
Aperture masking interferometry
Encyclopedia
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was carried into orbit by a Space Shuttle in 1990 and remains in operation. A 2.4 meter aperture telescope in low Earth orbit, Hubble's four main instruments observe in the near ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared...
. The principal limitation of the technique is that it is limited to relatively bright astronomical objects. A mask is placed over the telescope which only allows light through a small number of holes. This array of holes acts as a miniature astronomical interferometer
Astronomical interferometer
An astronomical interferometer is an array of telescopes or mirror segments acting together to probe structures with higher resolution by means of interferometry....
. The method was developed by John E. Baldwin
John E. Baldwin
John Evan Baldwin FRS has worked at the Cavendish Astrophysics Group since 1954. He played a pivotal role in the development of interferometry in Radio Astronomy, and later astronomical optical interferometry and lucky imaging...
and collaborators in the Cavendish Astrophysics Group
Cavendish Astrophysics Group
The Cavendish Astrophysics Group is based at the Cavendish Laboratory at the University of Cambridge. The group operates all of the telescopes at the Mullard Radio Astronomy Observatory except for the 32m MERLIN telescope, which is operated by Jodrell Bank.The group is the second largest of three...
.
In the aperture masking technique, the bispectral analysis
Speckle masking
Speckle masking is a speckle imaging method which involves estimation of the bispectrum or closure phases from each of the short exposures. The "average bispectrum" can then be calculated and then inverted to obtain an image. With a normal telescope aperture, a large number of short exposures must...
(speckle masking) method is typically applied to data taken through masked apertures, where most of the aperture is blocked off and light can only pass through a series of small holes (subapertures). The aperture mask removes atmospheric noise from these measurements, allowing the bispectrum to be measured more quickly than for an un-masked aperture. For simplicity the aperture masks are usually either placed in front of the secondary mirror
Secondary mirror
A secondary mirror is the second deflecting or focusing mirror element in a reflecting telescope. Light gathered by the primary mirror is directed towards a focal point typically past the location of the secondary. Secondary mirrors in the form of an optically flat diagonal mirror are used to...
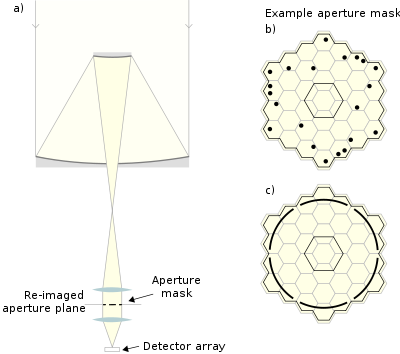
(e.g. Tuthill et al. (2000)) or placed in a re-imaged aperture plane as shown in Figure 1.a) (e.g. Haniff et al. (1987); Young et al. (2000); Baldwin et al. (1986)). The masks are usually categorised either as non-redundant or partially redundant. Non-redundant masks consist of arrays of small holes where no two pairs of holes have the same separation vector (the same baseline - see aperture synthesis
Aperture synthesis
Aperture synthesis or synthesis imaging is a type of interferometry that mixes signals from a collection of telescopes to produce images having the same angular resolution as an instrument the size of the entire collection...
). Each pair of holes provides a set of fringes at a unique spatial frequency in the image plane. Partially redundant masks are usually designed to provide a compromise between minimising the redundancy of spacings and maximizing both the throughput and the range of spatial frequencies investigated (Haniff & Buscher, 1992; Haniff et al. , 1989). Figures 1.b) and 1.c) show examples of aperture masks used in front of the secondary at the Keck telescope by Peter Tuthill and collaborators; Figure 1.b) is a non-redundant mask while Figure 1.c) is partially redundant. Although the signal-to-noise of speckle masking
Speckle masking
Speckle masking is a speckle imaging method which involves estimation of the bispectrum or closure phases from each of the short exposures. The "average bispectrum" can then be calculated and then inverted to obtain an image. With a normal telescope aperture, a large number of short exposures must...
observations at high light level can be improved with aperture masks, the faintest limiting magnitude cannot be significantly improved for photon-noise limited detectors (see Buscher & Haniff (1993)).

