Anti-saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies
Encyclopedia
Anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies (ASCA
), along with perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (pANCA), are among the two most useful and often discriminating markers for colitis. ASCA tends to recognize Crohn's disease more frequently, whereas pANCA tend to recognize ulcerative colitis.
ASCA antibodies react to the following yeast proteins
Diseases in which ASCA are found:
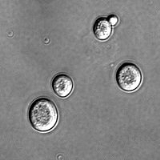
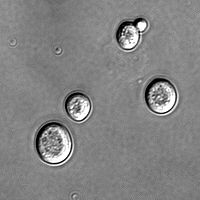 Intestinal yeast and ASCA+. Intestinal yeast infections are seen in malabsorptive diseases like coeliac disease. In Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis the presence of intestinal S. cerevisiae is rare, but the association with irritiable bowel in coeliac disease remains unstudied.
Intestinal yeast and ASCA+. Intestinal yeast infections are seen in malabsorptive diseases like coeliac disease. In Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis the presence of intestinal S. cerevisiae is rare, but the association with irritiable bowel in coeliac disease remains unstudied.
 Mannan
Mannan
(oligomannin) is a component of the yeast cell wall
. Antibodies to yeast mannans are found at increased frequency in Crohn's disease
and ASCA+ Crohn's tend to have lower low levels of mannan-binding lectin. Experimentally, antibodies to mannans from yeast can also crossreact to mannans of other types of yeast. Study of the sugars indicated that a mannotetraose (4-mer) was responsible for highest response.
Studies of the 200 kDa
glycoprotein antibodies found them commonly in healthy people, suggesting that the
disease associated antibodies are to their carbohydrate moieties. Mannans from other yeast, for example candida albicans, have found to cross react with ASCA which suggests that other yeast may induce ASCA associated diseases.
Mannan-binding lectin (MBL
) is a lectin
produced by humans. In ASCA+ Crohn's disease the serum level of this protein is lower. Cellular response to mannan in ASCA+ peripheral blood lymphocytes
could be inhibited by adding MBL, however, a high frequency of mutations in the MBL gene was found in ASCA+ patients.
/CD69
, upon proliferative stimulation of T-helper lymphocytes.
ASCA+ is a predictor for Crohn's disease with high specificity and positive predictive value (87% and 78% respectively). ASCA are associated with proximal (gastroduodenal and small bowel involvement) rather than purely colonic disease (P < 0.001) and with a more severe disease phenotype and requirement for surgery over a median follow-up time of 9 years (P < 0.0001).
There is no association between genetic markers for Crohn's disease and NOD2/CARD15 or MP (IgA or IgG) indicating heterogeneous causes for Crohn's disease. [Note: CD is a common abbreviation for Crohn's disease. It is more commonly used for coeliac disease which may be primary to some forms of colitis. When reviewing abstracts for colitis, it is important to note the abbreviation is used for both.]
ASCA
ASCA can refer to:* Association for Student Conduct Administration* ASCA * Advanced Satellite for Cosmology and Astrophysics* Australian Shepherd Club of America* Amsterdam School for Cultural Analysis* American School Counseling Association...
), along with perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (pANCA), are among the two most useful and often discriminating markers for colitis. ASCA tends to recognize Crohn's disease more frequently, whereas pANCA tend to recognize ulcerative colitis.
ASCA antibodies react to the following yeast proteins
- Mannans
- 200 kDA glycoprotein.
Diseases in which ASCA are found:
- Behçet's diseaseBehçet's diseaseBehçet's disease is a rare immune-mediated systemic vasculitis that often presents with mucous membrane ulceration and ocular involvements...
- The association with ASCA is not generally strong, but increased in patients with gastrointestinal symptoms. - Celiac disease
- ColitisColitisIn medicine, colitis refers to an inflammation of the colon and is often used to describe an inflammation of the large intestine .Colitides may be acute and self-limited or chronic, i.e...
- Ulcerative colitisUlcerative colitisUlcerative colitis is a form of inflammatory bowel disease . Ulcerative colitis is a form of colitis, a disease of the colon , that includes characteristic ulcers, or open sores. The main symptom of active disease is usually constant diarrhea mixed with blood, of gradual onset...
-familial. - Microscopic colitisMicroscopic colitisMicroscopic colitis refers to two medical conditions which cause diarrhea: collagenous colitis and lymphocytic colitis. Both conditions are characterised by the following triad of clinicopathological features:# Chronic watery diarrhoea;# Normal colonoscopy;...
- Collagenous colitis
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's diseaseCrohn's diseaseCrohn's disease, also known as regional enteritis, is a type of inflammatory bowel disease that may affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from mouth to anus, causing a wide variety of symptoms...

Anti-mannans

Mannan
Mannan is a plant polysaccharide that is a polymer of the sugar mannose.Detection of mannan leads to lysis in the mannan-binding lectin pathway.It is generally found in yeast, bacteria and plants. It shows α linkage. It is a form of storage polysaccharide.-See Also:Mannan Oligosaccharides...
(oligomannin) is a component of the yeast cell wall
Cell wall
The cell wall is the tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to...
. Antibodies to yeast mannans are found at increased frequency in Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease, also known as regional enteritis, is a type of inflammatory bowel disease that may affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from mouth to anus, causing a wide variety of symptoms...
and ASCA+ Crohn's tend to have lower low levels of mannan-binding lectin. Experimentally, antibodies to mannans from yeast can also crossreact to mannans of other types of yeast. Study of the sugars indicated that a mannotetraose (4-mer) was responsible for highest response.
Studies of the 200 kDa
glycoprotein antibodies found them commonly in healthy people, suggesting that the
disease associated antibodies are to their carbohydrate moieties. Mannans from other yeast, for example candida albicans, have found to cross react with ASCA which suggests that other yeast may induce ASCA associated diseases.
Mannan-binding lectin (MBL
Mannan-binding lectin
Mannose-binding lectin , also named mannose- or mannan-binding protein , is an important factor in innate immunity.-Function:MBL belongs to the class of collectins in the C-type lectin superfamily, whose function appears to be pattern recognition in the first line of defense in the pre-immune...
) is a lectin
Lectin
Lectins are sugar-binding proteins that are highly specific for their sugar moieties. They play a role in biological recognition phenomena involving cells and proteins. For example, some viruses use lectins to attach themselves to the cells of the host organism during infection...
produced by humans. In ASCA+ Crohn's disease the serum level of this protein is lower. Cellular response to mannan in ASCA+ peripheral blood lymphocytes
Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes
Peripheral blood lymphocytes are mature lymphocytes that circulate in the blood, rather than localising to organs . They comprise T cells, NK cells and B cells....
could be inhibited by adding MBL, however, a high frequency of mutations in the MBL gene was found in ASCA+ patients.
Crohn's disease
ASCA are consistently higher in frequency in Crohn's disease. Yeast cause a three-fold increase in lymphocyte proliferation relative to normal controls. The ASCA antibodies are also more frequently found in familial Crohn's disease. An altered humoral and cellular response to mannan is observed and may be due to a loss of yeast tolerance. This alteration is marked by increased activation markers, CD25CD25
CD25 is the alpha chain of the IL-2 receptor. It is a type I transmembrane protein present on activated T cells, activated B cells, some thymocytes, myeloid precursors, and oligodendrocytes that associates with CD122 to form a heterodimer that can act as a high-affinity receptor for IL-2.CD25 is...
/CD69
CD69
CD69 is a human transmembrane C-Type lectin protein encoded by the gene.-Further reading:...
, upon proliferative stimulation of T-helper lymphocytes.
ASCA+ is a predictor for Crohn's disease with high specificity and positive predictive value (87% and 78% respectively). ASCA are associated with proximal (gastroduodenal and small bowel involvement) rather than purely colonic disease (P < 0.001) and with a more severe disease phenotype and requirement for surgery over a median follow-up time of 9 years (P < 0.0001).
There is no association between genetic markers for Crohn's disease and NOD2/CARD15 or MP (IgA or IgG) indicating heterogeneous causes for Crohn's disease. [Note: CD is a common abbreviation for Crohn's disease. It is more commonly used for coeliac disease which may be primary to some forms of colitis. When reviewing abstracts for colitis, it is important to note the abbreviation is used for both.]

