Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization
Encyclopedia
Atmospheric-pressure chemical ionization (APCI) is an ionization method
used in mass spectrometry
. It is a form of chemical ionization
which takes place at atmospheric pressure.
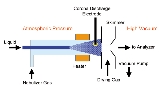
to be used directly, often without diverting the larger fraction of volume to waste. Typically the mobile phase containing eluting analyte is heated to relatively high temperatures (above 400 degrees Celsius), sprayed with high flow rates of nitrogen and the entire aerosol cloud is subjected to a corona discharge
that creates ion
s. Often APCI can be performed in a modified ESI source. The ionization occurs in the gas phase, unlike ESI, where the ionization occurs in the liquid phase. A potential advantage of APCI is that it is possible to use a nonpolar solvent as a mobile phase solution, instead of a polar solvent, because the solvent and molecules of interest are converted to a gaseous state before reaching the corona discharge pin. Typically, APCI is a less "soft" ionization technique than ESI, i.e. it generates more fragment ions relative to the parent ion.
Ion source
An ion source is an electro-magnetic device that is used to create charged particles. These are used primarily to form ions for mass spectrometers, optical emission spectrometers, particle accelerators, ion implanters and ion engines.- Electron ionization :...
used in mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of charged particles.It is used for determining masses of particles, for determining the elemental composition of a sample or molecule, and for elucidating the chemical structures of molecules, such as peptides and...
. It is a form of chemical ionization
Chemical ionization
Chemical ionization is an ionization technique used in mass spectrometry. Chemical ionization is a lower energy process than electron ionization. The lower energy yields less fragmentation, and usually a simpler spectrum...
which takes place at atmospheric pressure.
How it works
APCI allows for the high flow rates typical of standard bore HPLCHigh-performance liquid chromatography
High-performance liquid chromatography , HPLC, is a chromatographic technique that can separate a mixture of compounds and is used in biochemistry and analytical chemistry to identify, quantify and purify the individual components of the mixture.HPLC typically utilizes different types of stationary...
to be used directly, often without diverting the larger fraction of volume to waste. Typically the mobile phase containing eluting analyte is heated to relatively high temperatures (above 400 degrees Celsius), sprayed with high flow rates of nitrogen and the entire aerosol cloud is subjected to a corona discharge
Corona discharge
In electricity, a corona discharge is an electrical discharge brought on by the ionization of a fluid surrounding a conductor that is electrically energized...
that creates ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
s. Often APCI can be performed in a modified ESI source. The ionization occurs in the gas phase, unlike ESI, where the ionization occurs in the liquid phase. A potential advantage of APCI is that it is possible to use a nonpolar solvent as a mobile phase solution, instead of a polar solvent, because the solvent and molecules of interest are converted to a gaseous state before reaching the corona discharge pin. Typically, APCI is a less "soft" ionization technique than ESI, i.e. it generates more fragment ions relative to the parent ion.

