
Agni missile system
Encyclopedia
The Agni missile is a family of Medium
to Intercontinental
range ballistic missiles developed by India
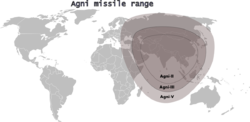
under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Program. As of 2008, the Agni missile family comprises three deployed variants:
on 25 january 2002. Weighing 12 tonne with a length of 15 metres, Agni-I has a range of 700–1200 km and is capable of carrying a conventional payload of 1000 kg (2,200 lb) or a nuclear
warhead at a speed of 2.5 km/s. Agni missiles consist of one (short range) or two stages
(intermediate range). These are rail and road mobile and powered by solid propellants. Agni-I is used by the Strategic Force Command (SFC) of the Indian Army
.
.jpg) Agni-II has a range of 2,000–2,500 km has a length of 20 metres, diameter of one metre and weighs around 17 tonnes. Agni - II uses solid propellant in first stage and liquid propellant in the upper stage. They are claimed to be a part of the "credible deterrence
Agni-II has a range of 2,000–2,500 km has a length of 20 metres, diameter of one metre and weighs around 17 tonnes. Agni - II uses solid propellant in first stage and liquid propellant in the upper stage. They are claimed to be a part of the "credible deterrence
" against China
and Pakistan
. India stated that its nuclear and missile development programmes are not Pakistan-centric, that the Pakistani threat is only a marginal factor in New Delhi's security calculus and that Agni is at the heart of deterrence in the larger context of Sino-Indian equation. The Agni-II can reach most parts of western, central and southern China.
. After the launch, it was reported that the second stage of the rocket had failed to separate and the missile had fallen well short of its target. Agni-III was again tested on April 12, 2007, this time successfully, from the Wheeler Island off the coast of Orissa.On May 7, 2008 India again successfully test fired this missile. This was the third consecutive test; it validated the missile's operational readiness while extending the reach of India's nuclear deterrent to most high-value targets of the nation's most likely adversaries. Agni-III has a range of 3,500 km, and can take a warhead of 1.5 tonnes. Its range falls within the reach of most major Chinese cities, including Beijing
and Shanghai
. Agni III uses solid propellant in both stages.
It has been reported that the missile's Circular Error Probable
(CEP) lies in the range of 40 meters, This would make the Agni-III most accurate strategic ballistic missiles of its range class in the world. This is of special significance because a highly accurate ballistic missile increases the "kill efficiency" of the weapon; it allows Indian weapons designers to use smaller yield nuclear warheads (200 Kiloton thermonuclear or boosted fission) while increase the lethality of the strike. This permits India to deploy a much larger nuclear force using less fissile/fusion material (Plutonium/Lithium Deuteride) than other World nuclear powers. Older ballistic missiles, such as those deployed by earlier nuclear powers required larger yield (1-2 Megaton) warheads to achieve the same level of lethality. It has also been reported that with smaller payloads, the Agni-III can hit strategic targets well beyond 3,500 km.
. With a range of 2,500-3,500 km Agni-IV bridges the gap between Agni II and Agni III. Agni IV can take a warhead of 1 tonne. It is designed to increase the kill efficiency along with a higher range performance. Agni IV is equipped with state-of-the-art technologies, that includes indigenously developed ring laser gyro and composite rocket motor. Its a two-stage missile powered by solid propellant. Its length is 20 meters and launch weight 17 tonnes. It can be fired from a road mobile launcher.
Agni-V ICBM has been designed with addition of a third composite stage to the two-stage Agni-III missile. To reduce the weight it is built with high composite content. The 17.5-metre-long Agni-V would be a canister launch missile system so as to ensure that it has the requisite operational flexibility and can be swiftly transported and fired from anywhere. Agni-V weighs around 49 tonnes, one tonne more than Agni III even then its range has gone up to far more.
Medium-range ballistic missile
A medium-range ballistic missile , is a type of ballistic missile with medium range, this last classification depending on the standards of certain organizations. Within the U.S. Department of Defense, a medium range missile is defined by having a maximum range of between 1,000 and 3,000 km1...
to Intercontinental
Intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile is a ballistic missile with a long range typically designed for nuclear weapons delivery...
range ballistic missiles developed by India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Program. As of 2008, the Agni missile family comprises three deployed variants:

- Agni-I Medium range ballistic missile, 700 – 1200 km range.
- Agni-II intermediate range ballistic missile, 2,000- 2,500 km range.
- Agni-III intermediate range ballistic missile, 3,000 - 5,500 km range.
- Agni-IVAgni-IVAgni-IV is the fourth in the Agni series of missiles which was earlier known as Agni II prime. Agni-IV was tested on November 15, 2011 from Wheeler island off the coast of the eastern state of Orissa. With a range of 2,500-3,500 km Agni-IV bridges the gap between Agni II and Agni III. Agni IV...
intermediate range ballistic missile, 3,200- 3,700 km range - Agni-V intercontinental ballistic missile, 5,000 km range (under development).
- Agni-VIAgni-VIAgni-VI is an intercontinental ballistic missile being developed by India and the latest & most advanced version among the Agni program...
intercontinental ballistic missile, 10,000 km range (under development)
Agni-I
Agni-I was first tested at the Integrated Test Range in ChandipurChandipur
Chandipur also known as Chandipur-on-sea is a small sea resort in Baleswar District, Orissa, India. The resort is on the Bay of Bengal and is approximately 16 kilometers from the Baleswar Railway Station. The beach is unique in that the water recedes anywhere from 1 kilometer to 4 kilometers during...
on 25 january 2002. Weighing 12 tonne with a length of 15 metres, Agni-I has a range of 700–1200 km and is capable of carrying a conventional payload of 1000 kg (2,200 lb) or a nuclear
Nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission or a combination of fission and fusion. Both reactions release vast quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first fission bomb test released the same amount...
warhead at a speed of 2.5 km/s. Agni missiles consist of one (short range) or two stages
Multistage rocket
A multistage rocket is a rocket that usestwo or more stages, each of which contains its own engines and propellant. A tandem or serial stage is mounted on top of another stage; a parallel stage is attached alongside another stage. The result is effectively two or more rockets stacked on top of or...
(intermediate range). These are rail and road mobile and powered by solid propellants. Agni-I is used by the Strategic Force Command (SFC) of the Indian Army
Indian Army
The Indian Army is the land based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. With about 1,100,000 soldiers in active service and about 1,150,000 reserve troops, the Indian Army is the world's largest standing volunteer army...
.
Agni-II
.jpg)
Deterrence theory
Deterrence theory gained increased prominence as a military strategy during the Cold War with regard to the use of nuclear weapons, and features prominently in current United States foreign policy regarding the development of nuclear technology in North Korea and Iran. Deterrence theory however was...
" against China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
and Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
. India stated that its nuclear and missile development programmes are not Pakistan-centric, that the Pakistani threat is only a marginal factor in New Delhi's security calculus and that Agni is at the heart of deterrence in the larger context of Sino-Indian equation. The Agni-II can reach most parts of western, central and southern China.
Agni-III
Agni-III is the third in the Agni series of missiles. Agni-III was tested on July 9, 2006 from Wheeler island off the coast of the eastern state of OrissaOrissa
Orissa , officially Odisha since Nov 2011, is a state of India, located on the east coast of India, by the Bay of Bengal. It is the modern name of the ancient nation of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Maurya Emperor Ashoka in 261 BC. The modern state of Orissa was established on 1 April...
. After the launch, it was reported that the second stage of the rocket had failed to separate and the missile had fallen well short of its target. Agni-III was again tested on April 12, 2007, this time successfully, from the Wheeler Island off the coast of Orissa.On May 7, 2008 India again successfully test fired this missile. This was the third consecutive test; it validated the missile's operational readiness while extending the reach of India's nuclear deterrent to most high-value targets of the nation's most likely adversaries. Agni-III has a range of 3,500 km, and can take a warhead of 1.5 tonnes. Its range falls within the reach of most major Chinese cities, including Beijing
Beijing
Beijing , also known as Peking , is the capital of the People's Republic of China and one of the most populous cities in the world, with a population of 19,612,368 as of 2010. The city is the country's political, cultural, and educational center, and home to the headquarters for most of China's...
and Shanghai
Shanghai
Shanghai is the largest city by population in China and the largest city proper in the world. It is one of the four province-level municipalities in the People's Republic of China, with a total population of over 23 million as of 2010...
. Agni III uses solid propellant in both stages.
It has been reported that the missile's Circular Error Probable
Circular error probable
In the military science of ballistics, circular error probable is an intuitive measure of a weapon system's precision...
(CEP) lies in the range of 40 meters, This would make the Agni-III most accurate strategic ballistic missiles of its range class in the world. This is of special significance because a highly accurate ballistic missile increases the "kill efficiency" of the weapon; it allows Indian weapons designers to use smaller yield nuclear warheads (200 Kiloton thermonuclear or boosted fission) while increase the lethality of the strike. This permits India to deploy a much larger nuclear force using less fissile/fusion material (Plutonium/Lithium Deuteride) than other World nuclear powers. Older ballistic missiles, such as those deployed by earlier nuclear powers required larger yield (1-2 Megaton) warheads to achieve the same level of lethality. It has also been reported that with smaller payloads, the Agni-III can hit strategic targets well beyond 3,500 km.
Agni-IV
Agni-IV is the fourth in the Agni series of missiles which was earlier known as Agni II prime. Agni-IV was tested on November 15, 2011 from Wheeler island off the coast of the eastern state of OrissaOrissa
Orissa , officially Odisha since Nov 2011, is a state of India, located on the east coast of India, by the Bay of Bengal. It is the modern name of the ancient nation of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Maurya Emperor Ashoka in 261 BC. The modern state of Orissa was established on 1 April...
. With a range of 2,500-3,500 km Agni-IV bridges the gap between Agni II and Agni III. Agni IV can take a warhead of 1 tonne. It is designed to increase the kill efficiency along with a higher range performance. Agni IV is equipped with state-of-the-art technologies, that includes indigenously developed ring laser gyro and composite rocket motor. Its a two-stage missile powered by solid propellant. Its length is 20 meters and launch weight 17 tonnes. It can be fired from a road mobile launcher.
Agni-V
Agni-V is a solid fueled Intercontinential Ballistic Missile (ICBM) under development by DRDO of India. It will greatly expand India's reach to strike targets up to 5,000 km away. Missile tests are expected to begin in December 2011.Agni-V ICBM has been designed with addition of a third composite stage to the two-stage Agni-III missile. To reduce the weight it is built with high composite content. The 17.5-metre-long Agni-V would be a canister launch missile system so as to ensure that it has the requisite operational flexibility and can be swiftly transported and fired from anywhere. Agni-V weighs around 49 tonnes, one tonne more than Agni III even then its range has gone up to far more.

