
Aluminized steel
Encyclopedia
Overview
Aluminized steel is steelSteel
Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten...
that has been hot-dip
Hot-dip galvanizing
Hot-dip galvanizing is a form of galvanization. It is the process of coating iron, steel, or aluminum with a thin zinc layer, by passing the metal through a molten bath of zinc at a temperature of around 860 °F...
coated both sides with aluminum-silicon
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
alloy
Alloy
An alloy is a mixture or metallic solid solution composed of two or more elements. Complete solid solution alloys give single solid phase microstructure, while partial solutions give two or more phases that may or may not be homogeneous in distribution, depending on thermal history...
. This process assures a tight metallurgical bond between the steel sheet and its aluminum coating, producing a material with a unique combination of properties possessed neither by steel nor by aluminum alone. Aluminized steel shows a better behavior against corrosion and keeps the properties of the base material steel for temperature lower than 800 °C(1,472 F). For example, it is commonly used for heat exchangers in residential furnaces, mufflers, ovens, ranges, water heaters, fireplaces, bar-b-que burners, and baking pans.
Characteristics are defined by the exact metals used, as well as the process used.
Types
- Type 1
Hot-dip coated with an aluminum/silicon alloy containing 5% to 11% silicon to promote better adherence. It is intended principally for heat resisting applications and also for uses where corrosion resistance and heat are involved. Possible end uses are mufflers, furnaces, ovens, ranges, heaters, water heaters, fireplaces, and baking pans. http://www.blocksteel.com/products.htm Type 1 is coated with a thin layer of aluminum and silicon
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
. Type 1 is more commonly found in industrial products.
- Type 2
Hot-dip coated with commercially pure aluminum. It is intended principally for applications requiring atmospheric corrosion resistance. Type 2 may ultimately be manufactured into corrugated roofing and siding, grain bins, air conditioner housings and drying ovens. http://www.blocksteel.com/products.htm Type 2 is coated with a thin layer of pure aluminum.
Properties
- Structure
The basic structure of aluminized steel is a thin aluminum oxide layer outside, then an intermetallic layer that is a mix of aluminum, silicon, and steel, and finally a steel core. Aluminized Steel is highly resistant to corrosion
Corrosion
Corrosion is the disintegration of an engineered material into its constituent atoms due to chemical reactions with its surroundings. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metals in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen...
and shows high levels of heat reflectivity.
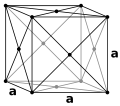
Crystal Structure
Aluminum has a Face Centered Cubic crystal structure.
- Heat Reflectivity
Both Type 1 and Type 2 show excellent high reflectivity characteristics. At temperatures up to 842°C(900°F), aluminized steel reflects up to 80% of heat projected onto it. Aluminized steel has the ability to maintain its strength at temperatures up to 677°C(1,250°F). Although stainless steel
Stainless steel
In metallurgy, stainless steel, also known as inox steel or inox from French "inoxydable", is defined as a steel alloy with a minimum of 10.5 or 11% chromium content by mass....
is the stronger of the two, aluminized steel has a greater electrostatic surface and can therefore reflect heat better.
- Corrosiveness of Aluminized Steel
Aluminized Steel is highly resistant to corrosion
Corrosion
Corrosion is the disintegration of an engineered material into its constituent atoms due to chemical reactions with its surroundings. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metals in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen...
because of the thin layers of aluminum and silicon, which keep the underlying steel from oxidizing. This thin layer also keeps pit corrosion from occurring when exposed to salts that effect most other metals. Now as resistant to corrosion as it may be, if the aluminum layer breaks exposing the steel, the steel may oxidize and corrosion may occur.
Consumption
In North America nearly 70,000 tons of aluminized steel are consumed annually. Some of the common products made from aluminized steel include water heaters, ranges, furnaces, space heaters and grills. http://www.differencebetween.net/science/nature/difference-between-aluminized-steel-and-stainless-steel-2/Processing
Aluminized steel can be made using a variety of processes, cladding,hot dipping, galvanic coating, metallizingMetallizing
Metallizing is the general name for the technique of coating metal on the surface of non-metallic objects.Techniques for metallization started as early as mirror making. In 1835, Justus von Liebig discovered the process of coating a glass surface with metallic silver, making the glass mirror one of...
, and calorizing, but the most effective process is hot dipping. The process of hot dipping starts by cleaning the steel, then placing the steel in a bath of Al-11%Si at a temperature of 988K and shaken, then pulled out and air dried. The aluminum diffuses into the steel, creating an intermetallic layer above the steel base layer, but below the outside aluminum coating. The aluminum coating is oxidized to help protect the inner steel from corrosion and further aluminum diffusion. The silicon is added to the aluminum bath to create a thinner layer of aluminum on the steel. The hot dipping process is cheaper and more effective to produce aluminized steel than any other process.
History and Development
Aluminized steel has a good history and was developed for providing more structural durability and a high yield strength in high corrosive environments. Aluminized steel maintains a high alloy’s steel strength at a fraction of the cost Aluminized steel is cheaper to produce than high alloy steels and thus a preferred material for manufacturing automobile and motorcycle exhaust gas systems.Pictures and Graphs
Structure of aluminized steel under a) light microscope and b) Scanning Electron MicroscopeScanning electron microscope
A scanning electron microscope is a type of electron microscope that images a sample by scanning it with a high-energy beam of electrons in a raster scan pattern...
. 1) oxidative layer 2) Aluminized layer 3) substrate

