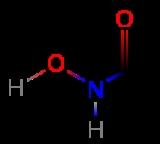
Acetohydroxamic acid
Encyclopedia
Acetohydroxamic acid is a drug
that is a potent and irreversible inhibitor of bacteria
l and plant
urease
usually used for urinary tract infection
s. The molecule is similar to urea
but is not hydrolyzable by the urease enzyme (Fishbein and Carbone, 1965).
Drug
A drug, broadly speaking, is any substance that, when absorbed into the body of a living organism, alters normal bodily function. There is no single, precise definition, as there are different meanings in drug control law, government regulations, medicine, and colloquial usage.In pharmacology, a...
that is a potent and irreversible inhibitor of bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
l and plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
urease
Urease
Urease is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia. The reaction occurs as follows:In 1926, James Sumner showed that urease is a protein. Urease is found in bacteria, yeast, and several higher plants. The structure of urease was first solved by P.A...
usually used for urinary tract infection
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
s. The molecule is similar to urea
Urea
Urea or carbamide is an organic compound with the chemical formula CO2. The molecule has two —NH2 groups joined by a carbonyl functional group....
but is not hydrolyzable by the urease enzyme (Fishbein and Carbone, 1965).

