
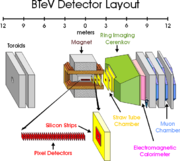
BTeV
Encyclopedia
B meson
B mesons are mesons composed of a bottom quark or bottom antiquark and either an up , down , strange or charm quark . The combination of a bottom antiquark and a top quark is not thought to be possible because of the top quark's short lifetime...
TeV
TEV
TEV may refer to:* TeV, or teraelectronvolt, a measure of energy* Total Enterprise Value, a financial measure* Total Economic Value, an economic measure* Tobacco etch virus, a plant pathogenic virus of the family Potyviridae....
(teraelectronvolt) — was an experiment in high-energy particle physics
Particle physics
Particle physics is a branch of physics that studies the existence and interactions of particles that are the constituents of what is usually referred to as matter or radiation. In current understanding, particles are excitations of quantum fields and interact following their dynamics...
designed to challenge the Standard Model
Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, which mediate the dynamics of the known subatomic particles. Developed throughout the mid to late 20th century, the current formulation was finalized in the mid 1970s upon...
explanation of CP violation
CP violation
In particle physics, CP violation is a violation of the postulated CP-symmetry: the combination of C-symmetry and P-symmetry . CP-symmetry states that the laws of physics should be the same if a particle were interchanged with its antiparticle , and left and right were swapped...
, mixing
Mixing (physics)
In physics, a dynamical system is said to be mixing if the phase space of the system becomes strongly intertwined, according to at least one of several mathematical definitions. For example, a measure-preserving transformation T is said to be strong mixing ifwhenever A and B are any measurable...
and rare decays of bottom
Bottom quark
The bottom quark, also known as the beauty quark, is a third-generation quark with a charge of − e. Although all quarks are described in a similar way by the quantum chromodynamics, the bottom quark's large bare mass , combined with low values of the CKM matrix elements Vub and Vcb, gives it a...
and charm
Charm quark
The charm quark or c quark is the third most massive of all quarks, a type of elementary particle. Charm quarks are found in hadrons, which are subatomic particles made of quarks...
quark
Quark
A quark is an elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. Due to a phenomenon known as color confinement, quarks are never directly...
states. The Standard Model has been the baseline particle physics
Particle physics
Particle physics is a branch of physics that studies the existence and interactions of particles that are the constituents of what is usually referred to as matter or radiation. In current understanding, particles are excitations of quantum fields and interact following their dynamics...
theory for several decades and BTeV aimed to find out what lies beyond the Standard Model. In doing so, the BTeV results could have contributed to shed light on phenomena associated with the early universe
Universe
The Universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists, including all matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. Definitions and usage vary and similar terms include the cosmos, the world and nature...
such as why the universe is made up of matter
Matter
Matter is a general term for the substance of which all physical objects consist. Typically, matter includes atoms and other particles which have mass. A common way of defining matter is as anything that has mass and occupies volume...
and not anti-matter.
The BTeV Collaboration was a group of about 170 physicist
Physicist
A physicist is a scientist who studies or practices physics. Physicists study a wide range of physical phenomena in many branches of physics spanning all length scales: from sub-atomic particles of which all ordinary matter is made to the behavior of the material Universe as a whole...
s drawn from more than 30 universities and physics institutes from Belarus, Canada, China, Italy, Russia, and the United States of America. The BTeV experiment was designed to utilize the Tevatron
Tevatron
The Tevatron is a circular particle accelerator in the United States, at the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory , just east of Batavia, Illinois, and is the second highest energy particle collider in the world after the Large Hadron Collider...
proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
-antiproton
Antiproton
The antiproton is the antiparticle of the proton. Antiprotons are stable, but they are typically short-lived since any collision with a proton will cause both particles to be annihilated in a burst of energy....
collider at the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory
Fermilab
Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory , located just outside Batavia, Illinois, near Chicago, is a US Department of Energy national laboratory specializing in high-energy particle physics...
, located in the far west suburbs of Chicago, Illinois in the USA. The experiment was scheduled to start in 2006, followed by commissioning in 2008, and data-taking in 2009.
The BTeV Project was terminated by the United States Department of Energy
United States Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy is a Cabinet-level department of the United States government concerned with the United States' policies regarding energy and safety in handling nuclear material...
on 2005-02-07 after being removed from the President's Budget for the 2006 fiscal year.

