
Air pollutant concentrations
Encyclopedia
Air pollutant concentrations, as measured or as calculated by air pollution dispersion modeling, must often be converted or corrected to be expressed as required by the regulations issued by various governmental agencies. Regulations that define and limit the concentration
of pollutant
s in the ambient air or in gaseous emissions to the ambient air are issued by various national and state (or provincial) environmental protection
and occupational health and safety agencies.
Such regulations involve a number of different expressions of concentration. Some express the concentrations as ppmv (parts per million by volume) and some express the concentrations as mg/m3 (milligrams per cubic meter), while others require adjusting or correcting the concentrations to reference conditions of moisture content, oxygen
content or carbon dioxide
content. This article presents methods for converting concentrations from ppmv to mg/m3 (and vice versa) and for correcting the concentrations to the required reference conditions.
All of the concentrations and concentration corrections in this article apply only to air and other gases. They are not applicable for liquids.
(101.325 kPa
or 1.01325 bar
), the general equation is:
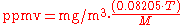
and for the reverse conversion:

Notes:
. The concentration decrease is directly proportional to the pressure decrease with increasing altitude. Some governmental regulatory jurisdictions require industrial sources of air pollution to comply with sea level standards corrected for altitude. In other words, industrial air pollution sources located at altitudes well above sea level must comply with significantly more stringent air quality standards than sources located at sea level (since it is more difficult to comply with lower standards). For example, New Mexico
's Department of the Environment has a regulation with such a requirement.
The change of atmospheric pressure with altitude can be obtained from this equation:
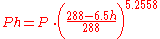
Given an air pollutant concentration at sea-level atmospheric pressure, the concentration at higher altitudes can be obtained from this equation:
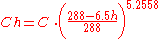
As an example, given an air pollutant concentration of 260 mg/m3 at sea level, calculate the equivalent pollutant concentration at an altitude of 2800 meters:
Note:
to 55 ppmv in a dry combustion exhaust gas (at a specified reference temperature and pressure) corrected to 3 volume percent O2
in the dry gas. As another example, a regulation might limit the concentration of total particulate matter to 200 mg/m3 of an emitted gas (at a specified reference temperature and pressure) corrected to a dry basis and further corrected to 12 volume percent CO2
in the dry gas.
Environmental agencies in the USA often use the terms "dscf" or "scfd" to denote a "standard" cubic foot of dry gas. Likewise, they often use the terms "dscm" or "scmd" to denote a "standard" cubic meter of gas. Since there is no universally accepted set of "standard" temperature and pressure, such usage can be and is very confusing. It is strongly recommended that the reference temperature and pressure always be clearly specified when stating gas volumes or gas flow rates. (See Reference conditions of gas temperature and pressure for more explanation)
" concentration:
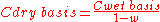
As an example, a wet basis concentration of 40 ppmv in a gas having 10 volume percent water vapor would have a:

As an example, a measured NOx concentration of 45 ppmv in a dry gas having 5 volume % O2 is:
when corrected to a dry gas having a specified reference O2 content of 3 volume %.
Note:

As an example, a measured particulates concentration of 200 mg/m3 in a dry gas that has a measured 8 volume % CO2 is:
when corrected to a dry gas having a specified reference CO2 content of 12 volume %.
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
of pollutant
Pollutant
A pollutant is a waste material that pollutes air, water or soil, and is the cause of pollution.Three factors determine the severity of a pollutant: its chemical nature, its concentration and its persistence. Some pollutants are biodegradable and therefore will not persist in the environment in the...
s in the ambient air or in gaseous emissions to the ambient air are issued by various national and state (or provincial) environmental protection
United States Environmental Protection Agency
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is an agency of the federal government of the United States charged with protecting human health and the environment, by writing and enforcing regulations based on laws passed by Congress...
and occupational health and safety agencies.
Such regulations involve a number of different expressions of concentration. Some express the concentrations as ppmv (parts per million by volume) and some express the concentrations as mg/m3 (milligrams per cubic meter), while others require adjusting or correcting the concentrations to reference conditions of moisture content, oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
content or carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
content. This article presents methods for converting concentrations from ppmv to mg/m3 (and vice versa) and for correcting the concentrations to the required reference conditions.
All of the concentrations and concentration corrections in this article apply only to air and other gases. They are not applicable for liquids.
Converting air pollutant concentrations
The conversion equations depend on the temperature at which the conversion is wanted (usually about 20 to 25 °C). At an ambient sea level atmospheric pressure of 1 atmAtmosphere (unit)
The standard atmosphere is an international reference pressure defined as 101325 Pa and formerly used as unit of pressure. For practical purposes it has been replaced by the bar which is 105 Pa...
(101.325 kPa
Pascal (unit)
The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
or 1.01325 bar
Bar (unit)
The bar is a unit of pressure equal to 100 kilopascals, and roughly equal to the atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level. Other units derived from the bar are the megabar , kilobar , decibar , centibar , and millibar...
), the general equation is:
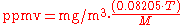
and for the reverse conversion:

| where: | |
| mg/m3 | = milligrams of pollutant per cubic meter of air at sea level atmospheric pressure and T |
| ppmv | = air pollutant concentration, in parts per million by volume |
| T | = ambient temperature in K = 273.15 + °C |
| 0.08205 | = Universal gas constant in atm·m3/(kmol·K) |
| M | = molecular mass Molecular mass The molecular mass of a substance is the mass of one molecule of that substance, in unified atomic mass unit u... (or molecular weight) of the air pollutant |
Notes:
- 1 atm = absolute pressure of 101.325 kPa or 1.01325 barBar (unit)The bar is a unit of pressure equal to 100 kilopascals, and roughly equal to the atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level. Other units derived from the bar are the megabar , kilobar , decibar , centibar , and millibar...
- mol = gram moleMole (unit)The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
and kmol = 1000 gram moles - Pollution regulations in the United States typically reference their pollutant limits to an ambient temperature of 20 to 25 °C as noted above. In most other nations, the reference ambient temperature for pollutant limits may be 0 °C or other values.
- Although ppmv and mg/m3 have been used for the examples in all of the following sections, concentrations such as ppbv (i.e., parts per billion by volume), volume percent, mole percent and many others may also be used for gaseous pollutants.
- Particulate matter (PM) in the atmospheric air or in any other gas cannot be expressed in terms of ppmv, ppbv, volume percent or mole percent. PM is most usually (but not always) expressed as mg/m3 of air or other gas at a specified temperature and pressure.
- For gases, volume percent = mole percent
- 1 volume percent = 10,000 ppmv (i.e., parts per million by volume) with a million being defined as 106.
- Care must be taken with the concentrations expressed as ppbv to differentiate between the British billion which is 1012 and the USA billion which is 109 (also referred to as the long scale and short scale billion, respectively).
Correcting concentrations for altitude
Air pollutant concentrations expressed as mass per unit volume of atmospheric air (e.g., mg/m3, µg/m3, etc.) at sea level will decrease with increasing altitudeAltitude
Altitude or height is defined based on the context in which it is used . As a general definition, altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The reference datum also often varies according to the context...
. The concentration decrease is directly proportional to the pressure decrease with increasing altitude. Some governmental regulatory jurisdictions require industrial sources of air pollution to comply with sea level standards corrected for altitude. In other words, industrial air pollution sources located at altitudes well above sea level must comply with significantly more stringent air quality standards than sources located at sea level (since it is more difficult to comply with lower standards). For example, New Mexico
New Mexico
New Mexico is a state located in the southwest and western regions of the United States. New Mexico is also usually considered one of the Mountain States. With a population density of 16 per square mile, New Mexico is the sixth-most sparsely inhabited U.S...
's Department of the Environment has a regulation with such a requirement.
The change of atmospheric pressure with altitude can be obtained from this equation:
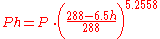
Given an air pollutant concentration at sea-level atmospheric pressure, the concentration at higher altitudes can be obtained from this equation:
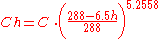
| where: | |
| h | = altitude, in km |
|---|---|
| P | = atmospheric pressure at sea level |
| Ph | = atmospheric pressure at altitude h |
| C |
= Air pollutant concentration, in mass per unit volume at sea level atmospheric pressure and specified temperature T |
| Ch | = Concentration, in mass per unit volume at altitude h and specified temperature T |
As an example, given an air pollutant concentration of 260 mg/m3 at sea level, calculate the equivalent pollutant concentration at an altitude of 2800 meters:
- Ch = 260 × [ { 288 - (6.5)(2.8) } / 288] 5.2558 = 260 × 0.71 = 185 mg/m3
Note:
- The above equation for the decrease of air pollution concentrations with increasing altitude is applicable only for about the first 10 km of altitude in the troposphereTroposphereThe troposphere is the lowest portion of Earth's atmosphere. It contains approximately 80% of the atmosphere's mass and 99% of its water vapor and aerosols....
(the lowest atmospheric layer) and is estimated to have a maximum error of about 3 percent. However, 10 km of altitude is sufficient for most purposes involving air pollutant concentrations.
Correcting concentrations for reference conditions
Many environmental protection agencies have issued regulations that limit the concentration of pollutants in gaseous emissions and define the reference conditions applicable to those concentration limits. For example, such a regulation might limit the concentration of NOxNitrogen oxide
Nitrogen oxide can refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds:* Nitric oxide, also known as nitrogen monoxide, , nitrogen oxide* Nitrogen dioxide , nitrogen oxide...
to 55 ppmv in a dry combustion exhaust gas (at a specified reference temperature and pressure) corrected to 3 volume percent O2
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
in the dry gas. As another example, a regulation might limit the concentration of total particulate matter to 200 mg/m3 of an emitted gas (at a specified reference temperature and pressure) corrected to a dry basis and further corrected to 12 volume percent CO2
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
in the dry gas.
Environmental agencies in the USA often use the terms "dscf" or "scfd" to denote a "standard" cubic foot of dry gas. Likewise, they often use the terms "dscm" or "scmd" to denote a "standard" cubic meter of gas. Since there is no universally accepted set of "standard" temperature and pressure, such usage can be and is very confusing. It is strongly recommended that the reference temperature and pressure always be clearly specified when stating gas volumes or gas flow rates. (See Reference conditions of gas temperature and pressure for more explanation)
Correcting to a dry basis
If a gaseous emission sample is analyzed and found to contain water vapor and a pollutant concentration of say 40 ppmv, then 40 ppmv should be designated as the "wet basis" pollutant concentration. The following equation can be used to correct the measured "wet basis" concentration to a "dry basisDry basis
Dry basis is a expression of the calculation in chemistry, chemical engineering and related subjects, in which the presence of water is ignored for the purposes of the calculation...
" concentration:
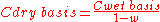
| where: | |
| C | = Concentration of the air pollutant in the emitted gas |
|---|---|
| w | = fraction, by volume, of the emitted gas |
As an example, a wet basis concentration of 40 ppmv in a gas having 10 volume percent water vapor would have a:
- Cdry basis = 40 ÷ ( 1 - 0.10 ) = 44.4 ppmv.
Correcting to a reference oxygen content
The following equation can be used to correct a measured pollutant concentration in a dry emitted gas with a measured O2 content to an equivalent pollutant concentration in a dry emitted gas with a specified reference amount of O2:
| where: | |
| Cr | = corrected concentration of a dry gas with a specified reference volume % O2 |
|---|---|
| Cm | = measured concentration in a dry gas having a measured volume % O2 |
As an example, a measured NOx concentration of 45 ppmv in a dry gas having 5 volume % O2 is:
- 45 × ( 20.9 - 3 ) ÷ ( 20.9 - 5 ) = 50.7 ppmv of NOx
when corrected to a dry gas having a specified reference O2 content of 3 volume %.
Note:
- The measured gas concentration Cm must first be corrected to a dry basis before using the above equation.
Correcting to a reference carbon dioxide content
The following equation can be used to correct a measured pollutant concentration in an emitted gas (containing a measured CO2 content) to an equivalent pollutant concentration in an emitted gas containing a specified reference amount of CO2:
| where: | |
| Cr | = corrected concentration of a dry gas having a specified reference volume % CO2 |
|---|---|
| Cm | = measured concentration of a dry gas having a measured volume % CO2 |
As an example, a measured particulates concentration of 200 mg/m3 in a dry gas that has a measured 8 volume % CO2 is:
- 200 × ( 12 ÷ 8 ) = 300 mg/m3
when corrected to a dry gas having a specified reference CO2 content of 12 volume %.

