Anga
Encyclopedia
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
in the 6th century BCE until taken over by Magadha
Magadha
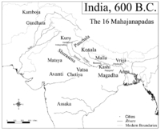
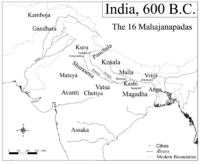
Magadha formed one of the sixteen Mahājanapadas or kingdoms in ancient India. The core of the kingdom was the area of Bihar south of the Ganga; its first capital was Rajagriha then Pataliputra...
in the same century. Counted among the "sixteen great nations" (solas Mahajanapadas) in Buddhist texts
Buddhist texts
Buddhist texts can be categorized in a number of ways. The Western terms "scripture" and "canonical" are applied to Buddhism in inconsistent ways by Western scholars: for example, one authority refers to "scriptures and other canonical texts", while another says that scriptures can be categorized...
like the Anguttara Nikaya
Anguttara Nikaya
The Anguttara Nikaya is a Buddhist scripture, the fourth of the five nikayas, or collections, in the Sutta Pitaka, which is one of the "three baskets" that comprise the Pali Tipitaka of Theravada Buddhism...
, Anga also finds mention in the Jain Vyakhyaprajnapti
Vyakhyaprajnapti
Vyākhyāprajñapti commonly known as Bhagavati sūtra is the fifth of the 12 Jain āagam said to be promulgated by Bhagwan Mahavara. Vyākhyāprajñapti translated as "Exposition of Explanations" is said to have been composed by Sudharma Swami Gandhara as per the Svethambara tradition. It is the largest...
’s list of ancient janapadas
Janapadas
The Janapadas were the major realms or kingdoms of Vedic India which, by the 6th century BC, evolved into the sixteen classical Mahajanapadas.-Etymology:...
.
Some refer that the Angas were grouped with people of ‘mixed origin’, generally in the later ages.
Location
Based on MahabharataMahabharata
The Mahabharata is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India and Nepal, the other being the Ramayana. The epic is part of itihasa....
evidence, the kingdom
Monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which the office of head of state is usually held until death or abdication and is often hereditary and includes a royal house. In some cases, the monarch is elected...
of the Angas roughly corresponded to the districts of Bhagalpur
Bhagalpur
Bhagdattpuram was one of the most influential towns in "Aryavarta" . It is supposed to have been concurrent to Patliputra or Patna. Bhagdattpuram finds its mention in the Vedas and Ramayana as well. It is supposed to be the kingdom of Daanvir Karna, the son of Kunti and the Sun God...
, Banka
Banka
Banka may refer to:* Banka, Bihar, a town in Bihar, India* Banka district, Bihar, India* Bankə, Azerbaijan*Banka, Cameroon* the Banka Gold Mining Project operated by Mwana Africa plc, in Ghana...
, Purnia
Purnia
Purnia is a city and a Municipal Corporation in Purnia district of the Indian state of Bihar. It is located 400 km from Patna.The Indian army, Border Security Force ,and the SSB and the have bases around the city...
, Munger
Munger
Munger town is the headquarters of Munger district, in the Indian state of Bihar. Historically, Munger is known for its manufacturing of iron articles such as firearms and swords. One of the major institutions in Munger is Bihar School of Yoga. It is one of the foremost learning center in the...
, Katihar
Katihar
Katihar is a town situated in the north eastern part of Bihar state in India. It is headquarters of Katihar district.- Geography :Katihar is located at...
, Jamui
Jamui
Jamui is a city and a municipality in Jamui district in the Indian state of Bihar. It is the district headquarters of Jamui district.-Geography:Jamui is located at...
, and Madhepura
Madhepura
Madhepura is a city and a municipality in Madhepura district in the Indian state of Bihar. Madhepura as it stands now was carved out of Saharsa district and got the status of revenue district on 9 May 1981. Prior to that, Madhepura was a sub-division under Bhagalpur district with effect from 3...
in Bihar
Bihar
Bihar is a state in eastern India. It is the 12th largest state in terms of geographical size at and 3rd largest by population. Almost 58% of Biharis are below the age of 25, which is the highest proportion in India....
and districts of Deoghar
Deoghar
Deoghar is the headquarters city of Deoghar District in the Santhal Parganas division of the state of Jharkhand, India. It is an important Hindu pilgrimage centre, having in Baidyanath Temple one of the twelve Shiva Jyothirlingams in India and also one of the 51 Shakti Peethas in India.-Origin of...
, Godda
Godda
Godda is a city and a municipality in Godda district in the Indian state of Jharkhand. The district has an area of 2110 km². The district headquarter is Godda.-Geography:...
, and Sahebganj
Sahebganj
Sahebganj is the district headquarters of Sahebganj district of Jharkhand state, India.Sahebganj means a place of masters . The place is likely to have gotten its name because a number of English and other European people lived and worked in and around the railway station during the British Raj...
in Jharkhand
Jharkhand
Jharkhand is a state in eastern India. It was carved out of the southern part of Bihar on 15 November 2000. Jharkhand shares its border with the states of Bihar to the north, Uttar Pradesh and Chhattisgarh to the west, Orissa to the south, and West Bengal to the east...
; later extended to include parts of Bengal
Bengal
Bengal is a historical and geographical region in the northeast region of the Indian Subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. Today, it is mainly divided between the sovereign land of People's Republic of Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, although some regions of the previous...
. The River Champa (modern Chandan) formed the boundaries between the Magadha
Magadha
Magadha formed one of the sixteen Mahājanapadas or kingdoms in ancient India. The core of the kingdom was the area of Bihar south of the Ganga; its first capital was Rajagriha then Pataliputra...
in the west and Anga in the east. Anga was bounded by river Koshi
Koshi River
The Kosi River or Koshi —also Saptakoshi for its seven Himalayan tributaries—is a trans-boundary river flowing through Nepal and India. Some of the rivers of the Koshi system, such as the Arun, the Sun Kosi and the Bhote Koshi, originate in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China...
on the north. According to the Mahabharata
Mahabharata
The Mahabharata is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India and Nepal, the other being the Ramayana. The epic is part of itihasa....
, Duryodhana
Duryodhana
In the Hindu epic the Mahābhārata, Duryodhana is the eldest son of the blind king Dhritarashtra by Queen Gandhari, the eldest of the one hundred Kaurava brothers, Emperor of the world at that time which means Emperor of India or Bharatvarsha as it was known at that time, cousin and the chief...
had named Karna
Karna
Karna or Radheya is one of the central characters in the epic Mahābhārata, from ancient India. He was the King of Anga...
the King of Anga.
Sabhaparava of Mahabharata (II.44.9) mentions Anga
Anga
Anga was a kingdom that flourished on the eastern Indian subcontinent in the 6th century BCE until taken over by Magadha in the same century. Counted among the "sixteen great nations" in Buddhist texts like the Anguttara Nikaya, Anga also finds mention in the Jain Vyakhyaprajnapti’s list of...
and Vanga
Vanga Kingdom
Vanga orBengal was a kingdom located in the eastern part of the Indian Subcontinent, comprising part of West Bengal, India and present-day modern Bangladesh. It was a seafaring nation of Ancient India.- References in Mahabharata :...
as forming one country. The Katha-Sarit-Sagara also attests that Vitankapur, a city of Anga was situated on the shores of the sea. Thus the boundaries of Anga may have extended to the sea in the east.
Capital
The capital of Anga was Champa (Campā). According to Mahabharata and HarivamsaHarivamsa
The Harivamsha is an important work of Sanskrit literature, containing 16,374 verses, mostly in metre. The text is also known as . This text is believed as a khila to the Mahabharata and is traditionally ascribed to Krishna Dvaipayana Veda Vyasa...
, Champa was formerly known as Malini. Champa was located on the right bank of river Ganges near its junction with river Champa. It was a very flourishing city and is referred to as one of six principal cities of ancient India (Digha Nikaya
Digha Nikaya
The Digha Nikaya is a Buddhist scripture, the first of the five nikayas, or collections, in the Sutta Pitaka, which is one of the "three baskets" that compose the Pali Tipitaka of Theravada Buddhism...
). In the Jataka
Jataka
The Jātakas refer to a voluminous body of literature native to India concerning the previous births of the Buddha....
stories, the city of Champa is also referred to as Kala-Champa. Maha-Janaka Jataka states that the city was located about sixty yojanas (one yojana = 16.4 km) from Mithila
Mithila
Mithila was a city in Ancient India, the capital of the Videha Kingdom. The name Mithila is also commonly used to refer to the Videha Kingdom itself, as well as to the modern-day territories that fall within the ancient boundaries of Videha...
. Bhagalpur
Bhagalpur
Bhagdattpuram was one of the most influential towns in "Aryavarta" . It is supposed to have been concurrent to Patliputra or Patna. Bhagdattpuram finds its mention in the Vedas and Ramayana as well. It is supposed to be the kingdom of Daanvir Karna, the son of Kunti and the Sun God...
in Bihar
Bihar
Bihar is a state in eastern India. It is the 12th largest state in terms of geographical size at and 3rd largest by population. Almost 58% of Biharis are below the age of 25, which is the highest proportion in India....
, usually identified as the site of Champa, still has two villages called Champa-nagara and Champa-pura.
Champa was noted for its wealth and commerce. It was also a great center of trade and commerce and its merchants regularly sailed to distant Suvarnabhumi
Suvarnabhumi
Suvarnabhumi or Suvannabhumi meaning the "Golden Land" or "Land of Gold", is a term coined by the ancient Indians which refers broadly to Lower Burma, Lower Thailand, Lower Malay Peninsula, the Sumatra, but more generally accepted to refer more specifically to Lower Burma...
for trading purposes. During his pilgrimage there in the end of the 4th century, the Chinese monk Faxan noted the numerous Buddhist temples that still existed in the city, transliterated Chanpo in Chinese (瞻波 ). The kingdom of Anga by then had long ceased to exist; it had been known as Yāngjiā (鴦伽) in Chinese.
The later kingdom of Champa
Champa
The kingdom of Champa was an Indianized kingdom that controlled what is now southern and central Vietnam from approximately the 7th century through to 1832.The Cham people are remnants...
(in present-day Vietnam) was thought to have originated from this east Indian Champa, although anthropological evidence indicates they are from Borneo
Borneo
Borneo is the third largest island in the world and is located north of Java Island, Indonesia, at the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia....
on the other side Indochinese Peninsula.
Other important cities of Anga are said to be Assapura and Bhadrika.
Origin of Name
MahabharataMahabharata
The Mahabharata is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India and Nepal, the other being the Ramayana. The epic is part of itihasa....
(I.104.53-54) and Puranic literature attest that the name Anga had originated eponymously from the name of Prince Anga, the founder of the kingdom.
Ramayana
Ramayana
The Ramayana is an ancient Sanskrit epic. It is ascribed to the Hindu sage Valmiki and forms an important part of the Hindu canon , considered to be itihāsa. The Ramayana is one of the two great epics of India and Nepal, the other being the Mahabharata...
(1.23.14) narrates the origin of name Anga as the place where Kamadeva was burnt to death by Siva and where his body parts(angas) are scattered.
Recorded History
The earliest mention occurs in the Atharava VedaAtharvaveda
The Atharvaveda is a sacred text of Hinduism and one of the four Vedas, often called the "fourth Veda"....
(V.22.14) where they find mention along with the Magadhas, Gandharis
Gandhara
Gandhāra , is the name of an ancient kingdom , located in northern Pakistan and eastern Afghanistan. Gandhara was located mainly in the vale of Peshawar, the Potohar plateau and on the Kabul River...
and the Mujavatas, all apparently as a despised people.
Puranic texts place the janapadas of the Angas, Kalingas, Vangas, Pundras (or Pundra Kingdom
Pundra Kingdom
Pundra was an eastern kingdom located in West Bengal, Bangladesh and Purnia . A Pundra king challenged Vasudeva Krishna by imitating his attributes. He called himself Paundraka Vasudeva. He was later killed by Vasudeva Krishna in a battle...
- now some part of Eastern Bihar
Bihar
Bihar is a state in eastern India. It is the 12th largest state in terms of geographical size at and 3rd largest by population. Almost 58% of Biharis are below the age of 25, which is the highest proportion in India....
, West Bengal
West Bengal
West Bengal is a state in the eastern region of India and is the nation's fourth-most populous. It is also the seventh-most populous sub-national entity in the world, with over 91 million inhabitants. A major agricultural producer, West Bengal is the sixth-largest contributor to India's GDP...
and Bangladesh
Bangladesh
Bangladesh , officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh is a sovereign state located in South Asia. It is bordered by India on all sides except for a small border with Burma to the far southeast and by the Bay of Bengal to the south...
), Vidarbhas, and Vindhya-vasis in the Purva-Dakshina division.
The Puranas also list several early kings of Anga. The Mahagovinda Suttanta refers to king Dhatarattha of Anga. Jain texts refer to Dhadhivahana, as a ruler of the Angas. Puranas and Harivamsa represent him as the son and immediate successor of Anga, the eponymous founder of the kingdom. Jain traditions place him at the beginning of sixth century BCE.
Between the Vatsas and the realm of Anga, lived the Magadhas, who initially were comparatively a weak people. A great struggle went on between the Angas and its eastern neighbors. The Vidhura Pandita Jataka describes Rajagriha (the Magadhan Capital) as the city of Anga and Mahabharata also refers to a sacrifice performed by the king of Anga at Mount Vishnupada (at Gaya
Gaya, India
Gaya is the second largest city of Bihar, India, and it is also the headquarters of Gaya District.Gaya is 100 kilometers south of Patna, the capital city of Bihar. Situated on the banks of Falgu River , it is a place sanctified by both the Hindu and the Buddhist religions...
). This indicates that Anga had initially succeeded in annexing the Magadhas, and thus its borders extended to the kingdom of Matsya
Matsya
Matsya was the first Avatar of Vishnu in Hinduism. The great flood finds mention in Hindu mythology texts like the Satapatha Brahmana, where in the Matsya Avatar takes place to save the pious and the first man, Manu and advices him to build a giant boat.-The Legend:According to the Matsya...
country.
This success of Angas did not last long. About the middle of 6th century BC, Bimbisara
Bimbisara
Bimbisara was a King, and later, Emperor of the Magadha empire from 543 BC to his death and belonged to the Hariyanka dynasty.-Career:There are many accounts of Bimbisara in the Jain texts and the Buddhist Jatakas, since he was a contemporary of Mahavira and Gautama Buddha. He was the king of...
, the crown prince of Magadha had killed Brahmadatta, the last independent king of Anga and seized Champa. Bimbisara made it as his head-quarters and ruled over it as his father's Viceroy. Thenceforth, Anga became an integral part of growing Magadha empire (PHAI, 1996).

