
Aminoshikimate pathway
Encyclopedia
Aminoshikimate pathway is a novel variation of the shikimate pathway. The aminoshikimate pathway was first discovered and studied in rifamycin
B producer Amycolatopsis mediterranei. Its end product, 3-amino-5-hydroxybenzoate, serves as an initiator for polyketide synthases in the biosynthesis of ansamycin
s.
, which is a promising starting material for the synthesis of antiinfluenza agent Tamiflu.
Rifamycin
The rifamycins are a group of antibiotics that are synthesized either naturally by the bacterium Amycolatopsis mediterranei or artificially. They are a subclass of the larger family Ansamycin...
B producer Amycolatopsis mediterranei. Its end product, 3-amino-5-hydroxybenzoate, serves as an initiator for polyketide synthases in the biosynthesis of ansamycin
Ansamycin
Ansamycins is a family of secondary metabolites that show antimicrobial activity against many gram-positive and some gram-negative bacteria and includes various compounds, among which: streptovaricins and rifamycins...
s.
Overview
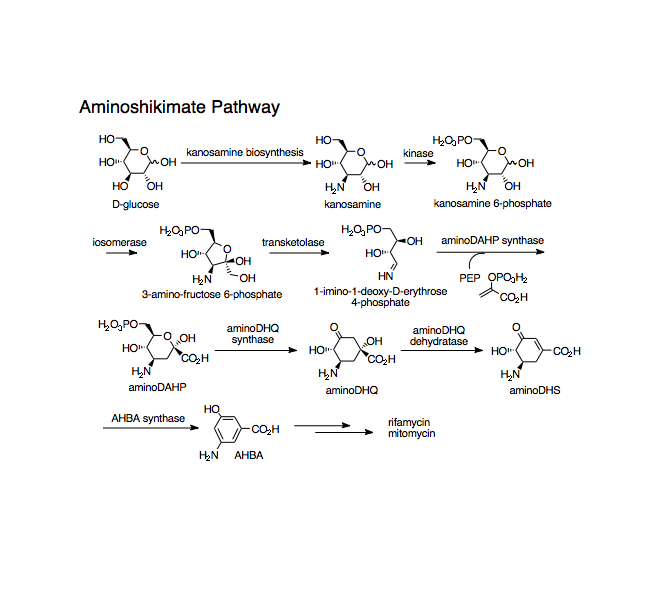
Floss and coworkers identified the gene cluster associated with the Aminoshikimate pathway in Amycolatopsis mediterranei. The enzyme-catalyzed condensation of 1-deoxy-1-imino-d-erythrose 4-phosphate with phosphoenolpyruvate to form 4-amino-3,4-dideoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonic acid 7-phosphate has been proposed to be the first committed step in the aminoshikimate pathway. Guo and Frost demonstrated that the unusual metabolite, 1-deoxy-1-imino-d-erythrose 4-phosphate, is derived from 3-amino-3-deoxy-d-fructose 6-phosphate. In addition, kanosamine biosynthesis has been directly implicated by Guo and Frost as the source of the aminoshikimate pathway's nitrogen atom.
Uses
Aminoshikimate pathway has been assembled in E. coli to synthesize aminoshikimic acidAminoshikimic acid
Aminoshikimic acid is a synthetic crystalline carboxylic acid. It is characterized by multiple stereogenic centers and functional groups arrayed around a six-membered carbocyclic ring...
, which is a promising starting material for the synthesis of antiinfluenza agent Tamiflu.

