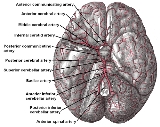
Anterior spinal artery
Encyclopedia
In human anatomy
, the anterior spinal artery is the blood vessel
that supplies the anterior portion of the spinal cord
. It arises from branches of the vertebral arteries
and is supplied by the anterior segmental medullary arteries, including the artery of Adamkiewicz
, and courses along the anterior aspect of the spinal cord.
, unites with its fellow of the opposite side at the level of the foramen magnum.
One of these vessels is usually larger than the other, but occasionally they are about equal in size.
The single trunk, thus formed, descends on the front of the medulla spinalis, and is reinforced by a succession of small branches which enter the vertebral canal through the intervertebral foramina
; these branches are derived from the vertebral artery
and the ascending cervical artery
of the inferior thyroid artery
in the neck; from the intercostal arteries
in the thorax
; and from the lumbar artery, iliolumbar artery
and lateral sacral arteries in the abdomen
and pelvis
.
They unite, by means of ascending and descending branches, to form a single anterior median artery, which extend as far as the lower part of the medulla spinalis, and is continued as a slender twig on the filum terminale
.
This vessel is placed in the pia mater
along the anterior median fissure
; it supplies that membrane, and the substance of the medulla spinalis, and sends off branches at its lower part to be distributed to the cauda equina.
, causing motor deficits, and bilateral disruption of the spinothalamic tract
, causing sensory deficits in the form of pain/temperature sense loss. This is Anterior spinal artery syndrome
. This occurs when the disruption of the anterior spinal artery is at the level of the spinal cord. Contrast this with Medial medullary syndrome
when the anterior spinal artery is occluded at the level of the medulla. This causes different symptoms. It affects the cortiospinal tract - contralaterally, medial lemniscus - contralaterally, and hypoglossal nerve - ipsilaterally.
Human anatomy
Human anatomy is primarily the scientific study of the morphology of the human body. Anatomy is subdivided into gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy. Gross anatomy is the study of anatomical structures that can be seen by the naked eye...
, the anterior spinal artery is the blood vessel
Blood vessel
The blood vessels are the part of the circulatory system that transports blood throughout the body. There are three major types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the capillaries, which enable the actual exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and...
that supplies the anterior portion of the spinal cord
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the brain . The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system...
. It arises from branches of the vertebral arteries
Vertebral artery
The vertebral arteries are major arteries of the neck. They branch from the subclavian arteries and merge to form the single midline basilar artery in a complex called the vertebrobasilar system, which supplies blood to the posterior part of the circle of Willis and thus significant portions of the...
and is supplied by the anterior segmental medullary arteries, including the artery of Adamkiewicz
Artery of Adamkiewicz
In human anatomy, the Artery of Adamkiewicz is the largest anterior segmental medullary artery.It has several other names, including:* Adamkiewicz artery* great radicular artery of Adamkiewicz* major anterior segmental medullary artery...
, and courses along the anterior aspect of the spinal cord.
Path
The anterior spinal artery is a small branch, which arises near the termination of the vertebral, and, descending in front of the medulla oblongataMedulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata is the lower half of the brainstem. In discussions of neurology and similar contexts where no ambiguity will result, it is often referred to as simply the medulla...
, unites with its fellow of the opposite side at the level of the foramen magnum.
One of these vessels is usually larger than the other, but occasionally they are about equal in size.
The single trunk, thus formed, descends on the front of the medulla spinalis, and is reinforced by a succession of small branches which enter the vertebral canal through the intervertebral foramina
Intervertebral foramina
When the spinal vertebrae are articulated with each other the bodies form a strong pillar for the support of the head and trunk, and the vertebral foramina constitute a canal for the protection of the medulla spinalis...
; these branches are derived from the vertebral artery
Vertebral artery
The vertebral arteries are major arteries of the neck. They branch from the subclavian arteries and merge to form the single midline basilar artery in a complex called the vertebrobasilar system, which supplies blood to the posterior part of the circle of Willis and thus significant portions of the...
and the ascending cervical artery
Ascending cervical artery
The ascending cervical artery is a small branch which arises from the inferior thyroid artery as that vessel is passing behind the carotid sheath; it runs up on the anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the cervical vertebræ in the interval between the Scalenus anterior and Longus...
of the inferior thyroid artery
Inferior thyroid artery
The inferior thyroid artery arrises from the thyrocervical trunk and passes upward, in front of the vertebral artery and Longus colli, then turns medially behind the carotid sheath and its contents, and also behind the sympathetic trunk, the middle cervical ganglion resting upon the...
in the neck; from the intercostal arteries
Intercostal arteries
The intercostal arteries are a group of arteries that supply the area between the ribs , called the intercostal space.* Highest intercostal artery - first and second intercostal spaces...
in the thorax
Thorax
The thorax is a division of an animal's body that lies between the head and the abdomen.-In tetrapods:...
; and from the lumbar artery, iliolumbar artery
Iliolumbar artery
The iliolumbar artery is the first branch of the posterior trunk of the internal iliac artery.-Course:The iliolumbar artery turns upward behind the obturator nerve and the external iliac artery and vein, to the medial border of the psoas major, behind which it divides into:* Lumbar branch of...
and lateral sacral arteries in the abdomen
Abdomen
In vertebrates such as mammals the abdomen constitutes the part of the body between the thorax and pelvis. The region enclosed by the abdomen is termed the abdominal cavity...
and pelvis
Pelvis
In human anatomy, the pelvis is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the lower limbs .The pelvis includes several structures:...
.
They unite, by means of ascending and descending branches, to form a single anterior median artery, which extend as far as the lower part of the medulla spinalis, and is continued as a slender twig on the filum terminale
Filum terminale
The filum terminale , is a delicate strand of fibrous tissue, about 20 cm. in length, proceeding downward from the apex of the conus medullaris. It gives longitudinal support to the spinal cord and consists of two parts:...
.
This vessel is placed in the pia mater
Pia mater
Pia mater often referred to as simply the pia, is the delicate innermost layer of the meninges, the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. The word finds its roots in Latin, meaning literally "tender mother." The other two meningeal membranes are the dura mater and the arachnoid mater....
along the anterior median fissure
Anterior median fissure
Anterior median fissure can refer to:* Anterior median fissure of the spinal cord* Anterior median fissure of the medulla oblongata...
; it supplies that membrane, and the substance of the medulla spinalis, and sends off branches at its lower part to be distributed to the cauda equina.
Disorders
Disruption of the anterior spinal cord leads to bilateral disruption of the corticospinal tractCorticospinal tract
The corticospinal or pyramidal tract is a collection of axons that travel between the cerebral cortex of the brain and the spinal cord....
, causing motor deficits, and bilateral disruption of the spinothalamic tract
Spinothalamic tract
The spinothalamic tract is a sensory pathway originating in the spinal cord. It transmits information to the thalamus about pain, temperature, itch and crude touch...
, causing sensory deficits in the form of pain/temperature sense loss. This is Anterior spinal artery syndrome
Anterior spinal artery syndrome
Ischemia or infarction of the spinal cord in the distribution of the anterior spinal artery, which supplies the ventral two-thirds of the spinal cord and Medulla.-Causes:...
. This occurs when the disruption of the anterior spinal artery is at the level of the spinal cord. Contrast this with Medial medullary syndrome
Medial medullary syndrome
Medial medullary syndrome, also known as inferior alternating syndrome, hypoglossal alternating hemiplegia, lower alternating hemiplegia, or Dejerine syndrome, is a type of alternating hemiplegia characterized by a set of clinical features resulting from occlusion of the anterior spinal artery...
when the anterior spinal artery is occluded at the level of the medulla. This causes different symptoms. It affects the cortiospinal tract - contralaterally, medial lemniscus - contralaterally, and hypoglossal nerve - ipsilaterally.
External links
- Yoshioka K, Niinuma H, Ohira A, Nasu K, Kawakami T, Sasaki M, Kawazoe K. MR angiography and CT angiography of the artery of Adamkiewicz: noninvasive preoperative assessment of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm. Radiographics. 2003 Sep-Oct;23(5):1215-25. PMID 12975511 Full Text
- Drawing of the anterior spinal artery
- Horizontal view of blood supply to the spinal cord
- Diagram at nih.gov

