
Ares V
Encyclopedia

Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle was a manned orbital rocket and spacecraft system operated by NASA on 135 missions from 1981 to 2011. The system combined rocket launch, orbital spacecraft, and re-entry spaceplane with modular add-ons...
after its retirement in 2011. Ares V was also planned to carry supplies for a human presence on Mars
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance...
. Ares V and the smaller Ares I were named after Ares
Ares
Ares is the Greek god of war. He is one of the Twelve Olympians, and the son of Zeus and Hera. In Greek literature, he often represents the physical or violent aspect of war, in contrast to the armored Athena, whose functions as a goddess of intelligence include military strategy and...
, the Greek god of war, which is the equivalent to the Roman god Mars
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance...
.
Initially, the Ares V would have launched the Earth Departure Stage
Earth Departure Stage
The Ares V Earth Departure Stage was a rocket stage which NASA planned to design at its Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama as part of Project Constellation...
and Altair lunar lander had NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
returned to the Moon
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
, which was planned for 2019, but would also have served as the principal launcher for missions beyond the Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
-Moon system, including the program's ultimate goal, a manned mission to Mars after 2030. The unmanned Ares V would complement the smaller, and human-rated
Human-rating certification
Human-rated or man-rated are terms used to describe the certification of a spacecraft, launch vehicleor airplaneas worthy of transporting humans. NASA and the U.S. GAO now uses "Human-rating" when describing requirements for these systems...
Ares I
Ares I
Ares I was the crew launch vehicle that was being developed by NASA as part of the Constellation Program. The name "Ares" refers to the Greek deity Ares, who is identified with the Roman god Mars...
rocket for the launching of the 4-6 person Orion spacecraft. Both rockets, deemed safer than the current Space Shuttle, would have utilized technologies developed for the Apollo program, the Shuttle, and the Delta IV EELV
EELV
Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle is an expendable launch system program of the United States Air Force , intended to assure access to space for Department of Defense and other United States government payloads...
programs. However, the Constellation program, including Ares V was canceled in October 2010 by the passage of the 2010 NASA authorization bill.
Early concepts
In the 1997 book The Case for MarsThe Case For Mars
The Case for Mars: The Plan to Settle the Red Planet and Why We Must is a nonfiction science book by Robert Zubrin, first published in 1996....
, Robert Zubrin
Robert Zubrin
Robert Zubrin is an American aerospace engineer and author, best known for his advocacy of the manned exploration of Mars. He was the driving force behind Mars Direct—a proposal intended to produce significant reductions in the cost and complexity of such a mission...
discussed a possible future heavy launch vehicle named Ares. In the book the rocket would have consisted of the Space Shuttle's External Tank powered by four Space Shuttle Main Engine
Space Shuttle main engine
The RS-25, otherwise known as the Space Shuttle Main Engine , is a reusable liquid-fuel rocket engine built by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne for the Space Shuttle, running on liquid hydrogen and oxygen. Each Space Shuttle was propelled by three SSMEs mated to one powerhead...
s and a second stage powered by an RL-10
RL-10
The RL10 was USA's first liquid hydrogen fueled rocket engine. An updated version is used in several current launch vehicles. Six RL10 engines were used in the S-IV second stage of the Saturn I rocket. One or two RL10 engines are used in the Centaur upper stages of Atlas and Titan rockets...
engine. One notable difference in the Zubrin et al. design is the mounting location of the SSMEs, which were side-mounted on a small flyback craft. This design was meant to allow the Ares to fly using existing Space Shuttle infrastructure.
Constellation

Saturn V
The Saturn V was an American human-rated expendable rocket used by NASA's Apollo and Skylab programs from 1967 until 1973. A multistage liquid-fueled launch vehicle, NASA launched 13 Saturn Vs from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida with no loss of crew or payload...
and Space Shuttle
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle was a manned orbital rocket and spacecraft system operated by NASA on 135 missions from 1981 to 2011. The system combined rocket launch, orbital spacecraft, and re-entry spaceplane with modular add-ons...
, where the crew and cargo were launched together on the same rocket, Project Constellation was planned to use two separate launch vehicles, the Ares I and the Ares V, for crew and cargo respectively. This configuration would have allowed the two launch vehicles to be optimized for their respective missions. Constellation therefore combined the Lunar Orbit Rendezvous
Lunar orbit rendezvous
Lunar orbit rendezvous is a key concept for human landing on the Moon and returning to Earth.In a LOR mission a main spacecraft and a smaller lunar module travel together into lunar orbit. The lunar module then independently descends to the lunar surface. After completion of the mission there, a...
used by Apollo with the Earth Orbit Rendezvous
Earth orbit rendezvous
Earth orbit rendezvous is a type of space rendezvous and a spaceflight methodology most notable for enabling round trip human missions to the moon...
mode proposed by Dr. Wernher von Braun
Wernher von Braun
Wernher Magnus Maximilian, Freiherr von Braun was a German rocket scientist, aerospace engineer, space architect, and one of the leading figures in the development of rocket technology in Nazi Germany during World War II and in the United States after that.A former member of the Nazi party,...
(along with the "Direct Ascent" proposal) during the early planning stage of Apollo.
Development of the rocket and its Earth departure stage was led by Marshall Space Flight Center
Marshall Space Flight Center
The George C. Marshall Space Flight Center is the U.S. government's civilian rocketry and spacecraft propulsion research center. The largest center of NASA, MSFC's first mission was developing the Saturn launch vehicles for the Apollo moon program...
. Ames Research Center was responsible for the Ares V integrated health management system supports in developing its payload shroud. Glenn Research Center
Glenn Research Center
NASA John H. Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field is a NASA center, located within the cities of Brook Park, Cleveland and Fairview Park, Ohio between Cleveland Hopkins International Airport and the Cleveland Metroparks's Rocky River Reservation, and has other subsidiary facilities in Ohio...
led the development of the lunar lander ascent stage as well as Ares V power system, thrust vector control system and payload shroud. Langley Research Center
Langley Research Center
Langley Research Center is the oldest of NASA's field centers, located in Hampton, Virginia, United States. It directly borders Poquoson, Virginia and Langley Air Force Base...
had a lead role on Ares V aerodynamics.
In 2007 NASA announced that Alliant Techsystems
Alliant Techsystems
Alliant Techsystems Inc., most commonly known by its ticker symbol, ', is one of the largest aerospace and defense companies in the United States with more than 18,000 employees in 22 states, Puerto Rico and internationally, and 2010 revenues in excess of an estimated...
will be the contractor for the SRBs of both Ares I and Ares V.
Further roles
Although the Ares V was a medium to long term project, NASANASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
planned to deploy its lift capability in a range of projects, along the lines of the former Apollo Applications Program
Apollo Applications program
The Apollo Applications Program was established by NASA headquarters in 1968 to develop science-based manned space missions using surplus material from the Apollo program...
.
One proposal was to build an 8 to 16-meter Advanced Technology Large-Aperture Space Telescope
Advanced Technology Large-Aperture Space Telescope
The Advanced Technology Large-Aperture Space Telescope is an 8 to 16.8-meter UV-optical-NIR space telescope proposed by Space Telescope Science Institute, the science operations center for the Hubble Space Telescope...
to be placed in the Sun/Earth L2 point
Lagrangian point
The Lagrangian points are the five positions in an orbital configuration where a small object affected only by gravity can theoretically be stationary relative to two larger objects...
. It would be a significant increase in dimension and performance over the Hubble Space Telescope
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was carried into orbit by a Space Shuttle in 1990 and remains in operation. A 2.4 meter aperture telescope in low Earth orbit, Hubble's four main instruments observe in the near ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared...
and the Ares V vehicle was expected to carry this to its destination in a single launch. Future Ares V missions could also have served as a cost-effective, mass transport of construction materials for future spacecraft
Spacecraft
A spacecraft or spaceship is a craft or machine designed for spaceflight. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, earth observation, meteorology, navigation, planetary exploration and transportation of humans and cargo....
and missions
Space exploration
Space exploration is the use of space technology to explore outer space. Physical exploration of space is conducted both by human spaceflights and by robotic spacecraft....
, delivering raw material
Raw material
A raw material or feedstock is the basic material from which a product is manufactured or made, frequently used with an extended meaning. For example, the term is used to denote material that came from nature and is in an unprocessed or minimally processed state. Latex, iron ore, logs, and crude...
s for example to a Moon dock.
In May 2010 NASA planned flight demonstrations of Ares V hardware along with Ares I hardware after the scheduled upcoming Ares I-X Prime test of the Ares I 5-segment SRB first stage. Several flights were listed as "Heavy Lift" test flights for testing the first stage of the Ares V simultaneously with the Ares I upper stage attached on top of the Ares V first stage. This would save both time and money in avoiding the gap between testing Ares I and Ares V hardware with current limited funding.
Cancellation
The Augustine CommissionReview of United States Human Space Flight Plans Committee
The Review of United States Human Space Flight Plans Committee was a group reviewing the human spaceflight plans of the United States...
concluded that "Under the FY 2010 funding profile, the Committee estimates that Ares V will not be available until the late 2020s". Even if NASA had been given the $3 billion increase and the ISS had been retired in 2015, the committee still believed that the Ares V would not be ready until the mid-2020s.
On February 1, 2010, President Barack Obama
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in...
announced a proposal to cancel the Constellation program effective with the U.S. 2011 fiscal year budget, but later announced changes to the proposal in a major space policy speech
Barack Obama space policy speech at Kennedy Space Center
The space policy of the Barack Obama administration was announced by U.S. President Barack Obama on April 15, 2010, at a major space policy speech at Kennedy Space Center. He committed to increasing NASA funding by $6 billion over five years and completing the design of a new heavy-lift launch...
at Kennedy Space Center on April 15, 2010. In October 2010, the NASA authorization bill for 2010 was signed into law, which canceled Constellation. But previous legislation keeps Constellation contracts in force until a new funding bill is passed for 2011.
Design

Ares V in heavy preliminary design review after the results of the 2009 Augustine Commission
Review of United States Human Space Flight Plans Committee
The Review of United States Human Space Flight Plans Committee was a group reviewing the human spaceflight plans of the United States...
. Like the Space Shuttle, the Ares vehicle was to utilize a pair of solid-fueled first stage rocket boosters that burn simultaneously with the liquid-fueled second (core) stage. The solid rocket booster on Ares V was envisioned as an improved version of the current Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster
Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster
The Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Boosters were the pair of large solid rockets used by the United States' NASA Space Shuttle during the first two minutes of powered flight. Together they provided about 83% of liftoff thrust for the Space Shuttle. They were located on either side of the rusty or...
, but with five or five and a half segments instead of the current four segments. The liquid-fueled second stage was derived from the Space Shuttle External Tank
Space Shuttle external tank
A Space Shuttle External Tank is the component of the Space Shuttle launch vehicle that contains the liquid hydrogen fuel and liquid oxygen oxidizer. During lift-off and ascent it supplies the fuel and oxidizer under pressure to the three Space Shuttle Main Engines in the orbiter...
, and was to use either five or six RS-68B engines attached to the bottom of a new 10 m tank, or five SSMEs attached to the bottom of a stretched version of the Space Shuttle's 8.4 m tank
Space Shuttle external tank
A Space Shuttle External Tank is the component of the Space Shuttle launch vehicle that contains the liquid hydrogen fuel and liquid oxygen oxidizer. During lift-off and ascent it supplies the fuel and oxidizer under pressure to the three Space Shuttle Main Engines in the orbiter...
. In either configuration, it was designed to be fueled by liquid oxygen (LOX
Lox
Lox is salmon fillet that has been cured. In its most popular form, it is thinly sliced—less than in thickness—and, typically, served on a bagel, often with cream cheese, onion, tomato, cucumber and capers...
) and liquid hydrogen (LH2).
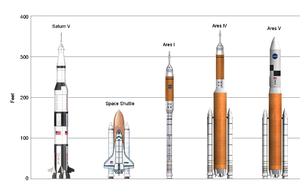
S-IVB
The S-IVB was built by the Douglas Aircraft Company and served as the third stage on the Saturn V and second stage on the Saturn IB. It had one J-2 engine...
upper stage used on the Saturn IB
Saturn IB
The Saturn IB was an American launch vehicle commissioned by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration for use in the Apollo program...
and Saturn V
Saturn V
The Saturn V was an American human-rated expendable rocket used by NASA's Apollo and Skylab programs from 1967 until 1973. A multistage liquid-fueled launch vehicle, NASA launched 13 Saturn Vs from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida with no loss of crew or payload...
rockets, was named the Earth Departure Stage (EDS). The EDS would be powered by the Apollo-derived J-2X
J-2 (rocket engine)
Rocketdyne's J-2 rocket engine was a major component of the Saturn V rocket used in the Apollo program to send men to the Moon. Five J-2 engines were used on the S-II second stage, and one J-2 was used on the S-IVB third stage. The S-IVB was also used as the second stage of the smaller Saturn IB...
rocket engine, which was also proposed to be used on the liquid-fueled upper stage of the Ares I booster. The EDS was to be used to steer the Altair lunar lander into its initial low-Earth "parking" orbit for later retrieval by the Orion spacecraft, and then would propel both the Altair and Orion to the Moon. The EDS could also have been used to haul large payloads into low-Earth orbit, along with placing large unmanned spacecraft onto trajectories beyond the Earth-Moon system.
The Ares V was designed to have a payload capacity of over 414,000 lb (188 metric tons) to Low Earth orbit
Low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit is generally defined as an orbit within the locus extending from the Earth’s surface up to an altitude of 2,000 km...
(LEO), and 157,000 lb (71 metric tons) to the Moon. Upon completion the Ares V would be the most powerful rocket ever built, lifting more into orbit than even the American Saturn V
Saturn V
The Saturn V was an American human-rated expendable rocket used by NASA's Apollo and Skylab programs from 1967 until 1973. A multistage liquid-fueled launch vehicle, NASA launched 13 Saturn Vs from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida with no loss of crew or payload...
, the failed Soviet
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
N-1 for the canceled Soviet Moonshot
Soviet Moonshot
The Soviet manned lunar programs were a series of programs pursued by the Soviet Union to land a man on the Moon in competition with the United States Apollo program to achieve the same goal set publicly by President John F. Kennedy on May 25, 1961...
, and the successful Soviet/Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
n Energia
Energia
Energia was a Soviet rocket that was designed by NPO Energia to serve as a heavy-lift expendable launch system as well as a booster for the Buran spacecraft. Control system main developer enterprise was the NPO "Electropribor"...
booster developed for the Buran Shuttle. Besides its lunar role, it could also support a manned Orion expedition to a Near-Earth asteroid, and could boost an 8 to 16-meter successor of the Hubble Space Telescope
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was carried into orbit by a Space Shuttle in 1990 and remains in operation. A 2.4 meter aperture telescope in low Earth orbit, Hubble's four main instruments observe in the near ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared...
to the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
-Earth point.
Ares IV
The Ares IV concept combines an Ares I upper stage with an Ares V first stage. Specifically, the vehicle would consist of the liquid-fueled core stage from the Ares V design, two five-segment solid rocket boosterSolid rocket booster
Solid rocket boosters or Solid Rocket Motors, SRM, are used to provide thrust in spacecraft launches from the launchpad up to burnout of the SRBs. Many launch vehicles include SRBs, including the Ariane 5, Atlas V , and the NASA Space Shuttle...
s, and the liquid-fueled upper stage from the Ares I, as described by NASA in January 2007. The Ares IV would be a combined 113 m (370.7 ft) tall and could be used to reach the Moon. Total payload capacity would be 41100 kg (90,610 lb) to 240 miles (386 km) for direct trans-lunar injection.
NASA was considered using Ares IV to evaluate high-speed "skip" reentry profiles of the Orion capsule in 2007. NASA had planned flight demonstrations of Ares I and Ares V hardware in "Heavy Lift" configurations from 2013. The "Heavy Lift" test flights were to test the first stage of the Ares V simultaneously with the Ares I upper stage attached on top to save both time and money. The later Heavy Lift test vehicle configurations are similar to the Ares IV vehicle.
Ares V Lite
Ares V Lite was an alternative launch vehicle for NASA's Constellation program suggested by the Augustine CommissionReview of United States Human Space Flight Plans Committee
The Review of United States Human Space Flight Plans Committee was a group reviewing the human spaceflight plans of the United States...
. Ares V Lite was a scaled down Ares V. It would have used five RS-68 engines and two five-segment SRBs and have had a low Earth orbit payload of approximately 140 metric tons (309,000 lb). If chosen, Ares V Lite would have replaced the Ares V and Ares I
Ares I
Ares I was the crew launch vehicle that was being developed by NASA as part of the Constellation Program. The name "Ares" refers to the Greek deity Ares, who is identified with the Roman god Mars...
launchers. One Ares V Lite version would have been a cargo lifter like Ares V and the second version would have carry astronauts in the Orion spacecraft.
See also
- Space Launch SystemSpace Launch SystemThe Space Launch System, or SLS, is a Space Shuttle-derived heavy launch vehicle being designed by NASA, following the cancellation of the Constellation Program, to replace the retired Space Shuttle. The NASA Authorization Act of 2010 envisions the transformation of the Ares I and Ares V vehicle...
- Comparison of super heavy lift launch systems
- Shuttle-Derived Launch VehicleShuttle-Derived Launch VehicleShuttle-Derived Launch Vehicle, or simply Shuttle-Derived Vehicle , is a term describing one of a wide array of concepts that have been developed for creating space launch vehicles from the components, technology and/or infrastructure of the Space Shuttle program. SDVs have also been part of...
- Shuttle-Derived Heavy Lift Launch VehicleShuttle-Derived Heavy Lift Launch VehicleThe Shuttle-Derived Heavy Lift Launch Vehicle, also known as the High Confidence Heavy Lift Launch Vehicle is an alternate launch vehicle proposal for the NASA Constellation program...
- Direct Launch Vehicle

