
Allochems
Encyclopedia
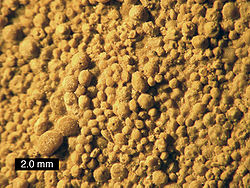
Peloids
Peloids are allochems that are composed of micrite, irrespective of size, shape, or origin. The two primary types of peloids are pellets and intraclasts. Another type of peloid is pseudo-oolith....
, oncolite
Oncolite
Oncolites are sedimentary structures formed out of oncoids, which are layered spherical growth structures formed by cyanobacterial growth. Oncolites are very similar to stromatolites, but instead of forming columns they form approximately spherical structures...
s, pellets
Pellets (petrology)
Pellets are small spherical to ovoid or rod-shaped grains that are common component of many limestones. They are typically 0.03 to 0.3 mm long and composed of carbonate mud . Their most common size is 0.04 to 0.08 mm. Pellets typically lack any internal structure and are remarkably uniform in size...
, fossil
Fossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
or pre-existing carbonate fragments. Fragments are still termed allochems if they have undergone chemical transformations - for example if an aragonite
Aragonite
Aragonite is a carbonate mineral, one of the two common, naturally occurring, crystal forms of calcium carbonate, CaCO3...
shell were to dissolve and be later replaced by calcite
Calcite
Calcite is a carbonate mineral and the most stable polymorph of calcium carbonate . The other polymorphs are the minerals aragonite and vaterite. Aragonite will change to calcite at 380-470°C, and vaterite is even less stable.-Properties:...
, the replacement would still be deemed an allochem.
The allochems are typically embedded in a matrix
Matrix (geology)
The matrix or groundmass of rock is the finer grained mass of material in which larger grains, crystals or clasts are embedded.The matrix of an igneous rock consists of finer grained, often microscopic, crystals in which larger crystals are embedded. This porphyritic texture is indicative of...
of micrite
Micrite
Micrite is a limestone constituent formed of calcareous particles ranging in diameter up to 4 μm formed by the recrystallization of lime mud.The term was coined in 1959 by Robert Folk for his carbonate rock classification system...
(lime mud) or sparry calcite.

