
Apparent molar property
Encyclopedia
An apparent molar property is a quantity that can be used to calculate a property of a solution. For instance, the volume
of the solution is given by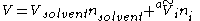
where Vsolvent is the molar volume
of the solvent, nsolvent is the number of mole
s of solvent,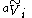 is the apparent molar volume of solute
is the apparent molar volume of solute
i, and ni is the number of moles of solute i in the solution. (The apparent molar volume can also be denoted Vφ.) This equation applied to a single-solute solution serves as the definition of the apparent molar volume of the solute. (For multi-solute solutions, the equation does not give an unambiguous definition of the apparent molar properties.)
Apparent molar properties are not in fact constants (even at a given temperature), but are functions of the composition. At infinite dilution
, they are equal to the partial molar property
.
Some apparent molar properties that are commonly used are apparent molar enthalpy
, heat capacity
, and volume.
The apparent molar volume of a salt is usually less than the molar volume of the solid salt. For instance, solid NaCl has a volume of 27 cm3 per mole, but the apparent molar volume at low concentrations is only 16.6 cc/mole. In fact, some aqueous electrolytes have negative apparent molar volumes: NaOH -6.7, LiOH -6.0, and Na2CO3
-6.7 cm3/mole. This means that their solutions in a given amount of water have a smaller volume than the same amount of pure water. The physical reason is that nearby water molecules are strongly attracted to the ions so that they occupy less space.
Volume
Volume is the quantity of three-dimensional space enclosed by some closed boundary, for example, the space that a substance or shape occupies or contains....
of the solution is given by
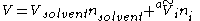
where Vsolvent is the molar volume
Molar volume
The molar volume, symbol Vm, is the volume occupied by one mole of a substance at a given temperature and pressure. It is equal to the molar mass divided by the mass density...
of the solvent, nsolvent is the number of mole
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
s of solvent,
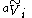 is the apparent molar volume of solute
is the apparent molar volume of soluteSolution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
i, and ni is the number of moles of solute i in the solution. (The apparent molar volume can also be denoted Vφ.) This equation applied to a single-solute solution serves as the definition of the apparent molar volume of the solute. (For multi-solute solutions, the equation does not give an unambiguous definition of the apparent molar properties.)
Apparent molar properties are not in fact constants (even at a given temperature), but are functions of the composition. At infinite dilution
Dilution
Dilution may refer to:* Reducing the concentration of a chemical* Serial dilution, a common way of going about this reduction of concentration* Homeopathic dilution* Dilution , an equation to calculate the rate a gas dilutes...
, they are equal to the partial molar property
Partial molar property
A partial molar property is a thermodynamic quantity which indicates how an extensive property of a solution or mixture varies with changes in the molar composition of the mixture at constant temperature and pressure, or for constant values of the natural variables of the extensive property...
.
Some apparent molar properties that are commonly used are apparent molar enthalpy
Enthalpy
Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system. It includes the internal energy, which is the energy required to create a system, and the amount of energy required to make room for it by displacing its environment and establishing its volume and pressure.Enthalpy is a...
, heat capacity
Heat capacity
Heat capacity , or thermal capacity, is the measurable physical quantity that characterizes the amount of heat required to change a substance's temperature by a given amount...
, and volume.
The apparent molar volume of a salt is usually less than the molar volume of the solid salt. For instance, solid NaCl has a volume of 27 cm3 per mole, but the apparent molar volume at low concentrations is only 16.6 cc/mole. In fact, some aqueous electrolytes have negative apparent molar volumes: NaOH -6.7, LiOH -6.0, and Na2CO3
Sodium carbonate
Sodium carbonate , Na2CO3 is a sodium salt of carbonic acid. It most commonly occurs as a crystalline heptahydrate, which readily effloresces to form a white powder, the monohydrate. Sodium carbonate is domestically well-known for its everyday use as a water softener. It can be extracted from the...
-6.7 cm3/mole. This means that their solutions in a given amount of water have a smaller volume than the same amount of pure water. The physical reason is that nearby water molecules are strongly attracted to the ions so that they occupy less space.
See also
- Volume fraction
- Ideal solutionIdeal solutionIn chemistry, an ideal solution or ideal mixture is a solution with thermodynamic properties analogous to those of a mixture of ideal gases. The enthalpy of solution is zero as is the volume change on mixing; the closer to zero the enthalpy of solution is, the more "ideal" the behavior of the...
- Solvation shellSolvation shellA Solvation shell is a shell of any chemical species acting as a solvent, surrounding a solute species. When the solvent is water it is often referred to as a hydration shell or hydration sphere....
- Partial molar propertyPartial molar propertyA partial molar property is a thermodynamic quantity which indicates how an extensive property of a solution or mixture varies with changes in the molar composition of the mixture at constant temperature and pressure, or for constant values of the natural variables of the extensive property...
- Excess molar quantityExcess molar quantityExcess molar quantities are properties of mixtures which characterize the nonideal behaviour of real mixtures. They are the difference between the partial molar property of a component in a mixture and that of the pure component...

