
Archeops
Encyclopedia
Archeops was a balloon-borne instrument dedicated to measuring the Cosmic microwave background (CMB) temperature anisotropies. The study of this radiation is essential to obtain precise information on the evolution of the Universe
: density, Hubble constant, age of the Universe
, etc. To achieve this goal, measurements were done with devices cooled down at 100mK temperature placed at the focus of a warm telescope. To avoid atmospheric disturbance the whole apparatus is placed on a gondola below a helium balloon that reaches 40 km altitude.
Archeops has four bands in the millimeter domain (143, 217, 353 and 545 GHz) with a high angular resolution (about 15 arcminutes) in order to constrain small anisotropy scales, as well as a large sky coverage fraction (30%) in order to minimize the intrinsic cosmic variance.
(Planck-HFI) and using balloon-borne constraints.
Namely, it consists of an open 3He-4He dilution cryostat cooling spiderweb-type bolometer
s at 100 mK; cold individual optics with horns at different temperature stages (0.1, 1.6, 10 K) and an off-axis Gregorian telescope
.
The CMB signal is measured by the 143 and 217 GHz detectors while interstellar dust emission and atmospheric emission are monitored with the 353 (polarized) and 545 GHz detectors.
The whole instrument is baffled so as to avoid stray radiation from the Earth and the balloon.
To cover as far as 30% of the sky, the payload was spinning mostly above the atmosphere, scanning the sky in circles with a fixed elevation of roughly 41 degrees. The gondola, at a float altitude above 32 km, spins across the sky at a rate of 2 rpm which, combined with the Earth rotation, produces a well sampled sky at each frequency.
Archeops flew for the first time in Trapani (Sicily) with four–hours integration time. Then, the upgraded instrument was launched three times from the Esrange base near Kiruna (Sweden) by the CNES during 2 consecutive Winter seasons (2001 and 2002). The last and best flight on Feb. 7th, 2002 yields 12.5 hours of CMB–type data (at ceiling altitude and by night) from a 19–hours total. The balloon landed in Siberia and it was recovered (with its precious data recorded on–board) by a Franco–Russian team with –40 deg.C. weather.
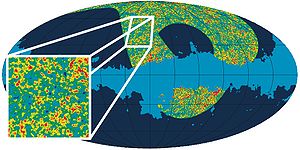 Archeops has linked, for the first time and before WMAP, the large angular scales (previously measured by COBE
Archeops has linked, for the first time and before WMAP, the large angular scales (previously measured by COBE
) to the first acoustic peak region.
From its results, inflation motivated cosmologies have been reinforced with a flat Universe (total energy density Ωtot = 1 within 3 %).
When combined with complementary cosmological datasets regarding the value of Hubble's constant, Archeops gives constraints on the dark energy density and the baryonic density in very good agreement with other independent estimations based on supernovae measurements and big bang nucleosynthesis.
Archeops has given the first and still unique polarized maps of the galactic dust emission with this resolution.
Universe
The Universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists, including all matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. Definitions and usage vary and similar terms include the cosmos, the world and nature...
: density, Hubble constant, age of the Universe
Age of the universe
The age of the universe is the time elapsed since the Big Bang posited by the most widely accepted scientific model of cosmology. The best current estimate of the age of the universe is 13.75 ± 0.13 billion years within the Lambda-CDM concordance model...
, etc. To achieve this goal, measurements were done with devices cooled down at 100mK temperature placed at the focus of a warm telescope. To avoid atmospheric disturbance the whole apparatus is placed on a gondola below a helium balloon that reaches 40 km altitude.
Archeops has four bands in the millimeter domain (143, 217, 353 and 545 GHz) with a high angular resolution (about 15 arcminutes) in order to constrain small anisotropy scales, as well as a large sky coverage fraction (30%) in order to minimize the intrinsic cosmic variance.
Instrument and flights
The instrument was designed by adapting concepts put forward for the High Frequency Instrument of Planck surveyorPlanck Surveyor
Planck is a space observatory of the European Space Agency and designed to observe the anisotropies of the cosmic microwave background over the entire sky, at a high sensitivity and angular resolution...
(Planck-HFI) and using balloon-borne constraints.
Namely, it consists of an open 3He-4He dilution cryostat cooling spiderweb-type bolometer
Bolometer
A bolometer is a device for measuring the power of incident electromagnetic radiation via the heating of a material with a temperature-dependent electrical resistance. It was invented in 1878 by the American astronomer Samuel Pierpont Langley...
s at 100 mK; cold individual optics with horns at different temperature stages (0.1, 1.6, 10 K) and an off-axis Gregorian telescope
Gregorian telescope
The Gregorian telescope is a type of reflecting telescope designed by Scottish mathematician and astronomer James Gregory in the 17th century, and first built in 1673 by Robert Hooke...
.
The CMB signal is measured by the 143 and 217 GHz detectors while interstellar dust emission and atmospheric emission are monitored with the 353 (polarized) and 545 GHz detectors.
The whole instrument is baffled so as to avoid stray radiation from the Earth and the balloon.
To cover as far as 30% of the sky, the payload was spinning mostly above the atmosphere, scanning the sky in circles with a fixed elevation of roughly 41 degrees. The gondola, at a float altitude above 32 km, spins across the sky at a rate of 2 rpm which, combined with the Earth rotation, produces a well sampled sky at each frequency.
Archeops flew for the first time in Trapani (Sicily) with four–hours integration time. Then, the upgraded instrument was launched three times from the Esrange base near Kiruna (Sweden) by the CNES during 2 consecutive Winter seasons (2001 and 2002). The last and best flight on Feb. 7th, 2002 yields 12.5 hours of CMB–type data (at ceiling altitude and by night) from a 19–hours total. The balloon landed in Siberia and it was recovered (with its precious data recorded on–board) by a Franco–Russian team with –40 deg.C. weather.
Results

COBE
The COsmic Background Explorer , also referred to as Explorer 66, was a satellite dedicated to cosmology. Its goals were to investigate the cosmic microwave background radiation of the universe and provide measurements that would help shape our understanding of the cosmos.This work provided...
) to the first acoustic peak region.
From its results, inflation motivated cosmologies have been reinforced with a flat Universe (total energy density Ωtot = 1 within 3 %).
When combined with complementary cosmological datasets regarding the value of Hubble's constant, Archeops gives constraints on the dark energy density and the baryonic density in very good agreement with other independent estimations based on supernovae measurements and big bang nucleosynthesis.
Archeops has given the first and still unique polarized maps of the galactic dust emission with this resolution.

