
Bathymetry
Encyclopedia
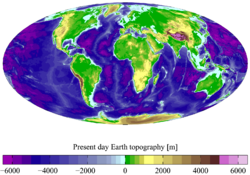
Hypsometry
Hypsometry is the measurement of land elevation relative to sea level. Bathymetry is the underwater equivalent...
. The name comes from Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
βαθύς (bathus), "deep", and μέτρον (metron), "measure". Bathymetric (or hydrographic
Hydrography
Hydrography is the measurement of the depths, the tides and currents of a body of water and establishment of the sea, river or lake bed topography and morphology. Normally and historically for the purpose of charting a body of water for the safe navigation of shipping...
) charts are typically produced to support safety of surface or sub-surface navigation, and usually show seafloor relief or terrain
Terrain
Terrain, or land relief, is the vertical and horizontal dimension of land surface. When relief is described underwater, the term bathymetry is used...
as contour lines (called depth contours or isobaths) and selected depths (soundings), and typically also provide surface navigation
Navigation
Navigation is the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another. It is also the term of art used for the specialized knowledge used by navigators to perform navigation tasks...
al information. Bathymetric maps (a more general term where navigation
Navigation
Navigation is the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another. It is also the term of art used for the specialized knowledge used by navigators to perform navigation tasks...
al safety is not a concern) may also use a Digital Terrain Model and artificial illumination techniques to illustrate the depths being portrayed. Paleobathymetry is the study of past underwater depths.
Measurement
Originally, bathymetry involved the measurement of oceanOcean
An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas.More than half of this area is over 3,000...
depth through depth sounding
Depth Sounding
Depth sounding refers to a historical nautical term for measuring depth; it is often referred to simply as sounding. Sounding is finding the depth of a given point in a body of water. Sounding data is used in bathymetry to make maps of the floor of a body of water. Soundings were traditionally...
. Early techniques used pre-measured heavy rope
Rope
A rope is a length of fibres, twisted or braided together to improve strength for pulling and connecting. It has tensile strength but is too flexible to provide compressive strength...
or cable lowered over a ship's side.This technique measures the depth only a single point at a time, and so is inefficient. It is also subject to movements of the ship and currents moving the line out of true and therefore is inaccurate.
The data used to make bathymetric maps today typically comes from an echosounder (sonar
Sonar
Sonar is a technique that uses sound propagation to navigate, communicate with or detect other vessels...
) mounted beneath or over the side of a boat, "pinging" a beam of sound downward at the seafloor or from remote sensing LIDAR
LIDAR
LIDAR is an optical remote sensing technology that can measure the distance to, or other properties of a target by illuminating the target with light, often using pulses from a laser...
or LADAR systems. The amount of time it takes for the sound or light to travel through the water, bounce off the seafloor, and return to the sounder tells the equipment what the distance to the seafloor is. LIDAR/LADAR surveys are usually conducted by airborne systems.

Swath width
Swath width refers to the strip of the Earth’s surface from which data are collected by a satellite. The longitudinal extent of the swath is defined by the motion of the satellite with respect to the surface, whereas the swath width is measured perpendicularly to the longitudinal extent of the...
of typically 90 to 170 degrees across. The tightly packed array of narrow individual beams provides very high angular resolution
Angular resolution
Angular resolution, or spatial resolution, describes the ability of any image-forming device such as an optical or radio telescope, a microscope, a camera, or an eye, to distinguish small details of an object...
and accuracy. In general a wide swath, which is depth dependent, allows a boat to map more seafloor in less time than a single-beam echosounder by making fewer passes. The beams update many times per second (typically 0.1-50 Hz
Hertz
The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
depending on water depth), allowing faster boat speed while maintaining 100% coverage of the seafloor. Attitude sensors allow for the correction of the boat's roll, pitch and yaw
Flight dynamics
Flight dynamics is the science of air vehicle orientation and control in three dimensions. The three critical flight dynamics parameters are the angles of rotation in three dimensions about the vehicle's center of mass, known as pitch, roll and yaw .Aerospace engineers develop control systems for...
on the ocean surface, and a gyrocompass provides accurate heading information to correct for vessel yaw. (Most modern MBES systems use an integrated motion-sensor and position system that measures yaw as well as the other dynamics and position.) The Global Positioning System
Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System is a space-based global navigation satellite system that provides location and time information in all weather, anywhere on or near the Earth, where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites...
(or other Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)) positions the soundings with respect to the surface of the earth. Sound speed profiles (speed of sound in water as a function of depth) of the water column correct for refraction or "ray-bending" of the sound waves owing to non-uniform water column characteristics such as temperature, conductivity, and pressure. A computer system processes all the data, correcting for all of the above factors as well as for the angle of each individual beam. The resulting sounding measurements are then processed either manually, semi-automatically or automatically (in limited circumstances) to produce a map of the area. a number of different outputs are generated, including a sub-set of the original measurements that satisfy some conditions (e.g., most representative likely soundings, shallowest in a region, etc.) or integrated Digital Terrain Models (DTM) (e.g., a regular or irregular grid of points connected into a surface). Historically, selection of measurements was more common in hydrographic
Hydrography
Hydrography is the measurement of the depths, the tides and currents of a body of water and establishment of the sea, river or lake bed topography and morphology. Normally and historically for the purpose of charting a body of water for the safe navigation of shipping...
applications while DTM construction was used for engineering surveys, geology, flow modeling, etc. Since ca. 2003-2005, DTMs have become more accepted in hydrographic practice.
Satellites are also used to measure bathymetry. Satellite radar maps deep-sea topography by detecting the subtle variations in sea level caused by the gravitational pull of undersea mountains, ridges, and other masses. On average, sea level is higher over mountains and ridges than over abyssal plains and trenches.
In the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
the United States Army Corps of Engineers
United States Army Corps of Engineers
The United States Army Corps of Engineers is a federal agency and a major Army command made up of some 38,000 civilian and military personnel, making it the world's largest public engineering, design and construction management agency...
performs or commissions most surveys of navigable inland waterways, while the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration , pronounced , like "noah", is a scientific agency within the United States Department of Commerce focused on the conditions of the oceans and the atmosphere...
(NOAA) performs the same role for ocean waterways. Coastal bathymetry data is available from NOAA's
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration , pronounced , like "noah", is a scientific agency within the United States Department of Commerce focused on the conditions of the oceans and the atmosphere...
National Geophysical Data Center (NGDC). Bathymetric data is usually referenced to tidal vertical datums. For deep-water bathymetry, this is typically Mean Sea Level (MSL), but most data used for nautical charting is referenced to Mean Lower Low Water (MLLW) in American surveys, and Lowest Astronomical Tide (LAT) in other countries. Many other datums are used in practice, depending on the locality and tidal regime.
Occupations or careers related to bathymetry include the study of oceans and rocks and minerals on the ocean floor, and the study of underwater earthquakes or volcanoes. The taking and analysis of bathymetric measurements is one of the core areas of modern hydrography
Hydrography
Hydrography is the measurement of the depths, the tides and currents of a body of water and establishment of the sea, river or lake bed topography and morphology. Normally and historically for the purpose of charting a body of water for the safe navigation of shipping...
, and a fundamental component in ensuring the safe transport of goods worldwide.
See also
- Bathymetric chart
- General Bathymetric Chart of the OceansGeneral Bathymetric Chart of the OceansThe General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans is a publicly available bathymetry of the world's oceans. The project was conceived with the aim of preparing a global series of charts showing the general shape of the seafloor...
- BathometerBathometerBathometer is an instrument by which is measured water depth. It is usually used in oceanographical measurements, although now it is rarely used....
- TerrainTerrainTerrain, or land relief, is the vertical and horizontal dimension of land surface. When relief is described underwater, the term bathymetry is used...

