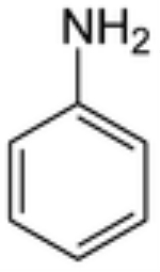
Aromatic amine
Encyclopedia
An aromatic amine is an amine
with an aromatic
substituent
- that is -N
H
2, -N
H
- or nitrogen
group(s) attached to an aromatic hydrocarbon
, whose structure usually contains one or more benzene rings. Aniline
is the simplest example.
Aromatic amines, when protonated, usually have lower pKa's (are more acidic) than their non-aromatic analogs. This is due to the delocalization of the lone pair of electrons from the nitrogen into the ring.
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
with an aromatic
Aromaticity
In organic chemistry, Aromaticity is a chemical property in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibit a stabilization stronger than would be expected by the stabilization of conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August...
substituent
Substituent
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a substituent is an atom or group of atoms substituted in place of a hydrogen atom on the parent chain of a hydrocarbon...
- that is -N
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
H
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
2, -N
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
H
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
- or nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
group(s) attached to an aromatic hydrocarbon
Aromatic hydrocarbon
An aromatic hydrocarbon or arene is a hydrocarbon with alternating double and single bonds between carbon atoms. The term 'aromatic' was assigned before the physical mechanism determining aromaticity was discovered, and was derived from the fact that many of the compounds have a sweet scent...
, whose structure usually contains one or more benzene rings. Aniline
Aniline
Aniline, phenylamine or aminobenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H5NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the prototypical aromatic amine. Being a precursor to many industrial chemicals, its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane...
is the simplest example.
Aromatic amines, when protonated, usually have lower pKa's (are more acidic) than their non-aromatic analogs. This is due to the delocalization of the lone pair of electrons from the nitrogen into the ring.
| Representative anilines | ||||
| Aromatic amine | CAS number | Properties | Uses | |
| Aniline Aniline Aniline, phenylamine or aminobenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H5NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the prototypical aromatic amine. Being a precursor to many industrial chemicals, its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane... |
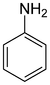 |
62-53-3 | ||
| o-Toluidine | 95-53-4 | |||
| 2,4,6-Trimethylaniline 2,4,6-Trimethylaniline 2,4,6-Trimethylaniline is a compound with formula 3C6H2NH2. It is an aromatic amine. 2,4,6-Trimethylaniline is used to synthesize 2nd generation Grubbs' catalyst.... |
88-05-1 | |||
| Anisidine Anisidine Anisidine can refer to any of the three possible isomers of methoxyaniline:*o-Anisidine *m-Anisidine *p-Anisidine... |
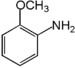 |
90-04-0 | ||
| 3-Trifluoromethylaniline | 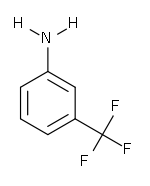 |
98-16-8 | Intermediate for herbicides, metabolite | |
| N-Methylaniline N-methylaniline N-Methylaniline is an aniline derivative. It is a toxic organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5NH. The substance exists as a colorless or slightly yellow viscous liquid, which is insoluble in water and brown when exposed to air... |
100-61-8 |

