
Alpha beta filter
Encyclopedia
An alpha beta filter is a simplified form of observer
for estimation, data smoothing and control applications. It is closely related to Kalman filter
s and to linear state observers used in control theory
. Its principal advantage is that it does not require a detailed system model.
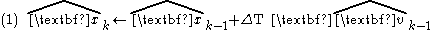
Since velocity variable v is presumed constant, so its projected value at the next sampling time equals the current value.
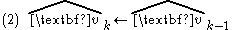
If additional information is known about how a driving function will change the v state during each time interval, equation 2 can be modified to include it.
The output measurement is expected to deviate from the prediction because of noise and dynamic effects not included in the simplified dynamic model. This prediction error r is also called the residual or innovation, based on statistical or Kalman filtering interpretations
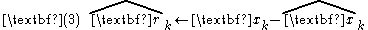
Suppose that residual r is positive. This could result because the previous x estimate was low, the previous v was low, or some combination of the two. The alpha beta filter takes selected alpha and beta constants (from which the filter gets its name), uses alpha times the deviation r to correct the position estimate, and uses beta times the deviation r to correct the velocity estimate. An extra ΔT factor conventionally serves to normalize magnitudes of the multipliers.
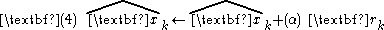

The corrections can be considered small steps along an estimate of the gradient direction. As these adjustments accumulate, error in the state estimates is reduced. For convergence and stability, the values of the alpha and beta multipliers should be positive and small.
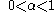
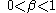
Values of alpha and beta typically are adjusted experimentally. In general, larger alpha and beta gains tend to produce faster response for tracking transient changes, while smaller alpha and beta gains reduce the level of noise in the state estimates. If a good balance between accurate tracking and noise reduction is found, and the algorithm is effective, filtered estimates are more accurate than the direct measurements. This motivates calling the alpha-beta process a filter.
Update. Repeat for each time step ΔT:
as follows:
In first image, the blue worm is input signal and red is output; in second image, blue worm is input signal and yellow is output; and, in third image, the blue worm is input and green is output. For first two images, the output signal is visibly smoother than the input signal. Output avoids extreme spokes generated in input; rather following a more subtle path to have a similar effect. Also, the output moves in an estimate of gradient
direction of input.
Higher is the alpha parameter, higher is the effect of input x and lesser is the dampening. Low value of beta is effective in controlling sudden surges in velocity. Also, as alpha increases beyond unity, we observe the opposite effect in output. The output gets rougher and uneven.
for linear control systems, use a rigorous system model. Linear observers use a gain matrix to determine state estimate corrections from multiple deviations between measured variables and predicted outputs that are linear combinations of state variables. In the case of alpha beta filters, this gain matrix reduces to two terms. There is no general theory for determining the best observer gain terms, and typically gains are adjusted experimentally for both.
The linear Luenberger observer equations
reduce to the alpha beta filter by applying the following specializations and simplifications.
estimates the values of state variables and corrects them in a manner similar to an alpha beta filter or a state observer. However, a Kalman filter does this in a much more formal and rigorous manner. The principal differences between Kalman filters and alpha beta filters are the following.
A Kalman filter designed to track a moving object using a constant-velocity target dynamics (process) model (i.e., constant velocity between measurement updates) with process noise covariance and measurement covariance held constant will converge to the same structure as an alpha-beta filter. However, a Kalman filter's gain is computed recursively at each time step using the assumed process and measurement error statistics, whereas the alpha-beta's gain is computed ad hoc.

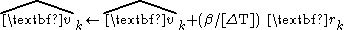
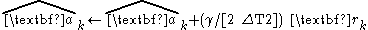
Similar extensions to additional higher orders are possible, but most systems of higher order tend to have significant interactions among the multiple states, so approximating the system dynamics as a simple integrator chain is less likely to prove useful.
State observer
In control theory, a state observer is a system that models a real system in order to provide an estimate of its internal state, given measurements of the input and output of the real system. It is typically a computer-implemented mathematical model....
for estimation, data smoothing and control applications. It is closely related to Kalman filter
Kalman filter
In statistics, the Kalman filter is a mathematical method named after Rudolf E. Kálmán. Its purpose is to use measurements observed over time, containing noise and other inaccuracies, and produce values that tend to be closer to the true values of the measurements and their associated calculated...
s and to linear state observers used in control theory
Control theory
Control theory is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and mathematics that deals with the behavior of dynamical systems. The desired output of a system is called the reference...
. Its principal advantage is that it does not require a detailed system model.
Filter equations
An alpha beta filter presumes that a system is adequately approximated by a model having two internal states, where the first state is obtained by integrating the value of the second state over time. Measured system output values correspond to observations of the first model state, plus disturbances. This very low order approximation is adequate for many simple systems, for example, mechanical systems where position is obtained as the time integral of velocity. Based on a mechanical system analogy, the two states can be called position x and velocity v. Assuming that velocity remains approximately constant over the small time interval ΔT between measurements, the position state is projected forward to predict its value at the next sampling time using equation 1.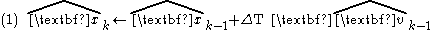
Since velocity variable v is presumed constant, so its projected value at the next sampling time equals the current value.
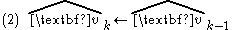
If additional information is known about how a driving function will change the v state during each time interval, equation 2 can be modified to include it.
The output measurement is expected to deviate from the prediction because of noise and dynamic effects not included in the simplified dynamic model. This prediction error r is also called the residual or innovation, based on statistical or Kalman filtering interpretations
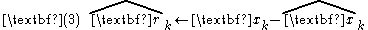
Suppose that residual r is positive. This could result because the previous x estimate was low, the previous v was low, or some combination of the two. The alpha beta filter takes selected alpha and beta constants (from which the filter gets its name), uses alpha times the deviation r to correct the position estimate, and uses beta times the deviation r to correct the velocity estimate. An extra ΔT factor conventionally serves to normalize magnitudes of the multipliers.
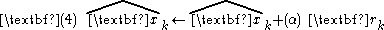

The corrections can be considered small steps along an estimate of the gradient direction. As these adjustments accumulate, error in the state estimates is reduced. For convergence and stability, the values of the alpha and beta multipliers should be positive and small.
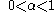
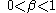
Values of alpha and beta typically are adjusted experimentally. In general, larger alpha and beta gains tend to produce faster response for tracking transient changes, while smaller alpha and beta gains reduce the level of noise in the state estimates. If a good balance between accurate tracking and noise reduction is found, and the algorithm is effective, filtered estimates are more accurate than the direct measurements. This motivates calling the alpha-beta process a filter.
Algorithm Summary
Initialize.- Set the initial values of state estimates x and v, using prior information or additional measurements; otherwise, set the initial state values to zero.
- Select values of the alpha and beta correction gains.
Update. Repeat for each time step ΔT:
Project state estimates x and v using equations 1 and 2
Obtain a current measurement of the output value
Compute the residual r using equation 3
Correct the state estimates using equations 4 and 5
Send updated x and optionally v as the filter outputs
Sample Program
Alpha Beta filter can be implemented in CC (programming language)
C is a general-purpose computer programming language developed between 1969 and 1973 by Dennis Ritchie at the Bell Telephone Laboratories for use with the Unix operating system....
as follows:
- include
- include
main
{
float dt = 0.5;
float xk_1 = 0, vk_1 = 0, a = 0.85, b = 0.005;
float xk, vk, rk;
float xm;
while( 1 )
{
xm = rand % 100;// input signal
xk = xk_1 + ( vk_1 * dt );
vk = vk_1;
rk = xm - xk;
xk += a * rk;
vk += ( b * rk ) / dt;
xk_1 = xk;
vk_1 = vk;
printf( "%f \t %f\n", xm, xk_1 );
sleep( 1 );
}
}
Result
The corresponding images depicts the outcome of above program in graphical format.In first image, the blue worm is input signal and red is output; in second image, blue worm is input signal and yellow is output; and, in third image, the blue worm is input and green is output. For first two images, the output signal is visibly smoother than the input signal. Output avoids extreme spokes generated in input; rather following a more subtle path to have a similar effect. Also, the output moves in an estimate of gradient
Gradient
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar field is a vector field that points in the direction of the greatest rate of increase of the scalar field, and whose magnitude is the greatest rate of change....
direction of input.
Higher is the alpha parameter, higher is the effect of input x and lesser is the dampening. Low value of beta is effective in controlling sudden surges in velocity. Also, as alpha increases beyond unity, we observe the opposite effect in output. The output gets rougher and uneven.
Relationship to general state observers
More general state observers, such as the Luenberger observerState observer
In control theory, a state observer is a system that models a real system in order to provide an estimate of its internal state, given measurements of the input and output of the real system. It is typically a computer-implemented mathematical model....
for linear control systems, use a rigorous system model. Linear observers use a gain matrix to determine state estimate corrections from multiple deviations between measured variables and predicted outputs that are linear combinations of state variables. In the case of alpha beta filters, this gain matrix reduces to two terms. There is no general theory for determining the best observer gain terms, and typically gains are adjusted experimentally for both.
The linear Luenberger observer equations
State observer
In control theory, a state observer is a system that models a real system in order to provide an estimate of its internal state, given measurements of the input and output of the real system. It is typically a computer-implemented mathematical model....
reduce to the alpha beta filter by applying the following specializations and simplifications.
- The discrete state transition matrix A is a square matrix of dimension 2, with all main diagonal terms equal to 1, and the first super-diagonal terms equal to ΔT.
- The observation equation matrix C has one row that selects the value of the first state variable for output.
- The filter correction gain matrix L has one column containing the alpha and beta gain values.
- Any known driving signal for the second state term is represented as part of the input signal vector u, otherwise the u vector is set to zero.
- Input coupling matrix B has a non-zero gain term as its last element if vector u is non-zero.
Relationship to Kalman Filters
A Kalman filterKalman filter
In statistics, the Kalman filter is a mathematical method named after Rudolf E. Kálmán. Its purpose is to use measurements observed over time, containing noise and other inaccuracies, and produce values that tend to be closer to the true values of the measurements and their associated calculated...
estimates the values of state variables and corrects them in a manner similar to an alpha beta filter or a state observer. However, a Kalman filter does this in a much more formal and rigorous manner. The principal differences between Kalman filters and alpha beta filters are the following.
- Like state observers, Kalman filters use a detailed dynamic system model that is not restricted to two states.
- Like state observers, Kalman filters in general use multiple observed variables to correct state variable estimates, and these do not have to be direct measurements of individual system states.
- A Kalman filter uses covariance noise models for states and observations. Using these, a time-dependent estimate of state covariance is updated automatically, and from this the Kalman gainKalman filterIn statistics, the Kalman filter is a mathematical method named after Rudolf E. Kálmán. Its purpose is to use measurements observed over time, containing noise and other inaccuracies, and produce values that tend to be closer to the true values of the measurements and their associated calculated...
matrix terms are calculated. Alpha beta filter gains are manually selected and static.
- For certain classes of problems, a Kalman filter is Wiener optimalWiener filterIn signal processing, the Wiener filter is a filter proposed by Norbert Wiener during the 1940s and published in 1949. Its purpose is to reduce the amount of noise present in a signal by comparison with an estimation of the desired noiseless signal. The discrete-time equivalent of Wiener's work was...
, while alpha beta filtering is in general suboptimal.
A Kalman filter designed to track a moving object using a constant-velocity target dynamics (process) model (i.e., constant velocity between measurement updates) with process noise covariance and measurement covariance held constant will converge to the same structure as an alpha-beta filter. However, a Kalman filter's gain is computed recursively at each time step using the assumed process and measurement error statistics, whereas the alpha-beta's gain is computed ad hoc.
The alpha beta gamma extension
It is sometimes useful to extend the assumptions of the alpha beta filter one level. The second state variable v is presumed to be obtained from integrating a third acceleration state, analogous to the way that the first state is obtained by integrating the second. An equation for the a state is added to the equation system. A third multiplier, gamma, is selected for applying corrections to the new a state estimates. This yields the alpha beta gamma update equations.
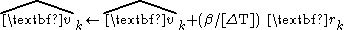
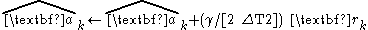
Similar extensions to additional higher orders are possible, but most systems of higher order tend to have significant interactions among the multiple states, so approximating the system dynamics as a simple integrator chain is less likely to prove useful.
See also
- Kalman filterKalman filterIn statistics, the Kalman filter is a mathematical method named after Rudolf E. Kálmán. Its purpose is to use measurements observed over time, containing noise and other inaccuracies, and produce values that tend to be closer to the true values of the measurements and their associated calculated...
- Control theoryControl theoryControl theory is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and mathematics that deals with the behavior of dynamical systems. The desired output of a system is called the reference...
- Masreliez’s theorem
- State space (controls)State space (controls)In control engineering, a state space representation is a mathematical model of a physical system as a set of input, output and state variables related by first-order differential equations...

