AmigaOS versions
Encyclopedia
There have been many different versions of the AmigaOS
operating system
during its two decades of history.
Initially the Amiga operating system had no strong name and branding, as it was seen as an integral part of the Amiga system as a whole. Early names used for the Amiga operating system included "CAOS" and "AmigaDOS". Another non-official name was "Workbench", from the name of the Amiga Desktop environment
, which was included on a floppy disk named "Amiga Workbench".
Version 3.1 of the Amiga operating system was the first version to be officially referred to as "Amiga OS" (with a space between "Amiga" and "OS") by Commodore, possibly inspired by Apple renaming the Mac operating system from "System" to "Mac OS
".
Version 4.0 of the Amiga operating system was the first version to be branded as a less generic "AmigaOS" (without the space).
What many consider the first versions of AmigaOS (Workbench 1.0 up to 3.0) are here indicated with the Workbench name of their original disks.
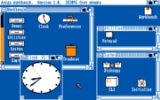
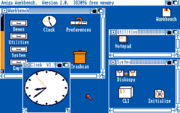 Workbench 1.0 was released for the first time in October 1985. The 1.x series of Workbench defaults to a distinctive blue and orange color scheme, designed to give high contrast on even the worst of television screens (the colors can be changed by the user). Versions 1.1 consists mostly of bug fixes and, like version 1.0, was distributed only for the Amiga 1000
Workbench 1.0 was released for the first time in October 1985. The 1.x series of Workbench defaults to a distinctive blue and orange color scheme, designed to give high contrast on even the worst of television screens (the colors can be changed by the user). Versions 1.1 consists mostly of bug fixes and, like version 1.0, was distributed only for the Amiga 1000
. The entire Workbench operating system consists of three floppy disks: Kickstart, Workbench and ABasic by MetaComCo
.
The Amiga 1000 model needs a Kickstart disk to be inserted into floppy drive to boot up. An image of a simple illustration of a hand
on a white screen, holding a blue Kickstart floppy, invited the user to perform this operation. After the kickstart was loaded into a special section of memory called the writable control store (WCS), the image of the hand appeared again, this time inviting the user to insert the Workbench disk.
Workbench Version 1.2 was the first to support Kickstart stored in a ROM
. Kickstart disk was still necessary for Amiga 1000 models, but it was no longer necessary for Amiga 500 or 2000, but the users of these systems must change the ROMs (which were socketed) to change the kickstart version.
Workbench now spanned two floppy disks, and supported installing and booting from hard drive (assuming the Amiga was equipped with one), the name of the main disk was still named "Workbench" (which is also the user interface portion of the operating system). The second disk was the Extras disk.
Workbench set of disks was still three disks, due to abolition of Kickstart disk. Users of Amiga 1000 could ask a Commodore dealer to obtain one. The third disk was now AmigaBasic by Microsoft
.
Kickstart Version 1.2 corrected various flaws and added AutoConfig
support. AutoConfig is a protocol similar to and is the predecessor of Plug and Play, in that it can configure expansion boards without user intervention.
Kickstart Version 1.3 improved little on its predecessor, the most notable change being auto booting from hard drives.
Into Workbench 1.3 floppy disk, on the other hand, users can find several significant improvements to Workbench, including FFS
a faster file system for hard disks storage which resolved the problem of old Amiga filesystem
which wasted too much hard disk space due to the fact it could store only 488bytes any block of 512bytes keeping 24 bytes for checksums. Many improvements were made to the CLI (command line interface) of Amiga which was now a complete text based Shell, named AmigaShell, and various additional tools and programs.
(this was the only software written by Microsoft for the Amiga).
AmigaBASIC was discontinued with the launch of Kickstart/Workbench 2.x. Version 1.0 shipped instead with a different BASIC language, called ABasiC, implemented by MetaComCo
. Where AmigaBASIC was oriented around creating graphical user interfaces, ABasiC was more similar to the BASIC interpreters shipped with older 8-bit systems, and was geared towards text-based applications.
AmigaBasic by Microsoft, for the first time, could avoid obliged use of numbering lines in programming, and was very advanced for its times, but suffered many flaws. For example it supported only NTSC
TV standard used in USA and not PAL
TV standard used in Europe
.
computers, where it is often referred to as the "Superkickstart ROM". In these machines it is only used to bootstrap the machine and load the Kickstart that will be used to actually boot the system. The appearance of a very early first release of 1.4 was similar to 1.3, but with colors slightly changed. A second version was similar to that of 2.0 and higher, with just minor differences. It is, however, possible to dump out of the OS selection screen by clicking where one would expect to see a close gadget. This will cause the machine to boot Kickstart 1.4 using either the wb_2.x: partition, or from a floppy.
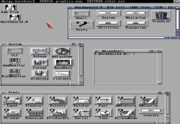 Workbench 2.0 was released in 1990 and introduced a lot of improvements and major advances to the GUI of the overall Amiga operating system. The harsh blue and orange colour scheme was replaced with a much easier on the eye grey and light blue with 3D aspect in the border of the windows. The Workbench was no longer tied to the 640×256 (PAL) or 640×200 (NTSC) display modes, and much of the system was improved with an eye to making future expansion easier. For the first time, a standardised "look and feel" was added. This was done by creating the Amiga Style Guide, and including libraries and software which assisted developers in making conformant software. Technologies included the GUI element creation library gadtools, the software installation scripting language Installer, and the AmigaGuide hypertext help system.
Workbench 2.0 was released in 1990 and introduced a lot of improvements and major advances to the GUI of the overall Amiga operating system. The harsh blue and orange colour scheme was replaced with a much easier on the eye grey and light blue with 3D aspect in the border of the windows. The Workbench was no longer tied to the 640×256 (PAL) or 640×200 (NTSC) display modes, and much of the system was improved with an eye to making future expansion easier. For the first time, a standardised "look and feel" was added. This was done by creating the Amiga Style Guide, and including libraries and software which assisted developers in making conformant software. Technologies included the GUI element creation library gadtools, the software installation scripting language Installer, and the AmigaGuide hypertext help system.
Workbench 2.04 introduced ARexx, a system-wide scripting language. Programmers could add so-called "ARexx ports" to their programs, which allowed them to be controlled from ARexx scripts. Using ARexx, you could make two completely different programs from different vendors work together seamlessly. For example, you could batch-convert a directory of files to thumbnail images with an ARexx-capable image-manipulation program, create and index HTML table of the thumbnails linking to the original images, and display it in a web browser, all from one script. ARexx became very popular, and was widely adopted by programmers.
The AmigaDOS, previously written in BCPL
and very difficult to develop for beyond basic file manipulation, was mostly rewritten in C.
Unfortunately, some badly written software – especially games – failed to run with 2.x, and so a lot of people were upset with this update. Most often, the failure occurred because programmers had used directly manipulated private structures maintained by the operating system, rather than using official function calls. Many users circumvented the problem by installing so-called "kickstart switchers", a small circuit board which held both a Kickstart 1.3 and 2.0 chip, with which they could swap between Kickstart versions at the flick of a switch.
2.x shipped with the A500+ (2.04), A600 (2.05), A3000 and A3000T. Workbench 2.1 was the last in this series, and only released as a software update. It included useful features such as CrossDOS
, to support working with floppy disks formatted for PCs
. Since 2.1 was a software-only release, there was no Kickstart 2.1 ROM.
2.x also introduced PCMCIA card support, for the slot on the A600.
Workbench 2.1 introduced also a standard hypertext markup language for easily building guides for the user or help files, or manuals.It was called Amigaguide
. Release 2.1 was also the first Workbench release to feature a system-standard localization system, allowing the user to make an ordered list of preferred languages; when a locale-aware application runs, it asks the operating system to find the catalog (a file containing translations of the application's strings) best matching the user's preferences.
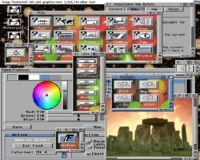 Workbench 3.0 was released in 1992 and version 3.1 in 1994, version 3.1 is the last AmigaOS released by Commodore. However 3.x did not have major changes but many important improvements were included to support new Amiga models. Updates included:
Workbench 3.0 was released in 1992 and version 3.1 in 1994, version 3.1 is the last AmigaOS released by Commodore. However 3.x did not have major changes but many important improvements were included to support new Amiga models. Updates included:
3.x shipped with the CD32
, A1200
, A4000
and A4000T
.

 After the demise of Commodore, Workbench 3.5 was released on 18 October 1999 and 3.9 in December 2000 by Haage & Partner
After the demise of Commodore, Workbench 3.5 was released on 18 October 1999 and 3.9 in December 2000 by Haage & Partner
. The later owners of the Amiga trademark granted a license to a German
company called Haage & Partner to update the Amiga's operating system.
Whereas all previous OS releases ran on Motorola 68000
new release 3.5 onwards required a 68020
or better, CD-ROM and at least 4 MB RAM. Unlike previous releases 3.5 was released on a CD-ROM. The Kickstart 3.1 was also required as the operating system didn't include new ROM.
Updates included:
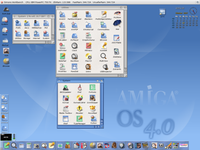 A new version of AmigaOS was released on December 24, 2006 after five years of development by Hyperion Entertainment
A new version of AmigaOS was released on December 24, 2006 after five years of development by Hyperion Entertainment
(Belgium
) under license from Amiga, Inc. for AmigaOne
registered users.
During the five years of development, users of AmigaOne
machines could download from Hyperion repository Pre-Release Versions of AmigaOS 4.0 as long as these were made available. As witnessed by many users into Amiga discussion forum sites, these versions were stable and reliable, despite the fact that they are technically labeled as "pre-releases".
Last stable version of AmigaOS 4.0 for AmigaOne computers is the "July 2007 Update", released for download 18 July 2007 to the registered users of AmigaOne machines.
AmigaOS 4 Classic was released commercially for older Amiga computers with CyberstormPPC and BlizzardPPC accelerator cards in November 2007. It had previously been available only to developers and beta-testers.
-native, finally abandoning the Motorola
68k
processor
. AmigaOS 4.0 will run on some PowerPC
hardware, which currently only includes A1200
, A3000
and A4000
with PowerPC accelerator boards and AmigaOne
motherboards. Amiga, Inc.'s distribution policies for AmigaOS 4.0 and any later versions require that for third-party hardware the OS must be bundled with it, with the sole exception of Amigas with Phase 5 PowerPC accelerator boards, for which the OS will be sold separately.
AmigaOS 4.0 Final introduced a new memory system based on the slab allocator.
Features, among others:
 AmigaOS 4.1 was presented to public July 11, 2008, and was put on sale for September 2008.
AmigaOS 4.1 was presented to public July 11, 2008, and was put on sale for September 2008.
This is a new version and not only a simple update as it features, among others:
AmigaOS
AmigaOS is the default native operating system of the Amiga personal computer. It was developed first by Commodore International, and initially introduced in 1985 with the Amiga 1000...
operating system
Operating system
An operating system is a set of programs that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for application software. The operating system is the most important type of system software in a computer system...
during its two decades of history.
Initially the Amiga operating system had no strong name and branding, as it was seen as an integral part of the Amiga system as a whole. Early names used for the Amiga operating system included "CAOS" and "AmigaDOS". Another non-official name was "Workbench", from the name of the Amiga Desktop environment
Desktop environment
In graphical computing, a desktop environment commonly refers to a style of graphical user interface derived from the desktop metaphor that is seen on most modern personal computers. These GUIs help the user in easily accessing, configuring, and modifying many important and frequently accessed...
, which was included on a floppy disk named "Amiga Workbench".
Version 3.1 of the Amiga operating system was the first version to be officially referred to as "Amiga OS" (with a space between "Amiga" and "OS") by Commodore, possibly inspired by Apple renaming the Mac operating system from "System" to "Mac OS
Mac OS
Mac OS is a series of graphical user interface-based operating systems developed by Apple Inc. for their Macintosh line of computer systems. The Macintosh user experience is credited with popularizing the graphical user interface...
".
Version 4.0 of the Amiga operating system was the first version to be branded as a less generic "AmigaOS" (without the space).
What many consider the first versions of AmigaOS (Workbench 1.0 up to 3.0) are here indicated with the Workbench name of their original disks.
Kickstart/Workbench 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.3

Amiga 1000
The A1000, or Commodore Amiga 1000, was Commodore's initial Amiga personal computer, introduced on July 23, 1985 at the Lincoln Center in New York City....
. The entire Workbench operating system consists of three floppy disks: Kickstart, Workbench and ABasic by MetaComCo
MetaComCo
MetaComCo was a computer systems software company started in 1981 and based in Bristol, England by Peter Mackeonis and Derek Budge.MetaComCo's first product was an MBASIC compatible interpreter for IBM PC's, which was licensed by Peter Mackeonis to Digital Research in 1982, and issued as the...
.
The Amiga 1000 model needs a Kickstart disk to be inserted into floppy drive to boot up. An image of a simple illustration of a hand
Hand
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered extremity located at the end of an arm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs...
on a white screen, holding a blue Kickstart floppy, invited the user to perform this operation. After the kickstart was loaded into a special section of memory called the writable control store (WCS), the image of the hand appeared again, this time inviting the user to insert the Workbench disk.
Workbench Version 1.2 was the first to support Kickstart stored in a ROM
Read-only memory
Read-only memory is a class of storage medium used in computers and other electronic devices. Data stored in ROM cannot be modified, or can be modified only slowly or with difficulty, so it is mainly used to distribute firmware .In its strictest sense, ROM refers only...
. Kickstart disk was still necessary for Amiga 1000 models, but it was no longer necessary for Amiga 500 or 2000, but the users of these systems must change the ROMs (which were socketed) to change the kickstart version.
Workbench now spanned two floppy disks, and supported installing and booting from hard drive (assuming the Amiga was equipped with one), the name of the main disk was still named "Workbench" (which is also the user interface portion of the operating system). The second disk was the Extras disk.
Workbench set of disks was still three disks, due to abolition of Kickstart disk. Users of Amiga 1000 could ask a Commodore dealer to obtain one. The third disk was now AmigaBasic by Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
.
Kickstart Version 1.2 corrected various flaws and added AutoConfig
Autoconfig
Autoconfig is an auto-configuration protocol of Amiga computers which is intended to automatically assign resources to expansion devices without the need for jumper settings...
support. AutoConfig is a protocol similar to and is the predecessor of Plug and Play, in that it can configure expansion boards without user intervention.
Kickstart Version 1.3 improved little on its predecessor, the most notable change being auto booting from hard drives.
Into Workbench 1.3 floppy disk, on the other hand, users can find several significant improvements to Workbench, including FFS
Amiga Fast File System
The Amiga Fast File System is a file system used on the Amiga personal computer. The previous Amiga filesystem upon the release of FFS became known as Amiga Old File System . OFS, while fine on floppy disk, soon proved too slow to keep up with era hard drives...
a faster file system for hard disks storage which resolved the problem of old Amiga filesystem
Amiga Old File System
On the Amiga, the Old File System was the filesystem for Amiga OS before the Amiga Fast File System. Even though it used 512-byte blocks, it reserved the first small portion of each block for metadata, leaving an actual data block capacity of 488 bytes per block...
which wasted too much hard disk space due to the fact it could store only 488bytes any block of 512bytes keeping 24 bytes for checksums. Many improvements were made to the CLI (command line interface) of Amiga which was now a complete text based Shell, named AmigaShell, and various additional tools and programs.
AmigaBASIC and ABasiC
Versions 1.1 through 1.3 shipped with AmigaBASIC, a BASIC implementation designed by MicrosoftMicrosoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
(this was the only software written by Microsoft for the Amiga).
AmigaBASIC was discontinued with the launch of Kickstart/Workbench 2.x. Version 1.0 shipped instead with a different BASIC language, called ABasiC, implemented by MetaComCo
MetaComCo
MetaComCo was a computer systems software company started in 1981 and based in Bristol, England by Peter Mackeonis and Derek Budge.MetaComCo's first product was an MBASIC compatible interpreter for IBM PC's, which was licensed by Peter Mackeonis to Digital Research in 1982, and issued as the...
. Where AmigaBASIC was oriented around creating graphical user interfaces, ABasiC was more similar to the BASIC interpreters shipped with older 8-bit systems, and was geared towards text-based applications.
AmigaBasic by Microsoft, for the first time, could avoid obliged use of numbering lines in programming, and was very advanced for its times, but suffered many flaws. For example it supported only NTSC
NTSC
NTSC, named for the National Television System Committee, is the analog television system that is used in most of North America, most of South America , Burma, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, the Philippines, and some Pacific island nations and territories .Most countries using the NTSC standard, as...
TV standard used in USA and not PAL
PAL
PAL, short for Phase Alternating Line, is an analogue television colour encoding system used in broadcast television systems in many countries. Other common analogue television systems are NTSC and SECAM. This page primarily discusses the PAL colour encoding system...
TV standard used in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
.
Kickstart/Workbench 1.4
Kickstart/Workbench 1.4 was a beta version of the upcoming 2.0 update and never released, but the Kickstart part was shipped in very small quantities with early Amiga 3000Amiga 3000
The Commodore Amiga 3000, or A3000, was the third major release in the Amiga computer family. Released in June 1990, it features improved processing speed, improved rendering of graphics, and a new revision of the operating system...
computers, where it is often referred to as the "Superkickstart ROM". In these machines it is only used to bootstrap the machine and load the Kickstart that will be used to actually boot the system. The appearance of a very early first release of 1.4 was similar to 1.3, but with colors slightly changed. A second version was similar to that of 2.0 and higher, with just minor differences. It is, however, possible to dump out of the OS selection screen by clicking where one would expect to see a close gadget. This will cause the machine to boot Kickstart 1.4 using either the wb_2.x: partition, or from a floppy.
Workbench 2.0, 2.04, 2.05, 2.1

Workbench 2.04 introduced ARexx, a system-wide scripting language. Programmers could add so-called "ARexx ports" to their programs, which allowed them to be controlled from ARexx scripts. Using ARexx, you could make two completely different programs from different vendors work together seamlessly. For example, you could batch-convert a directory of files to thumbnail images with an ARexx-capable image-manipulation program, create and index HTML table of the thumbnails linking to the original images, and display it in a web browser, all from one script. ARexx became very popular, and was widely adopted by programmers.
The AmigaDOS, previously written in BCPL
BCPL
BCPL is a procedural, imperative, and structured computer programming language designed by Martin Richards of the University of Cambridge in 1966.- Design :...
and very difficult to develop for beyond basic file manipulation, was mostly rewritten in C.
Unfortunately, some badly written software – especially games – failed to run with 2.x, and so a lot of people were upset with this update. Most often, the failure occurred because programmers had used directly manipulated private structures maintained by the operating system, rather than using official function calls. Many users circumvented the problem by installing so-called "kickstart switchers", a small circuit board which held both a Kickstart 1.3 and 2.0 chip, with which they could swap between Kickstart versions at the flick of a switch.
2.x shipped with the A500+ (2.04), A600 (2.05), A3000 and A3000T. Workbench 2.1 was the last in this series, and only released as a software update. It included useful features such as CrossDOS
CrossDOS
CrossDOS is file system for AmigaDOS. It was bundled with AmigaOS 2.1 and later, though it did work under Amiga OS 2.04. Its function was to allow working with floppy disks formatted for PCs...
, to support working with floppy disks formatted for PCs
IBM PC compatible
IBM PC compatible computers are those generally similar to the original IBM PC, XT, and AT. Such computers used to be referred to as PC clones, or IBM clones since they almost exactly duplicated all the significant features of the PC architecture, facilitated by various manufacturers' ability to...
. Since 2.1 was a software-only release, there was no Kickstart 2.1 ROM.
2.x also introduced PCMCIA card support, for the slot on the A600.
Workbench 2.1 introduced also a standard hypertext markup language for easily building guides for the user or help files, or manuals.It was called Amigaguide
Amigaguide
AmigaGuide is a hypertext document file format designed for the Amiga, files are stored in ASCII so it is possible to read and edit a file without the need for special software.Since Workbench 2.1 an Amiga Guide system for O.S...
. Release 2.1 was also the first Workbench release to feature a system-standard localization system, allowing the user to make an ordered list of preferred languages; when a locale-aware application runs, it asks the operating system to find the catalog (a file containing translations of the application's strings) best matching the user's preferences.
AmigaOS 3.0, 3.1

- A universal data system, known as datatypes, that allowed programs to load pictures, sound and text in formats they didn't understand directly, through the use of standard plugs (see object-oriented operating systemObject-oriented operating systemAn object-oriented operating system is an operating system which internally uses object-oriented methodologies.An object-oriented operating system is in contrast to an object-oriented user interface or programming framework, which can be placed above a non-object-oriented operating system like DOS,...
) - Better colour remapping for high colour display modes and support for new AGA chipset
- Improved visual appearance for Workbench
- CD-ROM support as required for Amiga CD32Amiga CD32The Amiga CD32, styled "CD32" , was the first 32-bit CD-ROM based video game console released in western Europe, Australia, Canada and Brazil. It was first announced at the Science Museum in London, United Kingdom on 16 July 1993, and was released in September of the same year...
(3.1)
3.x shipped with the CD32
Amiga CD32
The Amiga CD32, styled "CD32" , was the first 32-bit CD-ROM based video game console released in western Europe, Australia, Canada and Brazil. It was first announced at the Science Museum in London, United Kingdom on 16 July 1993, and was released in September of the same year...
, A1200
Amiga 1200
The Amiga 1200, or A1200 , was Commodore International's third-generation Amiga computer, aimed at the home market...
, A4000
Amiga 4000
The Commodore Amiga 4000, or A4000, is the successor of the A2000 and A3000 computers. There are two models, the A4000/040 released in October 1992 with a Motorola 68040 CPU, and the A4000/030 released in April 1993 with a Motorola 68EC030....
and A4000T
Amiga 4000T
The Amiga 4000T, also known as A4000T, was a tower version of the A4000 computer. Using the AGA chipset, it was originally released in small quantities in 1994 with a 25 MHz Motorola 68040 CPU, and re-released in greater numbers by Escom in 1995, after Commodore's demise, along with a new...
.
AmigaOS 3.5, 3.9


Haage & Partner
Haage & Partner is a German company established in 1995. They distribute software products where they usually are the exclusive distributor. Products are aimed at Microsoft Windows and Mac OS. The primary destination countries are Germany, Austria, and Switzerland.Other areas include translations...
. The later owners of the Amiga trademark granted a license to a German
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
company called Haage & Partner to update the Amiga's operating system.
Whereas all previous OS releases ran on Motorola 68000
Motorola 68000
The Motorola 68000 is a 16/32-bit CISC microprocessor core designed and marketed by Freescale Semiconductor...
new release 3.5 onwards required a 68020
Motorola 68020
The Motorola 68020 is a 32-bit microprocessor from Motorola, released in 1984. It is the successor to the Motorola 68010 and is succeeded by the Motorola 68030...
or better, CD-ROM and at least 4 MB RAM. Unlike previous releases 3.5 was released on a CD-ROM. The Kickstart 3.1 was also required as the operating system didn't include new ROM.
Updates included:
- Improved CD filesystem
- Supplied with TCP/IPInternet protocol suiteThe Internet protocol suite is the set of communications protocols used for the Internet and other similar networks. It is commonly known as TCP/IP from its most important protocols: Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol , which were the first networking protocols defined in this...
stack (unregistered time-limited free MiamiDX demo in 3.5, unrestricted AmiTCP/IP in 3.9), web browser (AWeb), and e-mail client - Improved GUI and new toolkit called "ReAction"
- AVI/MPEG movie player (OS3.9)
- New partitioning software to support hard disks larger than 4 GB
- HTML documentation in English and German
- MP3 and CD audio player (OS3.9)
- Dock program (OS3.9)
- Improved Workbench with asynchronous features
- Find utility (OS3.9)
- Unarchiving system called XAD (OS3.9)
- WarpOSWarpOSWarpOS was a multi-tasking kernel for the PowerPC architecture developed by Haage & Partner for the Amiga computer platform in the late 1990s and early 2000s. It ran on PowerUP accelerator boards developed by phase5 which contained both a Motorola 68000 family CPU and a PowerPC CPU with shared...
PowerPCPowerPCPowerPC is a RISC architecture created by the 1991 Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM...
kernel to support PowerUPPowerUP (accelerator)PowerUP boards were dual-processor 68k–PowerPC accelerator boards designed by Phase5 Digital Products for Amiga computers. They had two different processors working in parallel, sharing the complete address space of the Amiga computer system.-History:...
accelerator boards
AmigaOS 4

Hyperion Entertainment
Hyperion Entertainment CVBA is a Belgian software company which in its early years focused in porting Windows games to Amiga, Linux and Macintosh. Later on, they were contracted by Amiga Incorporated to develop AmigaOS 4 and retired from the gaming business...
(Belgium
Belgium
Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
) under license from Amiga, Inc. for AmigaOne
AmigaOne
AmigaOne is a series of computers intended to run AmigaOS 4 developed by Hyperion Entertainment. Earlier models were produced by Eyetech, and were based on the Teron series of PowerPC POP mainboards...
registered users.
During the five years of development, users of AmigaOne
AmigaOne
AmigaOne is a series of computers intended to run AmigaOS 4 developed by Hyperion Entertainment. Earlier models were produced by Eyetech, and were based on the Teron series of PowerPC POP mainboards...
machines could download from Hyperion repository Pre-Release Versions of AmigaOS 4.0 as long as these were made available. As witnessed by many users into Amiga discussion forum sites, these versions were stable and reliable, despite the fact that they are technically labeled as "pre-releases".
Last stable version of AmigaOS 4.0 for AmigaOne computers is the "July 2007 Update", released for download 18 July 2007 to the registered users of AmigaOne machines.
AmigaOS 4 Classic was released commercially for older Amiga computers with CyberstormPPC and BlizzardPPC accelerator cards in November 2007. It had previously been available only to developers and beta-testers.
Version 4.0
The new version is PowerPCPowerPC
PowerPC is a RISC architecture created by the 1991 Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM...
-native, finally abandoning the Motorola
Motorola
Motorola, Inc. was an American multinational telecommunications company based in Schaumburg, Illinois, which was eventually divided into two independent public companies, Motorola Mobility and Motorola Solutions on January 4, 2011, after losing $4.3 billion from 2007 to 2009...
68k
68k
The Motorola 680x0/m68000/68000 is a family of 32-bit CISC microprocessors. During the 1980s and early 1990s, they were popular in personal computers and workstations and were the primary competitors of Intel's x86 microprocessors...
processor
Central processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
. AmigaOS 4.0 will run on some PowerPC
PowerPC
PowerPC is a RISC architecture created by the 1991 Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM...
hardware, which currently only includes A1200
Amiga 1200
The Amiga 1200, or A1200 , was Commodore International's third-generation Amiga computer, aimed at the home market...
, A3000
Amiga 3000
The Commodore Amiga 3000, or A3000, was the third major release in the Amiga computer family. Released in June 1990, it features improved processing speed, improved rendering of graphics, and a new revision of the operating system...
and A4000
Amiga 4000
The Commodore Amiga 4000, or A4000, is the successor of the A2000 and A3000 computers. There are two models, the A4000/040 released in October 1992 with a Motorola 68040 CPU, and the A4000/030 released in April 1993 with a Motorola 68EC030....
with PowerPC accelerator boards and AmigaOne
AmigaOne
AmigaOne is a series of computers intended to run AmigaOS 4 developed by Hyperion Entertainment. Earlier models were produced by Eyetech, and were based on the Teron series of PowerPC POP mainboards...
motherboards. Amiga, Inc.'s distribution policies for AmigaOS 4.0 and any later versions require that for third-party hardware the OS must be bundled with it, with the sole exception of Amigas with Phase 5 PowerPC accelerator boards, for which the OS will be sold separately.
AmigaOS 4.0 Final introduced a new memory system based on the slab allocator.
Features, among others:
- Fully skinnable GUI
- Virtualized memory
- Integrated viewer for PDF and other document formats
- Support for PowerPC (native) and 68k (interpreted/JIT) applications
- New drivers for various hardware
- New memory allocation system
- Support for file sizes larger than 2 GB
- Integrated Picasso 96 2D Graphics API
- Integrated Warp3DWarp3DWarp3D was a project run by Haage & Partner in 1998, that aimed to provide a standard API which would enable programmers to access, and therefore use, 3D hardware on the Amiga....
3D Graphics API
Version 4.1

This is a new version and not only a simple update as it features, among others:
- Memory paging
- JXFS filesystem with the support for drives and partitions of multiple terabyte size
- Hardware compositing engine (RadeonRadeonRadeon is a brand of graphics processing units and random access memory produced by Advanced Micro Devices , first launched in 2000 by ATI Technologies, which was acquired by AMD in 2006. Radeon is the successor to the Rage line. There are four different groups, which can be differentiated by...
R1xx and R2xx family) - Implementation of the CairoCairo (graphics)cairo is a software library used to provide a vector graphics-based, device-independent API for software developers. It is designed to provide primitives for 2-dimensional drawing across a number of different backends...
device-independent 2D rendering library - New and improved DOS functionality (full 64 bit support, universal notification support, automatic expunge and reload of updated disk resources)
- Improved 3D hardware accelerated screen-dragging

