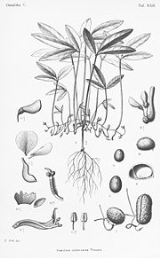
Bambara groundnut
Encyclopedia
The Bambara groundnut is a member of the family Fabaceae
. According to some authors it is Voandzeia subterranea, but others place it in Vigna
. The plant originated in West Africa
. Still a traditional food plant in Africa
, this little-known vegetable has potential to improve nutrition, boost food security, foster rural development and support sustainable landcare.
The bambara groundnut ripens its pods underground, much like the peanut
(also called a groundnut). They can be eaten fresh or boiled after drying.
The original local name for Bambara nut is cokon (Bamanankan). Bambara groundnuts are also known as jugo beans or in Swahili
, njugumawe. In the Republic of Zambia
, bambara groundnuts are known as either ntoyo (ciBemba
),katoyo (kiKaonde), or mbwiila (chiTonga
). In Shangaan
they are known as tindluwa. In Malagasy
they are known as voanjobory. In Hausa language it is variously referred to as "Gurjiya" or "Kwaruru". In Goemai language of Plateau State of Northern Nigeria it is known as "Kwam", and Kanuri people refer to it as "Ngamgala". In Indonesia it is called "kacang bogor", which literally means "Bogor peanut", because this plant is widely cultured in Bogor, West Java
. In the Shona language of Zimbabwe it is known as "Nyimo", and "indlubu" in the ndebele language. In the Ibo language in eastern Nigeria, it is commonly known as "Okpa". In the Northern part of Yoruba, it is commonly known as "Epa-kuta", and in the Gha Language, spoken by the people in Greater Accra, Ghana, the Bambara Bean is called "Akwei".


) and the subtropical dry summer (Cs
) climate zones. Optimal temperature is between 19°C and 30°C. Temperatures below 16°C and above 38°C are not suited for the production of bambara groundnut. The bambara groundnut is very drought resistant. The minimal annual rainfall requirement is about 300 mm and optimal annual rainfall is between 750 mm and 1400 mm and should not exceed 3000 mm.
. Best suited intercrops are sorghum, millet, maize, groundnut, yams and cassava.
Bambara groundnut is mainly cultivated as intercrop
, however the planting density varies between 6 to 29 plants per square meter. For woodland savannas of Côte d'Ivoire the highest yield is attainable with a plant density of 25 plants per square meter.
, no fertilizer is applied. A yield of 1000 kg seed and 925 kg leaves remove 55.7 kg N, 26.2 kg K, 25.1 kg C, 7.8 kg P and 6.6 kg Mg.
Since Bambara groundnut is a legume, phosphor is the most important nutrient. An application rate of 60 kg/ha of P2O5 is recommended for bambara groundnut in Yola, Adamawa State Nigeria.
Reported diseases:
Reported pests:
).
{Bambara nut: Originated yoruba name is Epa-kuta and it has a various way of praparation as food}
Fabaceae
The Fabaceae or Leguminosae, commonly known as the legume, pea, or bean family, is a large and economically important family of flowering plants. The group is the third largest land plant family, behind only the Orchidaceae and Asteraceae, with 730 genera and over 19,400 species...
. According to some authors it is Voandzeia subterranea, but others place it in Vigna
Vigna
The genus Vigna is in the plant family Fabaceae. The genus is named after Domenico Vigna, an Italian botanist of the 17th century. They include some well-known and other less well-known beans formerly — and sometimes still, especially in non-scholarly sources — included in the genus Phaseolus...
. The plant originated in West Africa
West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of the African continent. Geopolitically, the UN definition of Western Africa includes the following 16 countries and an area of approximately 5 million square km:-Flags of West Africa:...
. Still a traditional food plant in Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
, this little-known vegetable has potential to improve nutrition, boost food security, foster rural development and support sustainable landcare.
The bambara groundnut ripens its pods underground, much like the peanut
Peanut
The peanut, or groundnut , is a species in the legume or "bean" family , so it is not a nut. The peanut was probably first cultivated in the valleys of Peru. It is an annual herbaceous plant growing tall...
(also called a groundnut). They can be eaten fresh or boiled after drying.
The original local name for Bambara nut is cokon (Bamanankan). Bambara groundnuts are also known as jugo beans or in Swahili
Swahili language
Swahili or Kiswahili is a Bantu language spoken by various ethnic groups that inhabit several large stretches of the Mozambique Channel coastline from northern Kenya to northern Mozambique, including the Comoro Islands. It is also spoken by ethnic minority groups in Somalia...
, njugumawe. In the Republic of Zambia
Zambia
Zambia , officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. The neighbouring countries are the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Tanzania to the north-east, Malawi to the east, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana and Namibia to the south, and Angola to the west....
, bambara groundnuts are known as either ntoyo (ciBemba
Bemba language
The Bemba language, ChiBemba , is a major Bantu language spoken primarily in north-eastern Zambia by the Bemba people and as a lingua franca by about 18 related ethnic groups, including the Bisa people of Mpika and Lake Bangweulu, and to a lesser extent in Katanga in the Democratic Republic of the...
),katoyo (kiKaonde), or mbwiila (chiTonga
Tonga language
Tonga refers to four different languages:*Tonga language – a Bantu language spoken in Zambia and Zimbabwe*Tonga language – a Bantu language spoken in Malawi...
). In Shangaan
Shangaan
The Tsonga people inhabit the southern coastal plain of Mozambique, parts of Zimbabwe and Swaziland, and the Limpopo Province of South Africa...
they are known as tindluwa. In Malagasy
Malagasy language
Malagasy is the national language of Madagascar, a member of the Austronesian family of languages. Most people in Madagascar speak it as a first language as do some people of Malagasy descent elsewhere.-History:...
they are known as voanjobory. In Hausa language it is variously referred to as "Gurjiya" or "Kwaruru". In Goemai language of Plateau State of Northern Nigeria it is known as "Kwam", and Kanuri people refer to it as "Ngamgala". In Indonesia it is called "kacang bogor", which literally means "Bogor peanut", because this plant is widely cultured in Bogor, West Java
Bogor
Bogor is a city on the island of Java in the West Java province of Indonesia. The city is located in the center of the Bogor Regency , 60 kilometers south of the Indonesian capital Jakarta...
. In the Shona language of Zimbabwe it is known as "Nyimo", and "indlubu" in the ndebele language. In the Ibo language in eastern Nigeria, it is commonly known as "Okpa". In the Northern part of Yoruba, it is commonly known as "Epa-kuta", and in the Gha Language, spoken by the people in Greater Accra, Ghana, the Bambara Bean is called "Akwei".
Agronomic aspects


Origin and regions of cultivation
The origin of the Bambara groundnut is West Africa and the region of cultivation is Sub-Saharan Africa's warm tropics.Importance in the World Food System
Bambara groundnut represents the third most important grain legume in semi-arid Africa. “It is resistant to high temperature and is suitable for marginal soils where other leguminous crops cannot be grown”. In addition, it makes very little demand on the soil and has a high nutritive value with 65% carbohydrate and 18% protein content. For these reasons it is not prone to the risk of total harvest failure even in low and uncertain rainfall regions. "Due to its high protein value it is a very important crop for poorer people in Africa who cannot afford expensive animal protein."Product use
The seeds are used for food and beverage due to its high protein content and for digestive system applications. The entire plant is known for soil improvement due to nitrogen fixation.Soil requirements
Optimal soils for Bambara groundnut production are sandy soils to prevent water lodging. optimal soil depth is between 50 and 100 cm, with a light soil texture. soil fertility should be low and soil pH is best suited between 5 and 6.5 and should not by lower than 4.3 or higher than 7.Climate requirements
The production is best suited between a latitude of 20° - 30°, i.e. the tropical wet and dry (AwKöppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by Crimea German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen himself, notably in 1918 and 1936...
) and the subtropical dry summer (Cs
Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by Crimea German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen himself, notably in 1918 and 1936...
) climate zones. Optimal temperature is between 19°C and 30°C. Temperatures below 16°C and above 38°C are not suited for the production of bambara groundnut. The bambara groundnut is very drought resistant. The minimal annual rainfall requirement is about 300 mm and optimal annual rainfall is between 750 mm and 1400 mm and should not exceed 3000 mm.
Cropping system
The cropping system is semi-permanent and the Bambara groundnut can be cultivated as single crop or as intercropIntercropping
Intercropping is the practice of growing two or more crops in proximity. The most common goal of intercropping is to produce a greater yield on a given piece of land by making use of resources that would otherwise not be utilized by a single crop. Careful planning is required, taking into account...
. Best suited intercrops are sorghum, millet, maize, groundnut, yams and cassava.
Bambara groundnut is mainly cultivated as intercrop
Intercropping
Intercropping is the practice of growing two or more crops in proximity. The most common goal of intercropping is to produce a greater yield on a given piece of land by making use of resources that would otherwise not be utilized by a single crop. Careful planning is required, taking into account...
, however the planting density varies between 6 to 29 plants per square meter. For woodland savannas of Côte d'Ivoire the highest yield is attainable with a plant density of 25 plants per square meter.
Fertilization
Since Bamabara groundnut is usually intercroppedIntercropping
Intercropping is the practice of growing two or more crops in proximity. The most common goal of intercropping is to produce a greater yield on a given piece of land by making use of resources that would otherwise not be utilized by a single crop. Careful planning is required, taking into account...
, no fertilizer is applied. A yield of 1000 kg seed and 925 kg leaves remove 55.7 kg N, 26.2 kg K, 25.1 kg C, 7.8 kg P and 6.6 kg Mg.
Since Bambara groundnut is a legume, phosphor is the most important nutrient. An application rate of 60 kg/ha of P2O5 is recommended for bambara groundnut in Yola, Adamawa State Nigeria.
Production
World production of Bambara groundnut increased from 29'600 tonnes in 1961 to 79'160 tonnes in 2008, while the yield during this period did not increase. "As an under-utilised crop,bambara groundnut has not received sustained research" until the recent years and therefor no yield increase occurred.| Production Year 2008 (Source FAOSTAT) | Area Harvested (Ha) | Yield (kg/ha) | Production (tonnes) |
|---|---|---|---|
 Burkina Faso Burkina Faso |
44'000 | 864 | 38'000 |
 Cameroon Cameroon |
12'000 | 833 | 10'000 |
 Democratic Republic of the Congo Democratic Republic of the Congo |
23'000 | 442 | 10'160 |
 Mali Mali |
28'000 | 750 | 21'000 |
| World | 107'000 | 740 | 79'160 |
Pest & Diseases
Pest and diseases are not considered to be a serious problem for Bambara groundnut.Reported diseases:
- Leaf spot (Cerscospora canescens & Phyllosticta voandzeia)
- Powdery mildew (Erysiphe sp.)
- Wilt (Fusarium sp.)
- Leaf blotch (Phomopsis sp.)
- Stem rot (Scleorotium rolfsii)
Reported pests:
- AphidAphidAphids, also known as plant lice and in Britain and the Commonwealth as greenflies, blackflies or whiteflies, are small sap sucking insects, and members of the superfamily Aphidoidea. Aphids are among the most destructive insect pests on cultivated plants in temperate regions...
s (Aphis sp.) - Bruchids (Callosobruchus sp.)
- Leaf hoppers (Hilda patruelis)
- Termites
- Root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne javanica)
Growth
The growth cycle is between (min-max) 90–180 days and under optimal conditions the cycle is about 120–150 days to pod maturity. Flowers appear 40–60 days after planting. 30 days after pollination the pod reaches maturity and during another 10 days the seeds fully develop.Generative reproduction
Generative reproduction is for the Bambara groundnut autogamous (self-fertilization) and cleistogamous (self-pollinatingCleistogamy
Cleistogamy or automatic self-pollination describes the trait of certain plants to propagate by using non-opening, self-pollinating flowers...
).
External links
- Bambara Groundnut -- Voandzeia subterranea (L.) Thouars
- Bambara Groundnut ... a Link from the Past and Resource for the Future
{Bambara nut: Originated yoruba name is Epa-kuta and it has a various way of praparation as food}

