
Agriculture in India
Encyclopedia
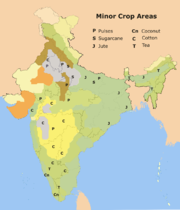

India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
has a significant history
History of agriculture
Agriculture was developed at least 10,000 years ago, and it has undergone significant developments since the time of the earliest cultivation. The Fertile Crescent of Western Asia, Egypt, and India were sites of the earliest planned sowing and harvesting of plants that had previously been gathered...
. Today, India ranks second worldwide in farm output. Agriculture
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
and allied sectors like forestry
Forestry
Forestry is the interdisciplinary profession embracing the science, art, and craft of creating, managing, using, and conserving forests and associated resources in a sustainable manner to meet desired goals, needs, and values for human benefit. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands...
and logging
Logging
Logging is the cutting, skidding, on-site processing, and loading of trees or logs onto trucks.In forestry, the term logging is sometimes used in a narrow sense concerning the logistics of moving wood from the stump to somewhere outside the forest, usually a sawmill or a lumber yard...
accounted for 16.6% of the GDP in 2007, % of the total workforce and despite a steady decline of its share in the GDP, is still the largest economic sector and plays a significant role in the overall social-economic development of India.
India is the largest producer in the world of fresh fruit, anise
Anise
Anise , Pimpinella anisum, also called aniseed, is a flowering plant in the family Apiaceae native to the eastern Mediterranean region and Southwest Asia. Its flavor resembles that of liquorice, fennel, and tarragon.- Biology :...
, fennel
Fennel
Fennel is a plant species in the genus Foeniculum . It is a member of the family Apiaceae . It is a hardy, perennial, umbelliferous herb, with yellow flowers and feathery leaves...
, badian
Star anise
Illicium verum, commonly called Star anise, star aniseed, or Chinese star anise, is a spice that closely resembles anise in flavor, obtained from the star-shaped pericarp of Illicium verum, a small native evergreen tree of northeast Vietnam and southwest China...
, coriander
Coriander
Coriander is an annual herb in the family Apiaceae. Coriander is native to southern Europe and North Africa to southwestern Asia. It is a soft, hairless plant growing to tall. The leaves are variable in shape, broadly lobed at the base of the plant, and slender and feathery higher on the...
, tropical fresh fruit, jute
Jute
Jute is a long, soft, shiny vegetable fibre that can be spun into coarse, strong threads. It is produced from plants in the genus Corchorus, which has been classified in the family Tiliaceae, or more recently in Malvaceae....
, pigeon pea
Pigeon pea
The pigeon pea , also known as tropical green pea, toor dāl or arhar dāl , ತೊಗರಿ ಬೇಳೆ kadios , or Congo pea or gungo pea , pois Congo , gandul , gunga pea, or no-eye pea, [Cajanus...
s, pulses, spice
Spice
A spice is a dried seed, fruit, root, bark, or vegetative substance used in nutritionally insignificant quantities as a food additive for flavor, color, or as a preservative that kills harmful bacteria or prevents their growth. It may be used to flavour a dish or to hide other flavours...
s, millet
Millet
The millets are a group of small-seeded species of cereal crops or grains, widely grown around the world for food and fodder. They do not form a taxonomic group, but rather a functional or agronomic one. Their essential similarities are that they are small-seeded grasses grown in difficult...
s, castor oil
Castor oil
Castor oil is a vegetable oil obtained from the castor bean . Castor oil is a colorless to very pale yellow liquid with mild or no odor or taste. Its boiling point is and its density is 961 kg/m3...
seed, sesame
Sesame
Sesame is a flowering plant in the genus Sesamum. Numerous wild relatives occur in Africa and a smaller number in India. It is widely naturalized in tropical regions around the world and is cultivated for its edible seeds, which grow in pods....
seeds, safflower
Safflower
Safflower is a highly branched, herbaceous, thistle-like annual. It is commercially cultivated for vegetable oil extracted from the seeds. Plants are 30 to 150 cm tall with globular flower heads having yellow, orange or red flowers. Each branch will usually have from one to five flower heads...
seeds, lemon
Lemon
The lemon is both a small evergreen tree native to Asia, and the tree's ellipsoidal yellow fruit. The fruit is used for culinary and non-culinary purposes throughout the world – primarily for its juice, though the pulp and rind are also used, mainly in cooking and baking...
s, lime
Lime (fruit)
Lime is a term referring to a number of different citrus fruits, both species and hybrids, which are typically round, green to yellow in color, 3–6 cm in diameter, and containing sour and acidic pulp. Limes are a good source of vitamin C. Limes are often used to accent the flavors of foods and...
s, cow's milk
Milk
Milk is a white liquid produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals before they are able to digest other types of food. Early-lactation milk contains colostrum, which carries the mother's antibodies to the baby and can reduce the risk of many...
, dry chillies and peppers, chick peas, cashew nuts, okra
Okra
Okra is a flowering plant in the mallow family. It is valued for its edible green seed pods. The geographical origin of okra is disputed, with supporters of South Asian, Ethiopian and West African origins...
, ginger
Ginger
Ginger is the rhizome of the plant Zingiber officinale, consumed as a delicacy, medicine, or spice. It lends its name to its genus and family . Other notable members of this plant family are turmeric, cardamom, and galangal....
, turmeric
Turmeric
Turmeric is a rhizomatous herbaceous perennial plant of the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. It is native to tropical South Asia and needs temperatures between 20 °C and 30 °C and a considerable amount of annual rainfall to thrive...
guava
Guava
Guavas are plants in the myrtle family genus Psidium , which contains about 100 species of tropical shrubs and small trees. They are native to Mexico, Central America, and northern South America...
s, mango
Mango
The mango is a fleshy stone fruit belonging to the genus Mangifera, consisting of numerous tropical fruiting trees in the flowering plant family Anacardiaceae. The mango is native to India from where it spread all over the world. It is also the most cultivated fruit of the tropical world. While...
es, goat
Goat
The domestic goat is a subspecies of goat domesticated from the wild goat of southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the Bovidae family and is closely related to the sheep as both are in the goat-antelope subfamily Caprinae. There are over three hundred distinct breeds of...
milk and buffalo
Water Buffalo
The water buffalo or domestic Asian water buffalo is a large bovine animal, frequently used as livestock in southern Asia, and also widely in South America, southern Europe, northern Africa, and elsewhere....
milk and meat. India is also the largest producer of millets like Jowar Bajra and Ragi. It is second only to China in the production of rice. India is the 6th largest coffee producer in the world It also has the world's largest cattle
Cattle
Cattle are the most common type of large domesticated ungulates. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae, are the most widespread species of the genus Bos, and are most commonly classified collectively as Bos primigenius...
population (281 million). It is the second largest producer of cashew
Cashew
The cashew is a tree in the family Anacardiaceae. Its English name derives from the Portuguese name for the fruit of the cashew tree, caju, which in turn derives from the indigenous Tupi name, acajú. It is now widely grown in tropical climates for its cashew nuts and cashew apples.-Etymology:The...
s, cabbage
Cabbage
Cabbage is a popular cultivar of the species Brassica oleracea Linne of the Family Brassicaceae and is a leafy green vegetable...
s, cotton
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective capsule, around the seeds of cotton plants of the genus Gossypium. The fiber is almost pure cellulose. The botanical purpose of cotton fiber is to aid in seed dispersal....
seed and lint, fresh vegetables, garlic
Garlic
Allium sativum, commonly known as garlic, is a species in the onion genus, Allium. Its close relatives include the onion, shallot, leek, chive, and rakkyo. Dating back over 6,000 years, garlic is native to central Asia, and has long been a staple in the Mediterranean region, as well as a frequent...
, egg plant, goat
Goat
The domestic goat is a subspecies of goat domesticated from the wild goat of southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the Bovidae family and is closely related to the sheep as both are in the goat-antelope subfamily Caprinae. There are over three hundred distinct breeds of...
meat, silk
Silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The best-known type of silk is obtained from the cocoons of the larvae of the mulberry silkworm Bombyx mori reared in captivity...
, nutmeg
Nutmeg
The nutmeg tree is any of several species of trees in genus Myristica. The most important commercial species is Myristica fragrans, an evergreen tree indigenous to the Banda Islands in the Moluccas of Indonesia...
. mace
Mace
A mace is a blunt weapon, a type of club or virge—that uses a heavy head on the end of a handle to deliver powerful blows. A development of the club, the military mace differs from a hammer in that the head of a mace is radially symmetric so that a blow can be delivered just as effectively with any...
, cardamom
Cardamom
Cardamom refers to several plants of the genera Elettaria and Amomum in the ginger family Zingiberaceae. Both genera are native to India and Bhutan; they are recognised by their small seed pod, triangular in cross-section and spindle-shaped, with a thin papery outer shell and small black seeds...
, onions, wheat
Wheat
Wheat is a cereal grain, originally from the Levant region of the Near East, but now cultivated worldwide. In 2007 world production of wheat was 607 million tons, making it the third most-produced cereal after maize and rice...
, rice
Rice
Rice is the seed of the monocot plants Oryza sativa or Oryza glaberrima . As a cereal grain, it is the most important staple food for a large part of the world's human population, especially in East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, and the West Indies...
, sugarcane
Sugarcane
Sugarcane refers to any of six to 37 species of tall perennial grasses of the genus Saccharum . Native to the warm temperate to tropical regions of South Asia, they have stout, jointed, fibrous stalks that are rich in sugar, and measure two to six metres tall...
, lentil
Lentil
The lentil is an edible pulse. It is a bushy annual plant of the legume family, grown for its lens-shaped seeds...
, dry bean
Bean
Bean is a common name for large plant seeds of several genera of the family Fabaceae used for human food or animal feed....
s, groundnut
Peanut
The peanut, or groundnut , is a species in the legume or "bean" family , so it is not a nut. The peanut was probably first cultivated in the valleys of Peru. It is an annual herbaceous plant growing tall...
, tea
Tea
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by adding cured leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant to hot water. The term also refers to the plant itself. After water, tea is the most widely consumed beverage in the world...
, green peas, cauliflower
Cauliflower
Cauliflower is one of several vegetables in the species Brassica oleracea, in the family Brassicaceae. It is an annual plant that reproduces by seed...
s, potato
Potato
The potato is a starchy, tuberous crop from the perennial Solanum tuberosum of the Solanaceae family . The word potato may refer to the plant itself as well as the edible tuber. In the region of the Andes, there are some other closely related cultivated potato species...
es, pumpkin
Pumpkin
A pumpkin is a gourd-like squash of the genus Cucurbita and the family Cucurbitaceae . It commonly refers to cultivars of any one of the species Cucurbita pepo, Cucurbita mixta, Cucurbita maxima, and Cucurbita moschata, and is native to North America...
s, squashes, gourd
Gourd
A gourd is a plant of the family Cucurbitaceae. Gourd is occasionally used to describe crops like cucumbers, squash, luffas, and melons. The term 'gourd' however, can more specifically, refer to the plants of the two Cucurbitaceae genera Lagenaria and Cucurbita or also to their hollow dried out shell...
s and inland fish
Fish
Fish are a paraphyletic group of organisms that consist of all gill-bearing aquatic vertebrate animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as various extinct related groups...
. It is the third largest producer of tobacco
Tobacco
Tobacco is an agricultural product processed from the leaves of plants in the genus Nicotiana. It can be consumed, used as a pesticide and, in the form of nicotine tartrate, used in some medicines...
, sorghum
Sorghum
Sorghum is a genus of numerous species of grasses, one of which is raised for grain and many of which are used as fodder plants either cultivated or as part of pasture. The plants are cultivated in warmer climates worldwide. Species are native to tropical and subtropical regions of all continents...
, rapeseed
Rapeseed
Rapeseed , also known as rape, oilseed rape, rapa, rappi, rapaseed is a bright yellow flowering member of the family Brassicaceae...
, coconut
Coconut
The coconut palm, Cocos nucifera, is a member of the family Arecaceae . It is the only accepted species in the genus Cocos. The term coconut can refer to the entire coconut palm, the seed, or the fruit, which is not a botanical nut. The spelling cocoanut is an old-fashioned form of the word...
s, hen's
Chicken
The chicken is a domesticated fowl, a subspecies of the Red Junglefowl. As one of the most common and widespread domestic animals, and with a population of more than 24 billion in 2003, there are more chickens in the world than any other species of bird...
eggs and tomato
Tomato
The word "tomato" may refer to the plant or the edible, typically red, fruit which it bears. Originating in South America, the tomato was spread around the world following the Spanish colonization of the Americas, and its many varieties are now widely grown, often in greenhouses in cooler...
es. India accounts for 10% of the world fruit production with first rank in the production of mango
Mango
The mango is a fleshy stone fruit belonging to the genus Mangifera, consisting of numerous tropical fruiting trees in the flowering plant family Anacardiaceae. The mango is native to India from where it spread all over the world. It is also the most cultivated fruit of the tropical world. While...
es, papaya
Papaya
The papaya , papaw, or pawpaw is the fruit of the plant Carica papaya, the sole species in the genus Carica of the plant family Caricaceae...
, banana
Banana
Banana is the common name for herbaceous plants of the genus Musa and for the fruit they produce. Bananas come in a variety of sizes and colors when ripe, including yellow, purple, and red....
and sapota.
India's population is growing faster than its ability to produce rice and wheat.
Initiatives
The required level of investment for the development of marketing, storage and cold storage infrastructure is estimated to be huge. The government has not been able to implement various schemes to raise investment in marketing infrastructure. Among these schemes are Construction of Rural Go downs, Market Research and Information Network, and Development / Strengthening of Agricultural MarketingAgricultural marketing
Agricultural marketing covers the services involved in moving an agricultural product from the farm to the consumer. Numerous interconnected activities are involved in doing this, such as planning production, growing and harvesting, grading, packing, transport, storage, agro- and food processing,...
Infrastructure, Grading and Standardization.
The Indian Agricultural Research Institute
Indian Agricultural Research Institute
The Indian Agricultural Research Institute is India's premier national Institute for agricultural research, education and extension. It has served the cause of science and society with distinction through first rate research, generation of appropriate technologies and development of human resources...
(IARI), established in 1905, was responsible for the research leading to the "Indian Green Revolution" of the 1970s. The Indian Council of Agricultural Research
Indian Council of Agricultural Research
Indian Council of Agricultural Research , New Delhi, India is an autonomous organisation under the Department of Agricultural Research and Education, Ministry of Agriculture, Government of India...
(ICAR) is the apex body in agriculture and related allied fields, including research and education. The Union Minister of Agriculture is the President of the ICAR. The Indian Agricultural Statistics Research Institute
Indian Agricultural Statistics Research Institute
The Indian Agricultural Statistics Research Institute is an institute under the Indian Council of Agricultural Research with the mandate for developing new techniques for the design of agricultural experiments as well as to analyze data in agriculture....
develops new techniques for the design of agricultural experiments, analyses data in agriculture, and specializes in statistical techniques for animal and plant breeding.
Recently Government of India has set up Farmers Commission to completely evaluate the agriculture program. However the recommendations have had a mixed reception.
Indian agriculture policy
Indian agriculture policy is aimed essentially at improving food self sufficiency and alleviating hunger through food distribution. Aside from investing in agricultural infrastructureInfrastructure
Infrastructure is basic physical and organizational structures needed for the operation of a society or enterprise, or the services and facilities necessary for an economy to function...
, the government supports agriculture through measures including minimum support prices (MSP) for the major agricultural crops, farm input subsidies and preferential credit schemes.Under the price support policy, MSPs are set annually for basic staples to protect producers from sharp price falls, to stabilise prices and to ensure adequate food stocks for public distribution. In the past guaranteed prices have been below the prevailing market prices, according to the International Food Policy Research Institute
International Food Policy Research Institute
The International Food Policy Research Institute is an international agricultural research center founded in the early 1970s to improve the understanding of national agricultural and food policies to promote the adoption of innovations in agricultural technology...
(IFPRI) in 2007.At the same time subsidies on farm inputs including fertilisers, electrical power and irrigation water have led to inefficient use of inputs and indirectly subsidise income. IFPRI concluded that “support for agriculture (from 1985-2002) has been largely counter cyclical to world prices”.
Problems
The low productivity in India is a result of the following factors:- According to the World BankWorld BankThe World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programmes.The World Bank's official goal is the reduction of poverty...
, Indian Branch: Priorities for Agriculture and Rural Development", India's large agricultural subsidies are hampering productivity-enhancing investment. Overregulation of agriculture has increased costs, price risks and uncertainty. Government intervenes in labour, land, and credit markets. India has inadequate infrastructure and services. World Bank also says that the allocation of water is inefficient, unsustainable and inequitable. The irrigationIrrigationIrrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
infrastructure is deteriorating. The overuse of water is currently being covered by over pumping aquifers, but as these are falling by foot of groundwater each year, this is a limited resource. - Illiteracy, general socio-economic backwardness, slow progress in implementing land reforms and inadequate or inefficient finance and marketing services for farm produce.
- Inconsistent government policy. Agricultural subsidies and taxes often changed without notice for short term political ends.
- The average size of land holdings is very small (less than 20,000 m²) and is subject to fragmentation due to land ceiling acts, and in some cases, family disputes. Such small holdings are often over-manned, resulting in disguised unemployment and low productivity of labour.
- Adoption of modern agricultural practices and use of technologyAgricultural machineryAgricultural machinery is machinery used in the operation of an agricultural area or farm.-Hand tools:The first person to turn from the hunting and gathering lifestyle to farming probably did so by using his bare hands, and perhaps some sticks or stones. Tools such as knives, scythes, and wooden...
is inadequate, hampered by ignorance of such practices, high costs and impracticality in the case of small land holdings. - Irrigation facilities are inadequate, as revealed by the fact that only 52.6% of the land was irrigated in 2003–04, which result in farmers still being dependent on rainfall, specifically the MonsoonMonsoonMonsoon is traditionally defined as a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation, but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with the asymmetric heating of land and sea...
season. A good monsoon results in a robust growth for the economy as a whole, while a poor monsoon leads to a sluggish growth. Farm credit is regulated by NABARD, which is the statutory apex agent for rural development in the subcontinent. At the same time overpumping made possible by subsidized electric power is leading to an alarming drop in aquifer levels.
History
Indian agriculture began by 9000 BC as a result of early cultivation of plants, and domestication of crops and animals. Settled life soon followed with implements and techniques being developed for agriculture. Double monsoonMonsoon
Monsoon is traditionally defined as a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation, but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with the asymmetric heating of land and sea...
s led to two harvests being reaped in one year. Indian products soon reached the world via existing trading networks and foreign crops were introduced to India. Plants and animals—considered essential to their survival by the Indians—came to be worshiped and venerated.
The middle ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
saw irrigation channels reach a new level of sophistication in India and Indian crops affecting the economies of other regions of the world under Islam
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
ic patronage. Land and water management systems were developed with an aim of providing uniform growth. Despite some stagnation during the later modern era the independent Republic of India was able to develop a comprehensive agricultural program.
See also
- Agriculture in Tamil NaduAgriculture in Tamil NaduAgriculture is the most predominant sector of the economy of Tamil Nadu, a state in India. 70% of the states population is engaged in agriculture and allied activities for their livelihood...
- Animal husbandry in Tamil NaduAnimal husbandry in Tamil NaduThe livelihoods of most rural and low income communities in Tamil Nadu are to a large extent based on agriculture / livestock / poultry. The animal husbandry sector plays a vital role in providing subsidiary employment to rural folk and guaranteed household income to landless agricultural...
- Fishing in IndiaFishing in Indiathumb|Fishing in [[Orissa]].Fish production has increased more than fivefold since Indias independence and is a major industry in the coastal states.-Growth:It rose from only 800,000 tons in FY 1950 to 4.1 million tons in the early 1990s...
- Forestry in IndiaForestry in IndiaForestry is a major government enterprise in India which faces the challenges of dwindling forest cover area due to overpopulation, farming and environmental factors.-History:...
- Agricultural Debt Waiver and Debt Relief Scheme (India)Loan waiverA loan waiver is the waiving of the real or potential liability of the person or party who has taken out a loan through the voluntary action of the person or party who has made the loan...
External links
- Indian Agriculture. U.S. Library of Congress.
- of India, Department of Agriculture & cooperation
- Indian Council for Agricultural Research Home Page.
- Website of The Indian Farmers Association
- Commodity Research, Food and Agribusiness, Commodity News and Analysis (in English) (based in India)
- Agropedia - One Stop Shop For All Kinds Of Information On Agriculture In India
- Agriculture Commodity Market News - Agri Commodity News, Rates, Daily Trading Prices, The Trade News Agency NNS - Daily commodity prices of Agricultural and Agri based Commodities from different Markets of India. Indian Agriculture Industry business to business (b2b) News and Directory (in English) (based in India)

