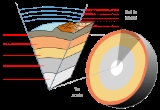
Asthenosphere
Overview
Ductility
In materials science, ductility is a solid material's ability to deform under tensile stress; this is often characterized by the material's ability to be stretched into a wire. Malleability, a similar property, is a material's ability to deform under compressive stress; this is often characterized...
-deforming region of the upper mantle
Mantle (geology)
The mantle is a part of a terrestrial planet or other rocky body large enough to have differentiation by density. The interior of the Earth, similar to the other terrestrial planets, is chemically divided into layers. The mantle is a highly viscous layer between the crust and the outer core....
of the Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
. It lies below the lithosphere
Lithosphere
The lithosphere is the rigid outermost shell of a rocky planet. On Earth, it comprises the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of thousands of years or greater.- Earth's lithosphere :...
, at depths between 100 and 200 km (~ 62 and 124 miles) below the surface, but perhaps extending as deep as 700 km (435 mi).
The asthenosphere is a portion of the upper mantle just below the lithosphere
Lithosphere
The lithosphere is the rigid outermost shell of a rocky planet. On Earth, it comprises the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of thousands of years or greater.- Earth's lithosphere :...
that is involved in plate tectonic movements
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that describes the large scale motions of Earth's lithosphere...
and isostatic
Isostasy
Isostasy is a term used in geology to refer to the state of gravitational equilibrium between the earth's lithosphere and asthenosphere such that the tectonic plates "float" at an elevation which depends on their thickness and density. This concept is invoked to explain how different topographic...
adjustments. In spite of its high temperature, pressures keep it plastic
Plasticity (physics)
In physics and materials science, plasticity describes the deformation of a material undergoing non-reversible changes of shape in response to applied forces. For example, a solid piece of metal being bent or pounded into a new shape displays plasticity as permanent changes occur within the...
, and it has a relatively low density.
Unanswered Questions

