
Atomic mass constant
Encyclopedia
In physics
and chemistry
, the atomic mass constant, mu, is one twelfth of the mass of an unbound atom of carbon-12 at rest and in its ground state. It serves to define the atomic mass unit
and is, by definition, equal to 1 u. The 2006 CODATA recommended value is .
In practice, the atomic mass constant is determined as the ratio of the electron rest mass
me to the electron relative atomic mass Ar(e) (that is, the mass of the electron on a scale where C = 12). The relative atomic mass of the electron can be measured in cyclotron
experiments, while the rest mass of the electron can be derived from other physical constants.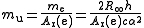
The current uncertainty in the value of the atomic mass constant – one part in 20 million – is almost entirely due to the uncertainty in the value of the Planck constant
.
The megaelectronvolt
(MeV) is commonly used as a unit of mass in particle physics
, and these values are also important for the practical determination of relative atomic masses. Although relative atomic masses are defined for neutral atoms, they are measured (by mass spectrometry
) for ions: hence, the measured values must be correct for the mass of the electrons that were removed to form the ions, and also for the mass equivalent of the electron binding energy, Eb/muc2. The total binding energy of the six electrons in a carbon-12 atom is 1030.1089 eV = : Eb/muc2 = , or about one part in 10 million of the mass of the atom.
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
and chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, the atomic mass constant, mu, is one twelfth of the mass of an unbound atom of carbon-12 at rest and in its ground state. It serves to define the atomic mass unit
Atomic mass unit
The unified atomic mass unit or dalton is a unit that is used for indicating mass on an atomic or molecular scale. It is defined as one twelfth of the rest mass of an unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state, and has a value of...
and is, by definition, equal to 1 u. The 2006 CODATA recommended value is .
In practice, the atomic mass constant is determined as the ratio of the electron rest mass
Electron rest mass
The electron rest mass is the mass of a stationary electron. It is one of the fundamental constants of physics, and is also very important in chemistry because of its relation to the Avogadro constant...
me to the electron relative atomic mass Ar(e) (that is, the mass of the electron on a scale where C = 12). The relative atomic mass of the electron can be measured in cyclotron
Cyclotron
In technology, a cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator. In physics, the cyclotron frequency or gyrofrequency is the frequency of a charged particle moving perpendicularly to the direction of a uniform magnetic field, i.e. a magnetic field of constant magnitude and direction...
experiments, while the rest mass of the electron can be derived from other physical constants.
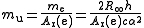
The current uncertainty in the value of the atomic mass constant – one part in 20 million – is almost entirely due to the uncertainty in the value of the Planck constant
Planck constant
The Planck constant , also called Planck's constant, is a physical constant reflecting the sizes of energy quanta in quantum mechanics. It is named after Max Planck, one of the founders of quantum theory, who discovered it in 1899...
.
Energy equivalents
The atomic mass constant can also be expressed as its energy equivalent, that is muc2. The 2006 CODATA recommended values are:- 1.492 417 830(74) J
- 931.494 028(23) MeV
The megaelectronvolt
Electronvolt
In physics, the electron volt is a unit of energy equal to approximately joule . By definition, it is equal to the amount of kinetic energy gained by a single unbound electron when it accelerates through an electric potential difference of one volt...
(MeV) is commonly used as a unit of mass in particle physics
Particle physics
Particle physics is a branch of physics that studies the existence and interactions of particles that are the constituents of what is usually referred to as matter or radiation. In current understanding, particles are excitations of quantum fields and interact following their dynamics...
, and these values are also important for the practical determination of relative atomic masses. Although relative atomic masses are defined for neutral atoms, they are measured (by mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of charged particles.It is used for determining masses of particles, for determining the elemental composition of a sample or molecule, and for elucidating the chemical structures of molecules, such as peptides and...
) for ions: hence, the measured values must be correct for the mass of the electrons that were removed to form the ions, and also for the mass equivalent of the electron binding energy, Eb/muc2. The total binding energy of the six electrons in a carbon-12 atom is 1030.1089 eV = : Eb/muc2 = , or about one part in 10 million of the mass of the atom.

