
Alesia (city)
Encyclopedia

Mandubii
The Mandubii were a confederation of Gaulish tribes who lived in the areas of modern-day Bourgogne and Jura. Their capital was Alesia....
, one of the Gaul
Gaul
Gaul was a region of Western Europe during the Iron Age and Roman era, encompassing present day France, Luxembourg and Belgium, most of Switzerland, the western part of Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the left bank of the Rhine. The Gauls were the speakers of...
ish tribes allied with the Aedui
Aedui
Aedui, Haedui or Hedui , were a Gallic people of Gallia Lugdunensis, who inhabited the country between the Arar and Liger , in today's France. Their territory thus included the greater part of the modern departments of Saône-et-Loire, Côte-d'Or and Nièvre.-Geography:The country of the Aedui is...
, and after Julius Caesar
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar was a Roman general and statesman and a distinguished writer of Latin prose. He played a critical role in the gradual transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire....
's conquest a Roman town (oppidum
Oppidum
Oppidum is a Latin word meaning the main settlement in any administrative area of ancient Rome. The word is derived from the earlier Latin ob-pedum, "enclosed space," possibly from the Proto-Indo-European *pedóm-, "occupied space" or "footprint."Julius Caesar described the larger Celtic Iron Age...
) in Gaul
Gaul
Gaul was a region of Western Europe during the Iron Age and Roman era, encompassing present day France, Luxembourg and Belgium, most of Switzerland, the western part of Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the left bank of the Rhine. The Gauls were the speakers of...
. There have been archeological excavations since the time of Napoléon III in Alise-Sainte-Reine
Alise-Sainte-Reine
Alise-Sainte-Reine is a commune in the Côte-d'Or department in Bourgogne in eastern France.It is thought to be the site of the ancient city of Alesia, where Caesar defeated the Gauls under Vercingetorix in the Battle of Alesia...
in Côte d'Or
Côte-d'Or
Côte-d'Or is a department in the eastern part of France.- History :Côte-d'Or is one of the original 83 departments created during the French Revolution on 4 March 1790. It was formed from part of the former province of Burgundy.- Geography :...
near Dijon
Dijon
Dijon is a city in eastern France, the capital of the Côte-d'Or département and of the Burgundy region.Dijon is the historical capital of the region of Burgundy. Population : 151,576 within the city limits; 250,516 for the greater Dijon area....
, which have claimed that the historical Alesia is located there. New discoveries are constantly being made about this Gallo-Roman settlement on the plateau of Mont-Auxois. As a result of the latest excavation, a find was presented to the museum there with the inscription: IN ALISIIA, which finally dispelled the doubts of some archeologists on the town's identity.
Early doubts
Earlier there were other, less academically valid theories about Alesia's location that claimed it was in Franche-Comté or around Salins-les-BainsSalins-les-Bains
Salins-les-Bains is a commune in the Jura department in Franche-Comté in eastern France.Salins owes its name to its saline waters, used for bathing and drinking. There are also salt works and gypsum deposits. In 2009 the historic saltworks were added to the list of UNESCO World Heritage sites...
in Jura. The uncertainty surrounding Alesia's location is humorously parodied in the Asterix
Asterix
Asterix or The Adventures of Asterix is a series of French comic books written by René Goscinny and illustrated by Albert Uderzo . The series first appeared in French in the magazine Pilote on October 29, 1959...
volume Asterix and the Chieftain's Shield
Asterix and the Chieftain's Shield
Asterix and the Chieftain's Shield is the eleventh volume in the Asterix comic book series, written by René Goscinny and drawn by Albert Uderzo. It was originally published as a serial in Pilote issues 399-421 in 1967.The book is inspired by the battle of Alesia, where the Gaulish warrior chief...
, in which, in this case because of Gaulish pride, characters repeatedly deny that they know its location ("I don't know where Alesia is! No one knows where Alesia is!").
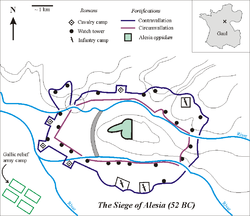
Caesar's battle
Around 52 BC52 BC
Year 52 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Pompeius and Scipio...
, Alesia was the site of the decisive battle
Battle of Alesia
The Battle of Alesia or Siege of Alesia took place in September, 52 BC around the Gallic oppidum of Alesia, a major town centre and hill fort of the Mandubii tribe...
between the Romans
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic was the period of the ancient Roman civilization where the government operated as a republic. It began with the overthrow of the Roman monarchy, traditionally dated around 508 BC, and its replacement by a government headed by two consuls, elected annually by the citizens and...
under Julius Caesar
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar was a Roman general and statesman and a distinguished writer of Latin prose. He played a critical role in the gradual transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire....
and the Gauls
Gauls
The Gauls were a Celtic people living in Gaul, the region roughly corresponding to what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland and Northern Italy, from the Iron Age through the Roman period. They mostly spoke the Continental Celtic language called Gaulish....
under Vercingetorix
Vercingetorix
Vercingetorix was the chieftain of the Arverni tribe, who united the Gauls in an ultimately unsuccessful revolt against Roman forces during the last phase of Julius Caesar's Gallic Wars....
. The battle's outcome determined the fate of all of Gaul: in winning the battle, the Romans won both the Gallic War and dominion over Gaul. The fight is described in detail by Caesar in his Commentarii de Bello Gallico
Commentarii de Bello Gallico
Commentarii de Bello Gallico is Julius Caesar's firsthand account of the Gallic Wars, written as a third-person narrative. In it Caesar describes the battles and intrigues that took place in the nine years he spent fighting local armies in Gaul that opposed Roman domination.The "Gaul" that Caesar...
(Book 7, 68-69). The latest analysis at Alise-Sainte-Reine can corroborate the described siege in detail. The enormous measures taken there are impressive: in only six weeks a 15 km long fortification ring (circumvallation
Investment (military)
Investment is the military tactic of surrounding an enemy fort with armed forces to prevent entry or escape.A circumvallation is a line of fortifications, built by the attackers around the besieged fortification facing towards the enemy fort...
) around Alesia and an additional 21 km long ring (contravallation) around that to stop reinforcements (around 250,000 men according to Caesar) from reaching the Gauls. These have been identified by archeologists
Archaeology
Archaeology, or archeology , is the study of human society, primarily through the recovery and analysis of the material culture and environmental data that they have left behind, which includes artifacts, architecture, biofacts and cultural landscapes...
using aerial photography
Aerial photography
Aerial photography is the taking of photographs of the ground from an elevated position. The term usually refers to images in which the camera is not supported by a ground-based structure. Cameras may be hand held or mounted, and photographs may be taken by a photographer, triggered remotely or...
.

