
Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation
Encyclopedia
Sea surface temperature
Sea surface temperature is the water temperature close to the oceans surface. The exact meaning of surface varies according to the measurement method used, but it is between and below the sea surface. Air masses in the Earth's atmosphere are highly modified by sea surface temperatures within a...
(SST) field. While there is some support for this mode in models and in historical observations, controversy exists with regard to its amplitude, and in particular, the attribution of sea surface temperature
Sea surface temperature
Sea surface temperature is the water temperature close to the oceans surface. The exact meaning of surface varies according to the measurement method used, but it is between and below the sea surface. Air masses in the Earth's atmosphere are highly modified by sea surface temperatures within a...
change to natural or anthropogenic causes, especially in tropical Atlantic areas important for hurricane development.
Definition
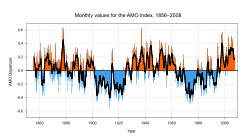
The Atlantic multidecadal oscillation (AMO) was identified by Schlesinger and Ramankutty in 1994.The AMO signal is usually defined from the patterns of SST variability in the North Atlantic once any linear trend has been removed. This detrending is intended to remove the influence of greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone...
-induced global warming
Global warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
from the analysis. However, if the global warming signal is significantly non-linear in time (i.e. not just a smooth increase), variations in the forced signal will leak into the AMO definition. Consequently, correlations with the AMO index may alias effects of global warming
Global warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
.
Mechanisms
In models, AMO-like variability is associated with small changes in the North Atlantic branch of the Thermohaline Circulation, however historical oceanic observations are not sufficient to associate the derived AMO index to present day circulation anomalies.Climate impacts worldwide
The AMO index is correlated to air temperatures and rainfall over much of the Northern Hemisphere, in particular, North America and Europe such as North Eastern Brazilian and African Sahel rainfall and North American and European summer climate. It is also associated with changes in the frequency of North American droughtDrought
A drought is an extended period of months or years when a region notes a deficiency in its water supply. Generally, this occurs when a region receives consistently below average precipitation. It can have a substantial impact on the ecosystem and agriculture of the affected region...
s and is reflected in the frequency of severe Atlantic hurricanes. It alternately obscures and exaggerates the global increase in temperatures due to human-induced global warming
Global warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
.
Recent research suggests that the AMO is related to the past occurrence of major droughts in the US Midwest and the Southwest. When the AMO is in its warm phase, these droughts tend to be more frequent or prolonged. Two of the most severe droughts of the 20th century occurred during the positive AMO between 1925 and 1965: The Dust Bowl
Dust Bowl
The Dust Bowl, or the Dirty Thirties, was a period of severe dust storms causing major ecological and agricultural damage to American and Canadian prairie lands from 1930 to 1936...
of the 1930s and the 1950s drought. Florida and the Pacific Northwest tend to be the opposite—warm AMO, more rainfall.
Climate model
Climate model
Climate models use quantitative methods to simulate the interactions of the atmosphere, oceans, land surface, and ice. They are used for a variety of purposes from study of the dynamics of the climate system to projections of future climate...
s suggest that a warm phase of the AMO strengthens the summer rainfall over India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and Sahel
Sahel
The Sahel is the ecoclimatic and biogeographic zone of transition between the Sahara desert in the North and the Sudanian Savannas in the south.It stretches across the North African continent between the Atlantic Ocean and the Red Sea....
and the North Atlantic tropical cyclone activity. Paleoclimatologic
Paleoclimatology
Paleoclimatology is the study of changes in climate taken on the scale of the entire history of Earth. It uses a variety of proxy methods from the Earth and life sciences to obtain data previously preserved within rocks, sediments, ice sheets, tree rings, corals, shells and microfossils; it then...
studies have confirmed this pattern—increased rainfall in AMO warmphase, decreased in cold phase—for the Sahel over the past 3,000 years.
Relation to Atlantic hurricanes

Global warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
, it is currently obscured by the AMO quasi-periodic cycle. The AMO alternately obscures and exaggerates the global increase in temperatures due to human-induced global warming. Based on the typical duration of negative and positive phases of the AMO, the current warm regime is expected to persist at least until 2015 and possibly as late as 2035. Enfield et al. assume a peak around 2020.
Florida rainfall
The AMO has a strong effect on Florida rainfall. Rainfall in central and south Florida becomes more plentiful when the Atlantic is in its warm phase and droughts and wildfires are more frequent in the cool phase. As a result of these variations, the inflow to Lake OkeechobeeLake Okeechobee
Lake Okeechobee , locally referred to as The Lake or The Big O, is the largest freshwater lake in the state of Florida. It is the seventh largest freshwater lake in the United States and the second largest freshwater lake contained entirely within the lower 48 states...
— the reservoir for South Florida’s water supply — changes by as much as 40% between AMO extremes. In northern Florida the relationship begins to reverse — less rainfall when the Atlantic is warm.
Periodicity and prediction of AMO shifts
There are only about 130–150 years of data based on instrument data which are too few samples for conventional statistical approaches. With aid of multi –century proxy reconstruction, a longer period of 424 years was used by Enfield and Cid–Serrano as an illustration of an approach as described in their paper called "The Probabilistic Projection of Climate Risk". Their histogram of zero crossing intervals from a set of five re-sampled and smoothed version of Gray et al (2004) index together with the Maximum Likelihood Estimate gamma distribution fit to the histogram, showed that the largest frequency of regime interval was around 10–20 year. The cumulative probability for all intervals 20 years or less was about 70%There is no demonstrated predictability for when the AMO will switch, in any deterministic sense. Computer models, such as those that predict El Niño, are far from being able to do this. Enfield and colleagues have calculated the probability that a change in the AMO will occur within a given future time frame, assuming that historical variability persists. Probabilistic projections of this kind may prove to be useful for long-term planning in climate sensitive applications, such as water management.
Assuming that the AMO continues with its quasi-cycle of roughly 70 years, the peak of the current warm phase would be expected in c. 2020, or based on its 50–90 year quasi-cycle, between 2000 and 2040 (after peaks in c. 1880 and c. 1950).
Further reading
- "Climate change: the next ten years" by Fred PearceFred PearceFred Pearce is an English author and journalist based in London. He has been described as one of Britain's finest science writers and has reported on environment, popular science and development issues from 64 countries over the past 20 years. He specializes in global environmental issues,...
and Michael Le Page, New ScientistNew ScientistNew Scientist is a weekly non-peer-reviewed English-language international science magazine, which since 1996 has also run a website, covering recent developments in science and technology for a general audience. Founded in 1956, it is published by Reed Business Information Ltd, a subsidiary of...
, 13 Aug. 2008, pp. 26–30.

