
BQM-74 Chukar
Encyclopedia
The BQM-74 Chukar is a series of aerial target drones
produced by Northrop
. The Chukar has gone through three major revisions, including the initial MQM-74A Chukar I, the MQM-74C Chukar II, and the BQM-74C Chukar III. They are recoverable, remote controlled, subsonic aerial target, capable of speeds up to Mach
0.86 and altitudes from 30 to 40,000 ft (10 to 12,000 m).
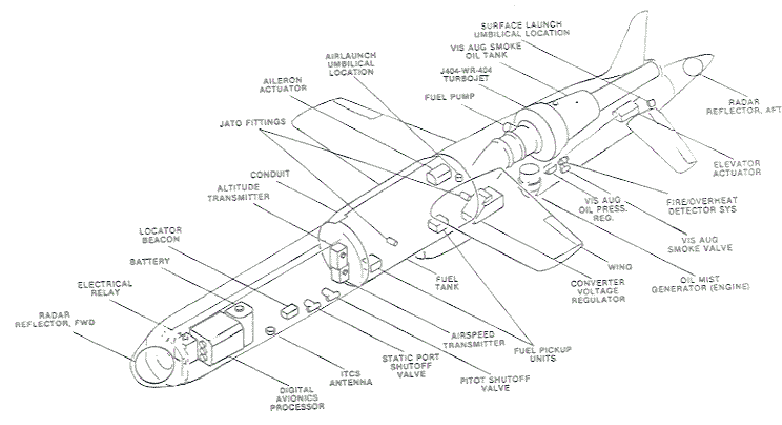
J400 (J400-WR-404) turbojet engine, which produces a maximum thrust of 240 pounds force (1068 N) at sea level. The BQM-74 is launched from a zero length ground launcher utilizing dual Jet Assisted Takeoff (JATO
) bottles. When equipped with an air launch kit, the BQM-74 can be air launched from a TA-4J
, F-16
, Grumman Gulfstream I
or DC-130 aircraft. The BQM-74 is used primarily as a realistic aerial target, capable of simulating enemy threats for gunnery and missile training exercises.
Drones are capable of being recovered following a training exercise. A parachute is deployed by remote control or if the remote control link is severed and a flotation kit can be added for sea-based recovery. If recovery of the drone is required, special telemetry warheads are used on the defensive missile in place of explosives. This telemetry warhead is desirable since it allows for extensive analysis of the performance of the defensive missile, including miss distance information that determines if a real warhead would have damaged the target. A direct hit would likely destroy the drone. Gunnery systems would use non-explosive dummy munitions. Since gunnery systems are aimed in front of a moving target so it will fly through the blast-fragments, dummy munitions do not have to directly hit a target. Analysis of radar data would determine if the dummy munitions would have damaged the target drone.
The MQM-74A had a neatly tapered cigar-shaped fuselage, straight mid-mounted wings, an underslung jet engine with the intake under the wings, and a conventional tail configuration with the tailplanes set in an inverted vee. It was powered by a Williams International
WR24-6 turbojet engine with a thrust of 121 pounds (538 N), and was launched by RATO booster from the ground or a ship. The Navy purchased 1,800 MQM-74A Chukar Is. Several hundred more were purchased in total by NATO for a multinational test range on the island of Crete
, as well as the Royal Navy
and the Italian Navy
.
Chukar
is the name of an Asian species of partridge
, introduced to America and as they are hunted for sport, it seems that Northrop felt that the name was appropriate for an aircraft whose purpose in life is to be shot at. The name Chukar is only formally applied to export versions of the drone, but informally it is used for all variants.
used the MQM-74A as the basis for an experimental drone designated the XBQM-108, which was to be used to as a demonstrator for a "pogo" or "tailsitter" aircraft that could take off and land straight up and down on its tail. The fuselage
, tailfin
, radio control
system, and parachute recovery system of the MQM-74A were retained, but the drone was fitted with a new wing, a Teledyne CAE J402 engine with a rotating vectored thrust exhaust, fixed tricycle landing gear, and additional flight control systems. The demonstrator was completed and was making tethered flights when the program was cancelled.
 The Navy liked the Chukar I but wanted a somewhat faster version, and in the early 1970s Northrop developed the improved experimental MQM-74B, which was followed by the production MQM-74C Chukar II. The Chukar II is difficult to distinguish from the Chukar I, but the Chukar II is slightly scaled up and uses an uprated Williams WR24-7 turbojet with 180 pound (800 N) thrust, giving it a top speed of 590 mph (950 km/h).
The Navy liked the Chukar I but wanted a somewhat faster version, and in the early 1970s Northrop developed the improved experimental MQM-74B, which was followed by the production MQM-74C Chukar II. The Chukar II is difficult to distinguish from the Chukar I, but the Chukar II is slightly scaled up and uses an uprated Williams WR24-7 turbojet with 180 pound (800 N) thrust, giving it a top speed of 590 mph (950 km/h).
Like the Chukar I, the Chukar II is ground or ship launched only. At least 1,400 Chukar IIs were built, mostly for the US Navy, but other customers included NATO, Great Britain
, West Germany
, Greece
, Iran
, Italy
, Japan
, the Netherlands
, Saudi Arabia
, and Spain
.
The BQM-74C incorporates a microprocessor
-based autopilot
that allows it to be programmed for much more sophisticated flight operations. The BQM-74C can be air launched as well as ground launched. The original engine was the Williams WR24-7A AKA J400-WR-402, with 180 pound (800 N) thrust, but in 1986 production was upgraded to the J400-WR-403 with 240 pound (1070 N) thrust. The BQM-74C is stressed for maneuvers of up to 6Gs. More than 1,600 BQM-74Cs have been built.
Northrop built ten BQM-74C Recce UAVs for tactical reconnaissance
for US Navy evaluation, but this variant did not go into production.
, BQM-74Cs were used as decoys during the initial air attacks into Iraq
. The USAF Big Safari
group was put in charge of the decoy effort, which was codenamed "Project Scathe Mean".
The Chukar drones that were available were usually launched from DC-130 director aircraft, and could also be launched from strike aircraft such as F-15s or F-16s. These launch resources were not available, though, so the Navy found twelve ground launchers in their inventory that could be made serviceable, while RATO
booster units were found stockpiled in Belgium
. Each BQM-74C was fitted with a pair of passive radar enhancement devices to give it a signature similar to that of a strike fighter.
A 40-person team of specialists, obtained from disbanded ground-launched cruise missile units, was assembled in a few days and designated the "4468th Tactical Reconnaissance Group". The 4468th moved on a fast track, with trucks modified and obtained from a California commercial trucking firm, tool kits purchased from Sears
, and field gear bought from war surplus stores. The teams were given quick training, equipped with 44 Navy BQM-74Cs, and sent to Saudi Arabia
in two six-launcher teams in about two weeks, arriving near the Iraqi border on 15 October 1990. The northern team was sited to cover Baghdad and large military bases in that area, while the southern team was sited to cover Basra
and Kuwait City
.
When the air war began on the night of 17 January 1991, Iraq was hit by waves of F-117 Nighthawk
stealth fighters and BGM-109 Tomahawk
cruise missiles. A group of 38 BQM-74Cs were assigned to be launched as diversion for the second wave of attacks, with the launches generally in groups of three, and 37 were launched successfully in precisely timed waves. One group of three was intercepted by Iraqi aircraft, while all the others made it to target.
The drones flew over 500 kilometers (310 miles) at 630 km/h (390 mph), then began to orbit Baghdad
for up to 20 minutes. Iraqi air defense radars probed for the drones, and were immediately destroyed by allied strike aircraft firing high-speed anti-radiation missiles (HARMs)
. The Navy also launched TALDs
to contribute to the countermeasures blitz. Iraqi air defenses never recovered from this blow, and though large Allied aircraft losses had been predicted, the Iraqis only succeeded in shooting down 44. After the war, the 4468th was disbanded, and one of the remaining BQM-74Cs was donated to the National Museum of the United States Air Force
at Wright-Patterson AFB in Ohio, where it is now on display.
Designation sequence:
BGM-71
-
MIM-72 -
UGM-73
-
BQM-74 -
BGM-75
-
AGM-76
-
FGM-77
Unmanned aerial vehicle
An unmanned aerial vehicle , also known as a unmanned aircraft system , remotely piloted aircraft or unmanned aircraft, is a machine which functions either by the remote control of a navigator or pilot or autonomously, that is, as a self-directing entity...
produced by Northrop
Northrop Grumman
Northrop Grumman Corporation is an American global aerospace and defense technology company formed by the 1994 purchase of Grumman by Northrop. The company was the fourth-largest defense contractor in the world as of 2010, and the largest builder of naval vessels. Northrop Grumman employs over...
. The Chukar has gone through three major revisions, including the initial MQM-74A Chukar I, the MQM-74C Chukar II, and the BQM-74C Chukar III. They are recoverable, remote controlled, subsonic aerial target, capable of speeds up to Mach
Mach number
Mach number is the speed of an object moving through air, or any other fluid substance, divided by the speed of sound as it is in that substance for its particular physical conditions, including those of temperature and pressure...
0.86 and altitudes from 30 to 40,000 ft (10 to 12,000 m).
Description
The BQM-74E is propelled during flight by a single WilliamsWilliams International
Williams International is a manufacturer of small gas turbine engines based in Walled Lake, Michigan, United States. It produces jet engines for cruise missiles and small jet-powered aircraft.- History :...
J400 (J400-WR-404) turbojet engine, which produces a maximum thrust of 240 pounds force (1068 N) at sea level. The BQM-74 is launched from a zero length ground launcher utilizing dual Jet Assisted Takeoff (JATO
JATO
JATO is an acronym for jet-fuel assisted take off. It is a system for helping overloaded aircraft into the air by providing additional thrust in the form of small rockets....
) bottles. When equipped with an air launch kit, the BQM-74 can be air launched from a TA-4J
A-4 Skyhawk
The Douglas A-4 Skyhawk is a carrier-capable ground-attack aircraft designed for the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps. The delta winged, single-engined Skyhawk was designed and produced by Douglas Aircraft Company, and later McDonnell Douglas. It was originally designated the A4D...
, F-16
F-16 Fighting Falcon
The General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon is a multirole jet fighter aircraft originally developed by General Dynamics for the United States Air Force . Designed as an air superiority day fighter, it evolved into a successful all-weather multirole aircraft. Over 4,400 aircraft have been built since...
, Grumman Gulfstream I
Grumman Gulfstream I
|-See also:-External links:*...
or DC-130 aircraft. The BQM-74 is used primarily as a realistic aerial target, capable of simulating enemy threats for gunnery and missile training exercises.
Drones are capable of being recovered following a training exercise. A parachute is deployed by remote control or if the remote control link is severed and a flotation kit can be added for sea-based recovery. If recovery of the drone is required, special telemetry warheads are used on the defensive missile in place of explosives. This telemetry warhead is desirable since it allows for extensive analysis of the performance of the defensive missile, including miss distance information that determines if a real warhead would have damaged the target. A direct hit would likely destroy the drone. Gunnery systems would use non-explosive dummy munitions. Since gunnery systems are aimed in front of a moving target so it will fly through the blast-fragments, dummy munitions do not have to directly hit a target. Analysis of radar data would determine if the dummy munitions would have damaged the target drone.
MQM-74A Chukar I
The Chukar series began in the early 1960s with a US Navy requirement for a new target drone. The company developed a prototype with the company designation of NV-105 and featuring a delta wing, flying it in 1964. The delta wing didn't work out and was replaced by a straight wing, resulting in the NV-105A, which was first flown in 1965. The NV-105A was accepted by the Navy and went into production as the MQM-74A in 1968.The MQM-74A had a neatly tapered cigar-shaped fuselage, straight mid-mounted wings, an underslung jet engine with the intake under the wings, and a conventional tail configuration with the tailplanes set in an inverted vee. It was powered by a Williams International
Williams International
Williams International is a manufacturer of small gas turbine engines based in Walled Lake, Michigan, United States. It produces jet engines for cruise missiles and small jet-powered aircraft.- History :...
WR24-6 turbojet engine with a thrust of 121 pounds (538 N), and was launched by RATO booster from the ground or a ship. The Navy purchased 1,800 MQM-74A Chukar Is. Several hundred more were purchased in total by NATO for a multinational test range on the island of Crete
Crete
Crete is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, and one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It forms a significant part of the economy and cultural heritage of Greece while retaining its own local cultural traits...
, as well as the Royal Navy
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the British Armed Forces. Founded in the 16th century, it is the oldest service branch and is known as the Senior Service...
and the Italian Navy
Italian Navy
Italian Navy may refer to:* Pre-unitarian navies of the Italian states* Regia Marina, the Royal Navy of the Kingdom of Italy * Italian Navy , the navy of the Italian Republic...
.
Chukar
Chukar
The Chukar Partridge or Chukar is a Eurasian upland gamebird in the pheasant family Phasianidae. It has been considered to form a superspecies complex along with the Rock Partridge, Philby's Partridge and Przevalski's Partridge and treated in the past as conspecific particularly with the first...
is the name of an Asian species of partridge
Partridge
Partridges are birds in the pheasant family, Phasianidae. They are a non-migratory Old World group.These are medium-sized birds, intermediate between the larger pheasants and the smaller quails. Partridges are native to Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Middle East...
, introduced to America and as they are hunted for sport, it seems that Northrop felt that the name was appropriate for an aircraft whose purpose in life is to be shot at. The name Chukar is only formally applied to export versions of the drone, but informally it is used for all variants.
XBQM-108
In the mid-1970s, the US Naval Weapons CenterNaval Air Weapons Station China Lake
- About : is part of under Commander, Navy Installation Command and is located in the Western Mojave Desert region of California, approximately north of Los Angeles. Occupying three counties – Kern, San Bernardino and Inyo – the installation’s closest neighbors are the cities of Ridgecrest,...
used the MQM-74A as the basis for an experimental drone designated the XBQM-108, which was to be used to as a demonstrator for a "pogo" or "tailsitter" aircraft that could take off and land straight up and down on its tail. The fuselage
Fuselage
The fuselage is an aircraft's main body section that holds crew and passengers or cargo. In single-engine aircraft it will usually contain an engine, although in some amphibious aircraft the single engine is mounted on a pylon attached to the fuselage which in turn is used as a floating hull...
, tailfin
Tailfin
The tailfin era of automobile styling encompassed the 1950s and 1960s, peaking between 1957 and 1960. It was a style that spread worldwide, as car designers picked up styling trends from the US automobile industry where it was the golden epoch of American autodesign.General Motors design chief...
, radio control
Radio control
Radio control is the use of radio signals to remotely control a device. The term is used frequently to refer to the control of model vehicles from a hand-held radio transmitter...
system, and parachute recovery system of the MQM-74A were retained, but the drone was fitted with a new wing, a Teledyne CAE J402 engine with a rotating vectored thrust exhaust, fixed tricycle landing gear, and additional flight control systems. The demonstrator was completed and was making tethered flights when the program was cancelled.
MQM-74C Chukar II

Like the Chukar I, the Chukar II is ground or ship launched only. At least 1,400 Chukar IIs were built, mostly for the US Navy, but other customers included NATO, Great Britain
Great Britain
Great Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles...
, West Germany
West Germany
West Germany is the common English, but not official, name for the Federal Republic of Germany or FRG in the period between its creation in May 1949 to German reunification on 3 October 1990....
, Greece
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
, Iran
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
, Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
, Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
, the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
, Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia , commonly known in British English as Saudi Arabia and in Arabic as as-Sa‘ūdiyyah , is the largest state in Western Asia by land area, constituting the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and the second-largest in the Arab World...
, and Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
.
BQM-74C Chukar III
In 1978, the US Navy requested a still more sophisticated drone, and Northrop responded with the BQM-74C Chukar III. This improved variant is visibly different from its predecessors, featuring a more cylindrical fuselage, in contrast with the tapered fuselage of its predecessors.The BQM-74C incorporates a microprocessor
Microprocessor
A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer's central processing unit on a single integrated circuit, or at most a few integrated circuits. It is a multipurpose, programmable device that accepts digital data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and...
-based autopilot
Autopilot
An autopilot is a mechanical, electrical, or hydraulic system used to guide a vehicle without assistance from a human being. An autopilot can refer specifically to aircraft, self-steering gear for boats, or auto guidance of space craft and missiles...
that allows it to be programmed for much more sophisticated flight operations. The BQM-74C can be air launched as well as ground launched. The original engine was the Williams WR24-7A AKA J400-WR-402, with 180 pound (800 N) thrust, but in 1986 production was upgraded to the J400-WR-403 with 240 pound (1070 N) thrust. The BQM-74C is stressed for maneuvers of up to 6Gs. More than 1,600 BQM-74Cs have been built.
Northrop built ten BQM-74C Recce UAVs for tactical reconnaissance
Reconnaissance
Reconnaissance is the military term for exploring beyond the area occupied by friendly forces to gain information about enemy forces or features of the environment....
for US Navy evaluation, but this variant did not go into production.
BQM-74E Chukar III
The BQM-74C has now been replaced in production by the BQM-74E, which is externally all but identical but incorporates the uprated J400-WR-404 engine as standard, and has a third greater range and endurance than its predecessor.Future versions
In the 1980s, Northrop built a next-generation target, the NV-144, that was substantially bigger and faster than the Chukar III, but the NV-144 did not enter production. Northrop, now part of Northrop Grumman, is now working toward delivery of the improved BQM-74F variant of the Chukar, previously known as Target 2000. The BQM-74F has general configuration along the lines of the BQM-74C, but features swept wings, an empty weight of 600 pounds (270 kilograms), an uprated engine with 300 pound (1.33 kN) thrust, speed of up to Mach 0.93, and a design lifetime of 20 flights. The BQM-74F will be able to simulate a range of different aircraft and cruise missiles. It will also be able to tow targets and decoys, and will be compatible with current Chukar support systems and infrastructure. The Navy awarded Northrop Grumman a development contract in 2002, and initial deliveries are scheduled for 2006.Gulf War combat use
In the 1991 Gulf WarGulf War
The Persian Gulf War , commonly referred to as simply the Gulf War, was a war waged by a U.N.-authorized coalition force from 34 nations led by the United States, against Iraq in response to Iraq's invasion and annexation of Kuwait.The war is also known under other names, such as the First Gulf...
, BQM-74Cs were used as decoys during the initial air attacks into Iraq
Iraq
Iraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
. The USAF Big Safari
Big Safari
Big Safari is a United States Air Force program which provides management, direction, and control of the acquisition, modification, and logistics support for special purpose weapons systems. The program itself receives some direction from NASIC. It is headquartered in Greenville, Texas and has...
group was put in charge of the decoy effort, which was codenamed "Project Scathe Mean".
The Chukar drones that were available were usually launched from DC-130 director aircraft, and could also be launched from strike aircraft such as F-15s or F-16s. These launch resources were not available, though, so the Navy found twelve ground launchers in their inventory that could be made serviceable, while RATO
JATO
JATO is an acronym for jet-fuel assisted take off. It is a system for helping overloaded aircraft into the air by providing additional thrust in the form of small rockets....
booster units were found stockpiled in Belgium
Belgium
Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
. Each BQM-74C was fitted with a pair of passive radar enhancement devices to give it a signature similar to that of a strike fighter.
A 40-person team of specialists, obtained from disbanded ground-launched cruise missile units, was assembled in a few days and designated the "4468th Tactical Reconnaissance Group". The 4468th moved on a fast track, with trucks modified and obtained from a California commercial trucking firm, tool kits purchased from Sears
Sears, Roebuck and Company
Sears, officially named Sears, Roebuck and Co., is an American chain of department stores which was founded by Richard Warren Sears and Alvah Curtis Roebuck in the late 19th century...
, and field gear bought from war surplus stores. The teams were given quick training, equipped with 44 Navy BQM-74Cs, and sent to Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia , commonly known in British English as Saudi Arabia and in Arabic as as-Sa‘ūdiyyah , is the largest state in Western Asia by land area, constituting the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and the second-largest in the Arab World...
in two six-launcher teams in about two weeks, arriving near the Iraqi border on 15 October 1990. The northern team was sited to cover Baghdad and large military bases in that area, while the southern team was sited to cover Basra
Basra
Basra is the capital of Basra Governorate, in southern Iraq near Kuwait and Iran. It had an estimated population of two million as of 2009...
and Kuwait City
Kuwait City
-Suburbs:Although the districts below are not usually recognized as suburbs, the following is a list of a few areas surrounding Kuwait city:Al-Salam ""السلام"" -Economy:...
.
When the air war began on the night of 17 January 1991, Iraq was hit by waves of F-117 Nighthawk
F-117 Nighthawk
The Lockheed F-117 Nighthawk was a single-seat, twin-engine stealth ground-attack aircraft formerly operated by the United States Air Force . The F-117A's first flight was in 1981, and it achieved initial operating capability status in October 1983...
stealth fighters and BGM-109 Tomahawk
BGM-109 Tomahawk
The Tomahawk is a long-range, all-weather, subsonic cruise missile. Introduced by General Dynamics in the 1970s, it was designed as a medium- to long-range, low-altitude missile that could be launched from a surface platform. It has been improved several times and, by way of corporate divestitures...
cruise missiles. A group of 38 BQM-74Cs were assigned to be launched as diversion for the second wave of attacks, with the launches generally in groups of three, and 37 were launched successfully in precisely timed waves. One group of three was intercepted by Iraqi aircraft, while all the others made it to target.
The drones flew over 500 kilometers (310 miles) at 630 km/h (390 mph), then began to orbit Baghdad
Baghdad
Baghdad is the capital of Iraq, as well as the coterminous Baghdad Governorate. The population of Baghdad in 2011 is approximately 7,216,040...
for up to 20 minutes. Iraqi air defense radars probed for the drones, and were immediately destroyed by allied strike aircraft firing high-speed anti-radiation missiles (HARMs)
AGM-88 HARM
The AGM-88 High-speed Anti-Radiation Missile is a tactical, air-to-surface missile designed to home in on electronic transmissions coming from surface-to-air radar systems. It was originally developed by Texas Instruments as a replacement for the AGM-45 Shrike and AGM-78 Standard ARM system...
. The Navy also launched TALDs
ADM-141 TALD
The ADM-141A/B TALD was an American decoy missile originally built by Brunswick Corporation for the USAF and the Israeli Air Force. Later it transitioned to joint US/Israeli manufacture with Israeli Military Industries Advanced Systems Division ....
to contribute to the countermeasures blitz. Iraqi air defenses never recovered from this blow, and though large Allied aircraft losses had been predicted, the Iraqis only succeeded in shooting down 44. After the war, the 4468th was disbanded, and one of the remaining BQM-74Cs was donated to the National Museum of the United States Air Force
National Museum of the United States Air Force
The National Museum of the United States Air Force is the official museum of the United States Air Force located at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base northeast of Dayton, Ohio. The NMUSAF is the world's largest and oldest military aviation museum with more than 360 aircraft and missiles on display...
at Wright-Patterson AFB in Ohio, where it is now on display.
Specifications

Related content
- History of UAVs decoys
Designation sequence:
BGM-71
BGM-71 TOW
The BGM-71 TOW is an anti-tank missile. "BGM" is a weapon classification that stands for "Multiple Environment , Surface-Attack , Missile ". "TOW" is an acronym that stands for "Tube-launched, Optically-tracked, Wire command data link, guided missile"...
-
MIM-72 -
UGM-73
UGM-73 Poseidon
The Poseidon missile was the second US Navy ballistic missile system, powered by a two-stage solid fuel rocket. It succeeded the Polaris missile beginning in 1972, bringing major advances in warheads and accuracy...
-
BQM-74 -
BGM-75
BGM-75 AICBM
The Advanced Intercontinental Ballistic Missile, also known as Weapons System 120A and ZBGM-75, was a program to develop an intercontinental ballistic missile, proposed by the United States Air Force in the 1960s...
-
AGM-76
AGM-76 Falcon
The AGM-76 Falcon is an air-to-surface missile developed by the United States of America.-Overview:The AGM-76 was developed as a ground attack version of the AIM-47 Falcon air-to-air missile, in much the same way that the AGM-87 Focus was developed from the AIM-9 Sidewinder. It was planned to use...
-
FGM-77

