
Aperture card
Encyclopedia
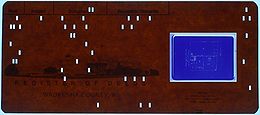
Punched card
A punched card, punch card, IBM card, or Hollerith card is a piece of stiff paper that contains digital information represented by the presence or absence of holes in predefined positions...
with a cut-out window into which a chip of microfilm
Microform
Microforms are any forms, either films or paper, containing microreproductions of documents for transmission, storage, reading, and printing. Microform images are commonly reduced to about one twenty-fifth of the original document size...
is mounted. Such a card is used for archiving
Archive
An archive is a collection of historical records, or the physical place they are located. Archives contain primary source documents that have accumulated over the course of an individual or organization's lifetime, and are kept to show the function of an organization...
or for making multiple inexpensive copies of a document for ease of distribution. The card is typically punched with machine-readable metadata
Metadata
The term metadata is an ambiguous term which is used for two fundamentally different concepts . Although the expression "data about data" is often used, it does not apply to both in the same way. Structural metadata, the design and specification of data structures, cannot be about data, because at...
associated with the microfilm image, and printed across the top of the card for visual identification. The microfilm chip is most commonly 35mm in height, and contains an optically reduced
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
image, usually of some type of reference document, such as an engineering drawing
Engineering drawing
An engineering drawing, a type of technical drawing, is used to fully and clearly define requirements for engineered items.Engineering drawing produces engineering drawings . More than just the drawing of pictures, it is also a language—a graphical language that communicates ideas and information...
, that is the focus of the archiving process. Aperture cards have several advantages and disadvantages when compared to digital systems. Machinery exists to automatically store, retrieve, sort, duplicate, create, and digitize cards with a high level of automation. While many aperture cards still play an important role in archiving, their role is gradually being replaced by digital systems.
Usage
Aperture cards are used for engineering drawings from all engineering disciplines. The U.S. Department of Defense once made extensive use of aperture cards, and some are still in use, but most data is now digital.Information about the drawing, for example the drawing number, could be both punched and printed on the remainder of the card. With the proper machinery, this allows for automated handling. In the absence of such machinery, the cards can still be read by a human with a lens and a light source.
Advantages
Aperture cards have, for archival purposes, some advantages over digital systems. They have a 100 year lifetime, they are human readable, and there is no expense or risk in converting from one digital format to the next when computer systems become obsolete.Disadvantages
Most of the disadvantages are related to the well established differences in analog and digital technology. In particular, searching for given strings within content is considerably slower. Handling physical cards requires proprietary machinery and processing optical film takes significant time.The very nature of microfilm cameras and the high contrast properties of microfilm stock itself also impose limits on the amount of detail that can be resolved particularly at the higher reduction ratios (36x or greater) needed to film larger drawings. Faded drawings or those of low or uneven contrast do not reproduce well and significant detail or annotations may be lost.
In common with other forms of microfilm mis-filing cards after use, particularly in large archives, results in the card being for all intents and purposes lost forever unless it's later found by accident.
Aperture cards created from 35mm roll film mounted on to blank cards have to be treated with great care. Bending the card can cause the film to detach and excessive pressure to a stack of cards can cause the mounting glue to ooze creating clumps of cards which will feed through duplicators and other machinery either poorly or not at all. Feeding a de-laminated card through machinery not only risks destroying the image it also risks jamming or damaging the machinery.
Machinery
A set of cards could be rapidly sorted by drawing number or other punched data using a card sorterIBM 80 series Card Sorters
A major activity in many unit record shops was sorting decks of punch card into the proper order as determined by information punched in the card. The same deck might be sorted differently depending on the processing step...
. Machines are now available that scan
Image scanner
In computing, an image scanner—often abbreviated to just scanner—is a device that optically scans images, printed text, handwriting, or an object, and converts it to a digital image. Common examples found in offices are variations of the desktop scanner where the document is placed on a glass...
aperture cards and produce a digital version. Aperture card plotters are machines that use a laser to create the image on the film.
External links
- 1959 Defense Technical Information Center report on the technology and its use for submitting engineering plans to the military.
- Detailed description of a particular format of Aperture cards from WIPO.
- Detailed information regarding duplicating microforms and aperture cards

