
Artificial intelligence systems integration
Encyclopedia
The core idea of A.I. systems integration is making individual software components, such as speech synthesizers, interoperable with other components, such as common sense knowledgebases, in order to create larger, broader and more capable A.I. systems. The main methods that have been proposed for integration are message routing, or communication protocols that the software components use to communicate with each other, often through a middleware blackboard system
.
Most artificial intelligence systems involve some sort of integrated technologies, for example the integration of speech synthesis technologies with that of speech recognition. However, in recent years there has been an increasing discussion on the importance of systems integration as a field in its own right. Proponents of this approach are researchers such as Marvin Minsky
, Aaron Sloman
, Deb Roy, Kristinn R. Thórisson
and Michael A. Arbib
. A reason for the recent attention A.I. integration is attracting is that there have already been created a number of (relatively) simple A.I. systems for specific problem domains (such as computer vision
, speech synthesis
, etc.), and that integrating what's already available is a more logical approach to broader A.I. than building monolithic systems from scratch.
 Collaboration is an integral part of software development
Collaboration is an integral part of software development
as evidenced by the size of software companies and the size of their software departments. Among the tools to ease software collaboration are various procedures and standards that developers can follow to ensure quality, reliability and that their software is compatible with software created by others (such as W3C standards for webpage development). However, collaboration in fields of A.I. has been lacking, for the most part not seen outside of the respected schools, departments or research institutes (and sometimes not within them either). This presents practitioners of A.I. systems integration with a substantial problem and often causes A.I. researchers to have to 're-invent the wheel' each time they want a specific functionality to work with their software. Even more damaging is the "not invented here" syndrome, which manifests itself in a strong reluctance of A.I. researchers to build on the work of others.
The outcome of this in A.I. is a large set of "solution islands": A.I. research has produced numerous isolated software components and mechanisms that deal with various parts of intelligence separately. To take some examples:
With the increased popularity of the free software movement
, a lot of the software being created, including A.I. systems, that is available for public exploit. The next natural step is to merge these individual software components into coherent, intelligent systems of a broader nature. As a multitude of components (that often serve the same purpose) have already been created by the community, the most accessible way of integration is giving each of these components an easy way to communicate with each other. By doing so, each component by itself becomes a module which can then be tried in various settings and configurations of larger architectures.
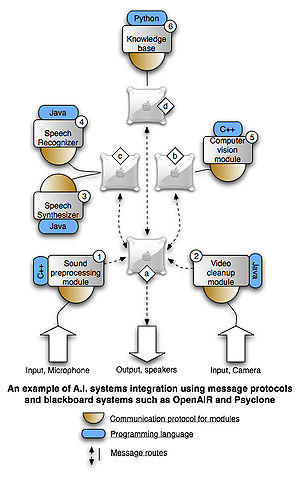
Many online communities for A.I. developers exist where tutorials, examples and forums aim at helping both beginners and experts build intelligent systems (for example the AI Depot, Generation 5). However, few communities have succeeded in making a certain standard or a code of conduct popular to allow the large collection of miscellaneous systems to be integrated with any ease. Recently, however, there have been focused attempts at producing standards for A.I. research collaboration, Mindmakers.org is an online community specifically created to harbor collaboration in the development of A.I. systems. The community has proposed the OpenAIR message and routing protocol for communication between software components, making it easier for individual developers to make modules instantly integrateble into other peoples' projects.
(CDM, or 'Constructionist A.I.') is a formal methodology proposed in the year 2004, for use in the development of cognitive robotics, communicative humanoids and broad AI systems. The creation of such systems requires integration of a large number of functionalities that must be carefully coordinated to achieve coherent system behavior. CDM is based on iterative design steps that lead to the creation of a network of named interacting modules, communicating via explicitly typed streams and discrete messages. The OpenAIR message protocol (see below) was inspired by the CDM, and has frequently been used to aid in development of intelligent systems using CDM.
One of the first projects to use CDM was Mirage, an embodied, graphical agent visualized through augmented reality
which could communicate with human users and talk about objects present in the user's physical room. Mirage was created by Kristinn R. Thórisson
, the creator of CDM, and a number of students at Columbia University
in 2004. The methodology is actively being developed at Reykjavik University
.
 OpenAIR
OpenAIR
is a message routing and communication protocol that has been gaining in popularity over the past two years. The protocol is managed by Mindmakers.org, and is described on their site in the following manner:
"OpenAIR is a routing and communication protocol based on a publish-subscribe architecture. It is intended to be the "glue" that allows numerous A.I. researchers to share code more effectively — "AIR to share". It is a definition or a blueprint of the "post office and mail delivery system" for distributed, multi-module systems. OpenAIR provides a core foundation upon which subsequent markup languages and semantics can be based, for e.g. gesture recognition and generation, computer vision, hardware-software interfacing etc.; for a recent example see CVML."http://www.mindmakers.org/openair/airPage.jsp
OpenAIR was created to allow software components that serve their own purpose to communicate with each other in order to produce large scale, overall behavior of an intelligent systems. A simple example would be to have a speech recognition system, and a speech synthesizer communicate with an expert system
through OpenAIR messages, to create a system that can hear and answer various questions through spoken dialogue. CORBA (see below) is an older but similar architecture that can be used for comparison, but OpenAIR was specifically created for A.I. research, while CORBA is a more general standard.
The OpenAIR protocol has been used for collaboration on a number of A.I. systems, a list can be found on the Mindmakers project pages. Psyclone is a popular platform to pair with the OpenAIR protocol (see below).
that supports the OpenAIR message protocol. Psyclone is available for free for non-commercial purposes and has therefore often been used by research institutes on low budgets and novice A.I. developers.
is a standard that enables software components written in multiple computer languages
and running on multiple computers to interoperate. CORBA is defined by the Object Management Group
(OMG). CORBA follows similar principles as the OpenAIR protocol (see above), and can be used for A.I. systems integration.
Blackboard system
A blackboard system is an artificial intelligence application based on the blackboard architectural model, where a common knowledge base, the "blackboard", is iteratively updated by a diverse group of specialist knowledge sources, starting with a problem specification and ending with a solution...
.
Most artificial intelligence systems involve some sort of integrated technologies, for example the integration of speech synthesis technologies with that of speech recognition. However, in recent years there has been an increasing discussion on the importance of systems integration as a field in its own right. Proponents of this approach are researchers such as Marvin Minsky
Marvin Minsky
Marvin Lee Minsky is an American cognitive scientist in the field of artificial intelligence , co-founder of Massachusetts Institute of Technology's AI laboratory, and author of several texts on AI and philosophy.-Biography:...
, Aaron Sloman
Aaron Sloman
Aaron Sloman is a philosopher and researcher on artificial intelligence and cognitive science. He is the author of several papers on philosophy, epistemology and artificial intelligence...
, Deb Roy, Kristinn R. Thórisson
Kristinn R. Thórisson
Dr. Kristinn R. Thórisson is an Icelandic artificial intelligence researcher, and co-founder of and . Thórisson is one of the leading proponents of artificial intelligence systems integration. Other proponents of this approach are researchers such as Marvin Minsky, Aaron Sloman and Michael A....
and Michael A. Arbib
Michael A. Arbib
Michael A. Arbib is the Fletcher Jones Professor of Computer Science, as well as a Professor of Biological Sciences, Biomedical Engineering, Electrical Engineering, Neuroscience and Psychology at the University of Southern California...
. A reason for the recent attention A.I. integration is attracting is that there have already been created a number of (relatively) simple A.I. systems for specific problem domains (such as computer vision
Computer vision
Computer vision is a field that includes methods for acquiring, processing, analysing, and understanding images and, in general, high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical or symbolic information, e.g., in the forms of decisions...
, speech synthesis
Speech synthesis
Speech synthesis is the artificial production of human speech. A computer system used for this purpose is called a speech synthesizer, and can be implemented in software or hardware...
, etc.), and that integrating what's already available is a more logical approach to broader A.I. than building monolithic systems from scratch.
Why integration?
The focus on systems integration, especially with regards to modular approaches, derive from the fact that most intelligences of signifact scales are composed of a multitude of processes and/or utilize multimodal input and output. For example, a humanoid-type of intelligence would preferably have to be able to talk using speech synthesis, hear using speech recognition, understand using a logical (or some other undefined) mechanism, and so forth. In order to produce artificially intelligent software of broader intelligence, integration of these modalities is necessary.Challenges & solutions

Software development
Software development is the development of a software product...
as evidenced by the size of software companies and the size of their software departments. Among the tools to ease software collaboration are various procedures and standards that developers can follow to ensure quality, reliability and that their software is compatible with software created by others (such as W3C standards for webpage development). However, collaboration in fields of A.I. has been lacking, for the most part not seen outside of the respected schools, departments or research institutes (and sometimes not within them either). This presents practitioners of A.I. systems integration with a substantial problem and often causes A.I. researchers to have to 're-invent the wheel' each time they want a specific functionality to work with their software. Even more damaging is the "not invented here" syndrome, which manifests itself in a strong reluctance of A.I. researchers to build on the work of others.
The outcome of this in A.I. is a large set of "solution islands": A.I. research has produced numerous isolated software components and mechanisms that deal with various parts of intelligence separately. To take some examples:
- Speech synthesis
- FreeTTS from CMUCarnegie Mellon UniversityCarnegie Mellon University is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States....
- FreeTTS from CMU
- Speech recognition
- Sphinx from CMUCarnegie Mellon UniversityCarnegie Mellon University is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States....
- Sphinx from CMU
- Logical reasoning
- OpenCycCycCyc is an artificial intelligence project that attempts to assemble a comprehensive ontology and knowledge base of everyday common sense knowledge, with the goal of enabling AI applications to perform human-like reasoning....
from Cycorp - Open Mind Common SenseOpen Mind Common SenseOpen Mind Common Sense is an artificial intelligence project based at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology Media Lab whose goal is to build and utilize a large commonsense knowledge base from the contributions of many thousands of people across the Web.Since its founding in 1999, it has...
Net from MIT
- OpenCyc
With the increased popularity of the free software movement
Free software movement
The free software movement is a social and political movement with the goal of ensuring software users' four basic freedoms: the freedom to run their software, to study and change their software, and to redistribute copies with or without changes. The alternative terms "software libre", "open...
, a lot of the software being created, including A.I. systems, that is available for public exploit. The next natural step is to merge these individual software components into coherent, intelligent systems of a broader nature. As a multitude of components (that often serve the same purpose) have already been created by the community, the most accessible way of integration is giving each of these components an easy way to communicate with each other. By doing so, each component by itself becomes a module which can then be tried in various settings and configurations of larger architectures.
Many online communities for A.I. developers exist where tutorials, examples and forums aim at helping both beginners and experts build intelligent systems (for example the AI Depot, Generation 5). However, few communities have succeeded in making a certain standard or a code of conduct popular to allow the large collection of miscellaneous systems to be integrated with any ease. Recently, however, there have been focused attempts at producing standards for A.I. research collaboration, Mindmakers.org is an online community specifically created to harbor collaboration in the development of A.I. systems. The community has proposed the OpenAIR message and routing protocol for communication between software components, making it easier for individual developers to make modules instantly integrateble into other peoples' projects.
Constructionist Design Methodology
The Constructionist design methodologyConstructionist design methodology
The Constructionist Design Methodology was developed by artificial intelligence researcher Kristinn R. Thórisson and his students at Columbia University and Reykjavik University for use in the development of cognitive robotics, communicative humanoids and broad AI systems...
(CDM, or 'Constructionist A.I.') is a formal methodology proposed in the year 2004, for use in the development of cognitive robotics, communicative humanoids and broad AI systems. The creation of such systems requires integration of a large number of functionalities that must be carefully coordinated to achieve coherent system behavior. CDM is based on iterative design steps that lead to the creation of a network of named interacting modules, communicating via explicitly typed streams and discrete messages. The OpenAIR message protocol (see below) was inspired by the CDM, and has frequently been used to aid in development of intelligent systems using CDM.
One of the first projects to use CDM was Mirage, an embodied, graphical agent visualized through augmented reality
Augmented reality
Augmented reality is a live, direct or indirect, view of a physical, real-world environment whose elements are augmented by computer-generated sensory input such as sound, video, graphics or GPS data. It is related to a more general concept called mediated reality, in which a view of reality is...
which could communicate with human users and talk about objects present in the user's physical room. Mirage was created by Kristinn R. Thórisson
Kristinn R. Thórisson
Dr. Kristinn R. Thórisson is an Icelandic artificial intelligence researcher, and co-founder of and . Thórisson is one of the leading proponents of artificial intelligence systems integration. Other proponents of this approach are researchers such as Marvin Minsky, Aaron Sloman and Michael A....
, the creator of CDM, and a number of students at Columbia University
Columbia University
Columbia University in the City of New York is a private, Ivy League university in Manhattan, New York City. Columbia is the oldest institution of higher learning in the state of New York, the fifth oldest in the United States, and one of the country's nine Colonial Colleges founded before the...
in 2004. The methodology is actively being developed at Reykjavik University
Reykjavík University
Reykjavík University is a private university in Reykjavík, Iceland, and is chartered by the Chamber of Commerce, the Federation of Icelandic Industries, and the Confederation of Icelandic Employers....
.
OpenAIR Protocol

OpenAIR
OpenAIR is a message routing and communication protocol for artificial intelligence systems that has been gaining in popularity in recent years . The protocol is managed by Mindmakers, and is described on their site in the following manner:...
is a message routing and communication protocol that has been gaining in popularity over the past two years. The protocol is managed by Mindmakers.org, and is described on their site in the following manner:
"OpenAIR is a routing and communication protocol based on a publish-subscribe architecture. It is intended to be the "glue" that allows numerous A.I. researchers to share code more effectively — "AIR to share". It is a definition or a blueprint of the "post office and mail delivery system" for distributed, multi-module systems. OpenAIR provides a core foundation upon which subsequent markup languages and semantics can be based, for e.g. gesture recognition and generation, computer vision, hardware-software interfacing etc.; for a recent example see CVML."http://www.mindmakers.org/openair/airPage.jsp
OpenAIR was created to allow software components that serve their own purpose to communicate with each other in order to produce large scale, overall behavior of an intelligent systems. A simple example would be to have a speech recognition system, and a speech synthesizer communicate with an expert system
Expert system
In artificial intelligence, an expert system is a computer system that emulates the decision-making ability of a human expert. Expert systems are designed to solve complex problems by reasoning about knowledge, like an expert, and not by following the procedure of a developer as is the case in...
through OpenAIR messages, to create a system that can hear and answer various questions through spoken dialogue. CORBA (see below) is an older but similar architecture that can be used for comparison, but OpenAIR was specifically created for A.I. research, while CORBA is a more general standard.
The OpenAIR protocol has been used for collaboration on a number of A.I. systems, a list can be found on the Mindmakers project pages. Psyclone is a popular platform to pair with the OpenAIR protocol (see below).
Psyclone AIOS
Psyclone is a software platform, or an AI operating system (AIOS), developed by Communicative Machines Laboratories for use in creating large, multi modal A.I. systems. The system is an implementation of a blackboard systemBlackboard system
A blackboard system is an artificial intelligence application based on the blackboard architectural model, where a common knowledge base, the "blackboard", is iteratively updated by a diverse group of specialist knowledge sources, starting with a problem specification and ending with a solution...
that supports the OpenAIR message protocol. Psyclone is available for free for non-commercial purposes and has therefore often been used by research institutes on low budgets and novice A.I. developers.
Elvin
Elvin is a content-based router with a central routing station, similar to the Psyclone AIOS (see above).OAA
The OOA is a hybrid architecture that relies on a special inter-agent communication language (ICL) – a logic-based declarative language which is good for expressing high-level, complex tasks and natural language expressions.CORBA
The Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA)Çorba
Chorba , ciorbă , shurpa , shorpo , or sorpa is one of various kinds of soup or stew found in national cuisines across Middle East...
is a standard that enables software components written in multiple computer languages
Programming language
A programming language is an artificial language designed to communicate instructions to a machine, particularly a computer. Programming languages can be used to create programs that control the behavior of a machine and/or to express algorithms precisely....
and running on multiple computers to interoperate. CORBA is defined by the Object Management Group
Object Management Group
Object Management Group is a consortium, originally aimed at setting standards for distributed object-oriented systems, and is now focused on modeling and model-based standards.- Overview :...
(OMG). CORBA follows similar principles as the OpenAIR protocol (see above), and can be used for A.I. systems integration.
MOSID
The Messaging Open Service Interface Definition (OSID) is an O.K.I. specification which provides a means of sending, subscribing and receiving messages. OSIDs are programmatic interfaces which comprise a Service Oriented Architecture for designing and building reusable and interoperable software.Examples of Integrated Systems
- MIRAGE, an A.I. embodied humanoid in an augmented reality environment.
- ASIMOASIMOis a humanoid robot created by Honda. Introduced in 2000, ASIMO, which is an acronym for "Advanced Step in Innovative MObility", was created to be a helper to people. With aspirations of helping people who lack full mobility, ASIMO is used to encourage young people to study science and mathematics...
, Honda's humanoid robot, and QRIOQRIOQRIO was to be a bipedal humanoid entertainment robot developed and marketed by Sony to follow up on the success of its AIBO toy. QRIO stood approximately 0.6 m tall and weighed 7.3 kg...
, Sony's version of a humanoid robot. - Cog, M.I.T. humanoid robot project under the direction of Rodney BrooksRodney BrooksRodney Allen Brooks is the former Panasonic professor of robotics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Since 1986 he has authored a series of highly influential papers which have inaugurated a fundamental shift in artificial intelligence research...
. - AIBOAIBOAIBO was one of several types of robotic pets designed and manufactured by Sony...
, Sony's robot dog integrates vision, hearing and motorskills. - TOPIOTOPIOTOPIO is a bipedal humanoid robot designed to play table tennis against a human being. It has been developed since 2005 by TOSY, a robotics firm in Vietnam. It was publicly demonstrated at the Tokyo International Robot Exhibition on November 28, 2007...
, TOSY's humanoid robot can play ping-pong with human
See also
- Artificial intelligenceArtificial intelligenceArtificial intelligence is the intelligence of machines and the branch of computer science that aims to create it. AI textbooks define the field as "the study and design of intelligent agents" where an intelligent agent is a system that perceives its environment and takes actions that maximize its...
- Hybrid intelligent systemHybrid intelligent systemHybrid intelligent system denotes a software system which employs, in parallel, a combination of methods and techniques from artificial intelligence subfields as:* Neuro-fuzzy systems* hybrid connectionist-symbolic models* Fuzzy expert systems...
, systems that combine the methods of Conventional A.I. (or GOFAI)GOFAIIn artificial intelligence research, GOFAI describes the oldest original approach to achieving artificial intelligence, based on logic and problem solving...
& that of Computational intelligenceComputational intelligenceComputational intelligence is a set of Nature-inspired computational methodologies and approaches to address complex problems of the real world applications to which traditional methodologies and approaches are ineffective or infeasible. It primarily includes Fuzzy logic systems, Neural Networks...
. - Humanoid robotHumanoid robotA humanoid robot or an anthropomorphic robot is a robot with its overall appearance, based on that of the human body, allowing interaction with made-for-human tools or environments. In general humanoid robots have a torso with a head, two arms and two legs, although some forms of humanoid robots...
s utilize systems integration intensely. - Constructionist design methodologyConstructionist design methodologyThe Constructionist Design Methodology was developed by artificial intelligence researcher Kristinn R. Thórisson and his students at Columbia University and Reykjavik University for use in the development of cognitive robotics, communicative humanoids and broad AI systems...
- Cognitive architectureCognitive architectureA cognitive architecture is a blueprint for intelligent agents. It proposes computational processes that act like certain cognitive systems, most often, like a person, or acts intelligent under some definition. Cognitive architectures form a subset of general agent architectures...
s
External links
- Mindmakers.org, a community portal for A.I. research collaboration and system integration.
- COG, a humanoid robot at M.I.T.
- The Open Knowledge Initiative Library

