Battle of Big Black River Bridge
Encyclopedia
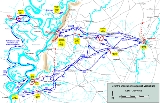
The Battle of Big Black River Bridge, or Big Black, fought May 17, 1863, was part of the Vicksburg Campaign
of the American Civil War
. Union
commander Maj. Gen.
Ulysses S. Grant
and the Army of the Tennessee
pursued the retreating Confederate
Lt. Gen. John C. Pemberton
following the Battle of Champion Hill
, in the final battle before the Siege of Vicksburg.
, with three brigades, to man the fortifications on the east bank of the river and impede any Union pursuit.
) on the morning of May 17. The corps encountered the Confederates behind breastworks of cotton bales fronted by a bayou and abatis
. They took cover as enemy artillery began firing. Union Brig. Gen.
Michael K. Lawler formed his 2nd Brigade, Eugene A. Carr's 14th Division, which surged out of a meander scar, across the front of the Confederate forces, through waist-deep water, and into the enemy's breastworks, held by Brig. Gen. John C. Vaughn
's East Tennessee Brigade.
Confused and panicked, the Rebels began to withdraw across the Big Black River on two bridges: the railroad bridge and the steamboat Dot, used as a bridge across the river. As soon as they had crossed, the Confederates set fire to the bridges, preventing close Union pursuit. The fleeing Confederates who arrived in Vicksburg later that day were disorganized.
Vicksburg Campaign
The Vicksburg Campaign was a series of maneuvers and battles in the Western Theater of the American Civil War directed against Vicksburg, Mississippi, a fortress city that dominated the last Confederate-controlled section of the Mississippi River. The Union Army of the Tennessee under Maj. Gen....
of the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
. Union
Union Army
The Union Army was the land force that fought for the Union during the American Civil War. It was also known as the Federal Army, the U.S. Army, the Northern Army and the National Army...
commander Maj. Gen.
Major general (United States)
In the United States Army, United States Marine Corps, and United States Air Force, major general is a two-star general-officer rank, with the pay grade of O-8. Major general ranks above brigadier general and below lieutenant general...
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant was the 18th President of the United States as well as military commander during the Civil War and post-war Reconstruction periods. Under Grant's command, the Union Army defeated the Confederate military and ended the Confederate States of America...
and the Army of the Tennessee
Army of the Tennessee
The Army of the Tennessee was a Union army in the Western Theater of the American Civil War, named for the Tennessee River. It should not be confused with the similarly named Army of Tennessee, a Confederate army named after the State of Tennessee....
pursued the retreating Confederate
Confederate States Army
The Confederate States Army was the army of the Confederate States of America while the Confederacy existed during the American Civil War. On February 8, 1861, delegates from the seven Deep South states which had already declared their secession from the United States of America adopted the...
Lt. Gen. John C. Pemberton
John C. Pemberton
John Clifford Pemberton , was a career United States Army officer who fought in the Seminole Wars and with distinction during the Mexican–American War. He also served as a Confederate general during the American Civil War, noted for his defeat and surrender in the critical Siege of Vicksburg in...
following the Battle of Champion Hill
Battle of Champion Hill
The Battle of Champion Hill, or Bakers Creek, fought May 16, 1863, was the pivotal battle in the Vicksburg Campaign of the American Civil War. Union commander Maj. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant and the Army of the Tennessee pursued the retreating Confederate Lt. Gen. John C...
, in the final battle before the Siege of Vicksburg.
Background
Reeling from their defeat at Champion Hill, the Confederates reached Big Black River Bridge, the night of May 16–17. Pemberton ordered Brig. Gen. John S. BowenJohn S. Bowen
John Stevens Bowen was a career United States Army officer and a general in the Confederate States Army, a commander in the Western Theater of the American Civil War. He is often said to have died just as his abilities were gaining attention.-Early life:Bowen was born in Bowen's Creek, Georgia...
, with three brigades, to man the fortifications on the east bank of the river and impede any Union pursuit.
Battle
Three divisions of Maj. Gen. John A. McClernand's XIII Corps moved out from Edwards Station (now the town of Edwards, MississippiEdwards, Mississippi
Edwards is a town in Hinds County, Mississippi, United States. The population was 1,347 at the 2000 census. It is part of the Jackson Metropolitan Statistical Area.-History:...
) on the morning of May 17. The corps encountered the Confederates behind breastworks of cotton bales fronted by a bayou and abatis
Abatis
Abatis, abattis, or abbattis is a term in field fortification for an obstacle formed of the branches of trees laid in a row, with the sharpened tops directed outwards, towards the enemy. The trees are usually interlaced or tied with wire...
. They took cover as enemy artillery began firing. Union Brig. Gen.
Brigadier general (United States)
A brigadier general in the United States Army, Air Force, and Marine Corps, is a one-star general officer, with the pay grade of O-7. Brigadier general ranks above a colonel and below major general. Brigadier general is equivalent to the rank of rear admiral in the other uniformed...
Michael K. Lawler formed his 2nd Brigade, Eugene A. Carr's 14th Division, which surged out of a meander scar, across the front of the Confederate forces, through waist-deep water, and into the enemy's breastworks, held by Brig. Gen. John C. Vaughn
John C. Vaughn
John C. Vaughn was a Confederate cavalry officer from East Tennessee.He served in the Mexican-American War, prospected in the California Gold Rush, and participated in American Civil War battles...
's East Tennessee Brigade.
Confused and panicked, the Rebels began to withdraw across the Big Black River on two bridges: the railroad bridge and the steamboat Dot, used as a bridge across the river. As soon as they had crossed, the Confederates set fire to the bridges, preventing close Union pursuit. The fleeing Confederates who arrived in Vicksburg later that day were disorganized.
Aftermath
The Union forces captured approximately 1,700 troops at Big Black and many drowned, a loss that the Confederates could ill-afford. Fewer than half of the Confederates who had fought at Champion Hill made it into the defenses at Vicksburg. This battle sealed Vicksburg's fate: the Confederate force was bottled up at Vicksburg.Further reading
- Ballard, Michael B. Vicksburg, The Campaign that Opened the Mississippi. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 2004. ISBN 0-8078-2893-9.
- Bearss, Edwin C.Ed BearssEdwin Cole Bearss , a United States Marine Corps veteran of World War II, is a military historian and author known for his work on the American Civil War and World War II eras and is a popular tour guide of historic battlefields...
The Campaign for Vicksburg. Vol. 2, Grant Strikes a Fatal Blow. Dayton, OH: Morningside House, 1986. ISBN 0-89029-313-9. - Fullenkamp, Leonard, Stephen Bowman, and Jay Luvaas. Guide to the Vicksburg Campaign. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas, 1998. ISBN 0-7006-0922-9.
- Grabau, Warren E. Ninety-Eighty Days: A Geographer's View of the Vicksburg Campaign. Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2000. ISBN 1-57233-068-6.
- Korn, Jerry, and the Editors of Time-Life Books. War on the Mississippi: Grant's Vicksburg Campaign. Alexandria, VA: Time-Life Books, 1985. ISBN 0-8094-4744-4.
- Winschel, Terrence J. Triumph & Defeat: The Vicksburg Campaign. Campbell, CA: Savas Publishing Company, 1999. ISBN 1-882810-31-7.
- Woodworth, Steven E., ed. Grant's Lieutenants: From Cairo to Vicksburg. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas, 2001. ISBN 0-7006-1127-4.
- CWSAC Report Update

