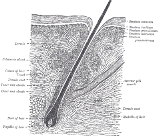
Arrectores pilorum
Encyclopedia
The arrectores pilorum are small muscles attached to hair follicles in mammals. Contraction of these muscles causes the hairs to stand on end - known colloquially as goose bumps
.
Each arrector pili is composed of a bundle of smooth muscle
fibres which attach to several follicles (a follicular unit), and is innervated by the sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system
. The contraction of the muscle is therefore involuntary - stresses such as cold, fear etc. may stimulate the sympathetic nervous system
and thus cause contraction, but the muscle is not under conscious control.
Contraction of the muscles has a number of different purposes. Its principal function in the majority of mammals is to provide insulation: air becomes trapped between the erect hairs, helping the animal retain heat. Erection of the porcupine
's long, thick hairs causes the animal to become more intimidating, scaring predators. Pressure exerted by the muscle may cause sebum to be forced along the hair follicle towards the surface, protecting the hair.
The effectiveness of the muscles' action in humans has been questioned, as humans have relatively little body hair to allow for thermal insulation.
Goose bumps
Goose bumps, also called goose flesh, goose pimples, chill bumps, chicken skin, funky spots, Dasler Bumps, chicken bumps or the medical term cutis anserina, are the bumps on a person's skin at the base of body hairs which may involuntarily develop when a person is cold or experiences strong...
.
Each arrector pili is composed of a bundle of smooth muscle
Smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle. It is divided into two sub-groups; the single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit smooth muscle tissues, the autonomic nervous system innervates a single cell within a sheet or bundle and the action potential is propagated by...
fibres which attach to several follicles (a follicular unit), and is innervated by the sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
. The contraction of the muscle is therefore involuntary - stresses such as cold, fear etc. may stimulate the sympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system is one of the three parts of the autonomic nervous system, along with the enteric and parasympathetic systems. Its general action is to mobilize the body's nervous system fight-or-flight response...
and thus cause contraction, but the muscle is not under conscious control.
Contraction of the muscles has a number of different purposes. Its principal function in the majority of mammals is to provide insulation: air becomes trapped between the erect hairs, helping the animal retain heat. Erection of the porcupine
Porcupine
Porcupines are rodents with a coat of sharp spines, or quills, that defend or camouflage them from predators. They are indigenous to the Americas, southern Asia, and Africa. Porcupines are the third largest of the rodents, behind the capybara and the beaver. Most porcupines are about long, with...
's long, thick hairs causes the animal to become more intimidating, scaring predators. Pressure exerted by the muscle may cause sebum to be forced along the hair follicle towards the surface, protecting the hair.
The effectiveness of the muscles' action in humans has been questioned, as humans have relatively little body hair to allow for thermal insulation.

