
Atkinson index
Encyclopedia
The Atkinson index is a measure of income inequality developed by British economist Anthony Barnes Atkinson
. The measure is useful in determining which end of the distribution contributed most to the observed inequality.
measure by imposing a coefficient
 to weight incomes. Greater weight can be placed on changes in a given portion of the income distribution by choosing
to weight incomes. Greater weight can be placed on changes in a given portion of the income distribution by choosing  , the level of "inequality aversion", appropriately. The Atkinson index becomes more sensitive to changes at the lower end of the income distribution as
, the level of "inequality aversion", appropriately. The Atkinson index becomes more sensitive to changes at the lower end of the income distribution as  approaches 1. Conversely, as the level of inequality aversion falls (that is, as
approaches 1. Conversely, as the level of inequality aversion falls (that is, as  approaches 0) the Atkinson becomes more sensitive to changes in the upper end of the income distribution.
approaches 0) the Atkinson becomes more sensitive to changes in the upper end of the income distribution.
The Atkinson index is defined as:
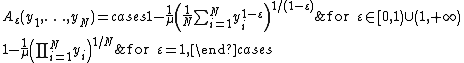
where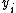 is individual income (i = 1, 2, ..., N) and
is individual income (i = 1, 2, ..., N) and  is the mean
is the mean
income.
The entropy measure developed by Atkinson can be computed from a "normalized Theil index
". This, however, only applies to the Theil index , which is derived from the "generalized entropy class" with
, which is derived from the "generalized entropy class" with 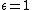 . The Atkinson index is computed using the function
. The Atkinson index is computed using the function  .
.
Atkinson index relies on the following axioms:
Anthony Barnes Atkinson
Sir Anthony Barnes "Tony" Atkinson, FBA, is a British economist and has been a Senior Research Fellow of Nuffield College, Oxford since 2005.-Career:Atkinson served as Warden of Nuffield College from 1994 to 2005...
. The measure is useful in determining which end of the distribution contributed most to the observed inequality.
Definition
The index can be turned into a normativeNormative economics
Normative economics is that part of economics that expresses value judgments about economic fairness or what the economy ought to be like or what goals of public policy ought to be....
measure by imposing a coefficient
Coefficient
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of an expression ; it is usually a number, but in any case does not involve any variables of the expression...
 to weight incomes. Greater weight can be placed on changes in a given portion of the income distribution by choosing
to weight incomes. Greater weight can be placed on changes in a given portion of the income distribution by choosing  , the level of "inequality aversion", appropriately. The Atkinson index becomes more sensitive to changes at the lower end of the income distribution as
, the level of "inequality aversion", appropriately. The Atkinson index becomes more sensitive to changes at the lower end of the income distribution as  approaches 1. Conversely, as the level of inequality aversion falls (that is, as
approaches 1. Conversely, as the level of inequality aversion falls (that is, as  approaches 0) the Atkinson becomes more sensitive to changes in the upper end of the income distribution.
approaches 0) the Atkinson becomes more sensitive to changes in the upper end of the income distribution.The Atkinson index is defined as:
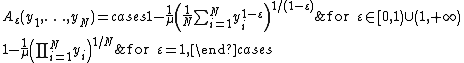
where
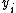 is individual income (i = 1, 2, ..., N) and
is individual income (i = 1, 2, ..., N) and  is the mean
is the meanMean
In statistics, mean has two related meanings:* the arithmetic mean .* the expected value of a random variable, which is also called the population mean....
income.
The entropy measure developed by Atkinson can be computed from a "normalized Theil index
Theil index
The Theil index is a statistic used to measure economic inequality. It has also been used to measure the lack of racial diversity. The basic Theil index TT is the same as redundancy in information theory which is the maximum possible entropy of the data minus the observed entropy. It is a special...
". This, however, only applies to the Theil index
 , which is derived from the "generalized entropy class" with
, which is derived from the "generalized entropy class" with 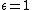 . The Atkinson index is computed using the function
. The Atkinson index is computed using the function  .
.Atkinson index relies on the following axioms:
- The index is symmetric in its arguments:
 for any permutation
for any permutation  .
. - The index is non-negative, and is equal to zero only if all incomes are the same:
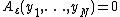 iff
iff 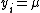 for all
for all 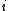 .
. - The index satisfies the principle of transfers: if a transfer
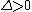 is made from an individual with income
is made from an individual with income 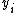 to another one with income
to another one with income 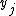 such that
such that 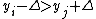 , then the inequality index cannot increase.
, then the inequality index cannot increase. - The index satisfies population replication axiom: if a new population is formed by replicating the existing population an arbitrary number of times, the inequality remains the same:
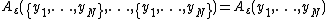
- The index satisfies mean independence, or income homogeneity, axiom: if all incomes are multiplied by a positive constant, the inequality remains the same:
 for any
for any 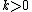 .
. - The index is subgroup decomposable. This means that overall inequality in the population can be computed as the sum of the corresponding Atkinson indices within each group, and the Atkinson index of the group mean incomes:
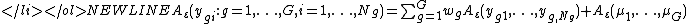
where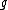 indexes groups,
indexes groups, 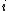 , individuals within groups,
, individuals within groups, 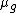 is the mean income in group
is the mean income in group 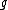 , and the weights
, and the weights 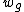 depend on
depend on 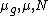 and
and 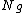 . The class of the subgroup-decomposable inequality indices is very restrictive. Many popular indices, including Gini index, do not satisfy this property.
. The class of the subgroup-decomposable inequality indices is very restrictive. Many popular indices, including Gini index, do not satisfy this property.
External links
Software:- Free Online Calculator computes the Gini Coefficient, plots the Lorenz curve, and computes many other measures of concentration for any dataset
- Free Calculator: Online and downloadable scripts (PythonPython (programming language)Python is a general-purpose, high-level programming language whose design philosophy emphasizes code readability. Python claims to "[combine] remarkable power with very clear syntax", and its standard library is large and comprehensive...
and LuaLua programming languageLua is a lightweight multi-paradigm programming language designed as a scripting language with extensible semantics as a primary goal. Lua has a relatively simple C API compared to other scripting languages.- History :...
) for Atkinson, Gini, and Hoover inequalities - Users of the R data analysis software can install the "ineq" package which allows for computation of a variety of inequality indices including Gini, Atkinson, Theil.
- A MATLAB Inequality Package, including code for computing Gini, Atkinson, Theil indexes and for plotting the Lorenz Curve. Many examples are available.
- StataStataStata is a general-purpose statistical software package created in 1985 by StataCorp. It is used by many businesses and academic institutions around the world...
inequality packages: ineqdeco to decompose inequality by groups; svygei and svyatk to compute design-consistent variances for the generalized entropy and Atkinson indices; glcurve to obtain generalized Lorenz curve. You can type ssc install ineqdeco etc. in Stata prompt to install these packages.

