
Altitude compensating nozzle
Encyclopedia
An altitude compensating nozzle is a class of rocket engine
nozzles that are designed to operate efficiently across a wide range of altitudes.
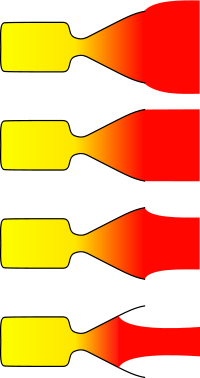 The basic concept of any engine bell is to efficiently direct the flow of exhaust gases from the rocket engine into one direction. The exhaust, a high-temperature mix of gases, has an effectively random momentum distribution, and if it is allowed to escape in that form, only a small part of the flow will be moving in the correct direction to contribute to forward thrust.
The basic concept of any engine bell is to efficiently direct the flow of exhaust gases from the rocket engine into one direction. The exhaust, a high-temperature mix of gases, has an effectively random momentum distribution, and if it is allowed to escape in that form, only a small part of the flow will be moving in the correct direction to contribute to forward thrust.
An engine bell works by confining the sideways flow of the gases, creating a local area of increased pressure with a region of lower pressure "below it". This causes the gases to preferentially flow in the direction of decreasing pressure. By careful design the engine bell grows wider so that the pressure decreases in such a way that by the time the exhaust flow has reached the exit of the bell, it is traveling almost completely rearward, maximizing thrust.
The problem with the conventional approach is that the outside air pressure also contributes to confining the flow of the exhaust gases. At any one altitude, and thus ambient air pressure, the bell can be designed to be nearly "perfect," but that same bell will not be perfect at other pressures, or altitudes. Thus, as a rocket climbs through the atmosphere its efficiency, and thus thrust, changes fairly dramatically, often as much as 30%.
Rocket engine
A rocket engine, or simply "rocket", is a jet engineRocket Propulsion Elements; 7th edition- chapter 1 that uses only propellant mass for forming its high speed propulsive jet. Rocket engines are reaction engines and obtain thrust in accordance with Newton's third law...
nozzles that are designed to operate efficiently across a wide range of altitudes.
Conventional designs

An engine bell works by confining the sideways flow of the gases, creating a local area of increased pressure with a region of lower pressure "below it". This causes the gases to preferentially flow in the direction of decreasing pressure. By careful design the engine bell grows wider so that the pressure decreases in such a way that by the time the exhaust flow has reached the exit of the bell, it is traveling almost completely rearward, maximizing thrust.
The problem with the conventional approach is that the outside air pressure also contributes to confining the flow of the exhaust gases. At any one altitude, and thus ambient air pressure, the bell can be designed to be nearly "perfect," but that same bell will not be perfect at other pressures, or altitudes. Thus, as a rocket climbs through the atmosphere its efficiency, and thus thrust, changes fairly dramatically, often as much as 30%.
Altitude compensating nozzles
- Aerospike engineAerospike engineThe aerospike engine is a type of rocket engine that maintains its aerodynamic efficiency across a wide range of altitudes through the use of an aerospike nozzle. It is a member of the class of altitude compensating nozzle engines. A vehicle with an aerospike engine uses 25–30% less fuel at low...
- Plug nozzlePlug nozzleThe plug nozzle is a type of nozzle which includes a centerbody or plug around which the working fluid flows. Plug nozzles have applications in aircraft, rockets, and numerous other fluid flows.-In Rockets:...
- Expanding nozzleExpanding nozzleThe expanding nozzle is a type of rocket nozzle that, unlike traditional designs, maintains its efficiency at a wide range of altitudes. It is a member of the class of altitude compensating nozzles, a class that also includes the plug nozzle and aerospike...
- Single expansion ramp nozzle
- Stepped nozzle
- Expansion deflection nozzleExpansion deflection nozzleThe expansion-deflection nozzle is an advanced rocket nozzle which achieves altitude compensation through interaction of the exhaust gas with the atmosphere, much like the plug and aerospike nozzles.- Description :...
- Nozzle extensionNozzle extensionNozzle extension — nozzle expander of reaction/rocket engine. The application of nozzle extensions improves efficiency of rocket engines in vacuum by increasing nozzle ratio. As a rule, their modern design assumes use of carbon-carbon materials without regenerative cooling...

