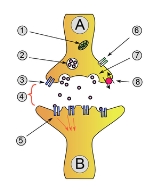
Axon terminal
Overview
Axon terminals are distal terminations of the branches of an axon
Axon
An axon is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body or soma....
. An axon nerve fiber is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
, that conducts electrical impulses
Action potential
In physiology, an action potential is a short-lasting event in which the electrical membrane potential of a cell rapidly rises and falls, following a consistent trajectory. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, called excitable cells, which include neurons, muscle cells, and...
(called "action potentials") away from the neuron's cell body, or soma, in order to transmit those impulses to other neurons.
Neurons are interconnected in complex arrangements, and use electrochemical signals and neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
chemicals to transmit impulses from one neuron to the next; axon terminals are separated from neighboring neurons by a small gap called a synapse
Synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another cell...
, across which impulses are sent.

