Battle of the Sun
Encyclopedia
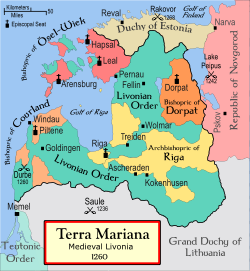
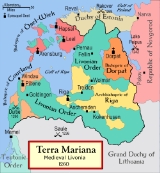
Livonian Brothers of the Sword
The Livonian Brothers of the Sword were a military order founded by Bishop Albert of Riga in 1202. Pope Innocent III sanctioned the establishment in 1204. The membership of the order comprised German "warrior monks"...
and pagan Samogitians
Samogitians
Samogitians are a part of the Lithuanian ethnicity inhabiting the region of Samogitia in Lithuania. Many speak the Samogitian dialect of the Lithuanian language.-History:...
. Between 48 and 60 knights were killed, including the Livonian Master, Volkwin. It was the earliest large-scale defeat suffered by the orders in Baltic lands. The Sword-Brothers, the first Catholic military order
Military order
A military order is a Christian society of knights that was founded for crusading, i.e. propagating or defending the faith , either in the Holy Land or against Islam or pagans in Europe...
established in the Baltic lands
Balts
The Balts or Baltic peoples , defined as speakers of one of the Baltic languages, a branch of the Indo-European language family, are descended from a group of Indo-European tribes who settled the area between the Jutland peninsula in the west and Moscow, Oka and Volga rivers basins in the east...
, was soundly defeated and its remnants accepted incorporation into the Teutonic Order in 1237. The battle inspired rebellions among the Curonians
Curonians
The Curonians or Kurs were a Baltic tribe living on the shores of the Baltic sea in what are now the western parts of Latvia and Lithuania from the 5th to the 16th centuries, when they merged with other Baltic tribes. They gave their name to the region of Courland , and they spoke the Old...
, Semigallians
Semigallians
Semigallians were the Baltic tribe that lived in the southcentral part of contemporary Latvia and northern Lithuania...
, Selonians
Selonians
Selonians were a tribe of Baltic peoples. The Selonians lived until the 15th century in Selonia, located in southeastern Latvia and northeastern Lithuania. They merged with neighbouring tribes, contributing to the ethnogenesis of Latvians and Lithuanians....
, Oeselians
Oeselians
The Oeselians were a historical Finnic people inhabiting Saaremaa , an Estonian island in the Baltic Sea. They are first thought to be mentioned as early as the 2nd century BC in Ptolemy's Geography III. The Oeselians along with Curonians were known in the Old Norse Icelandic Sagas and in...
, tribes previously conquered by the Sword-Brothers. Some thirty years' worth of conquests on the left bank of Daugava were lost. To commemorate the battle, in 2000 Lithuanian
Seimas
The Seimas is the unicameral Lithuanian parliament. It has 141 members that are elected for a four-year term. About half of the members of this legislative body are elected in individual constituencies , and the other half are elected by nationwide vote according to proportional representation...
and Latvian parliaments
Saeima
Saeima is the parliament of the Republic of Latvia. It is a unicameral parliament consisting of 100 members who are elected by proportional representation, with seats allocated to political parties which gain at least 5% of the popular vote. Elections are scheduled to be held once every four years,...
declared September 22 as the Day of Baltic Unity.
Background
The Sword-Brothers were established in 1202 in RigaRiga
Riga is the capital and largest city of Latvia. With 702,891 inhabitants Riga is the largest city of the Baltic states, one of the largest cities in Northern Europe and home to more than one third of Latvia's population. The city is an important seaport and a major industrial, commercial,...
to conquer and convert pagan Baltic tribes to Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
. By the 1230s under the leadership of Master Volkwin, the Order was coping with strained financial resources, decreasing manpower, and ill reputation. The Order was in conflict with the papacy under Pope Gregory IX
Pope Gregory IX
Pope Gregory IX, born Ugolino di Conti, was pope from March 19, 1227 to August 22, 1241.The successor of Pope Honorius III , he fully inherited the traditions of Pope Gregory VII and of his uncle Pope Innocent III , and zealously continued their policy of Papal supremacy.-Early life:Ugolino was...
and the Holy Roman Emperor
Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor is a term used by historians to denote a medieval ruler who, as German King, had also received the title of "Emperor of the Romans" from the Pope...
, two of its biggest supporters, over Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
. However, on February 19, 1236, Pope Gregory IX issued a papal bull
Papal bull
A Papal bull is a particular type of letters patent or charter issued by a Pope of the Catholic Church. It is named after the bulla that was appended to the end in order to authenticate it....
declaring a crusade against Lithuania. He targeted Samogitia
Samogitia
Samogitia is one of the five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. It is located in northwestern Lithuania. Its largest city is Šiauliai/Šiaulē. The region has a long and distinct cultural history, reflected in the existence of the Samogitian dialect...
, planning to conquer the coast of the Baltic Sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
and connect with the Teutonic Knights
Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem , commonly the Teutonic Order , is a German medieval military order, in modern times a purely religious Catholic order...
in Prussia. The Sword-Brothers wanted to keep expanding along the Daugava River and was somewhat reluctant to march against Samogitia. In fall of 1236 a party of crusaders arrived from Holstein
Holstein
Holstein is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider. It is part of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost state of Germany....
; it demanded to be led into a battle. Volkwin gathered a large war party, which included troops from Pskov Republic
Pskov Republic
Pskov, known at various times as the Principality of Pskov or the Pskov Republic , was a medieval state on the south shore of Lake Pskov. The capital city, also named Pskov, was located at the southern end of the Peipus–Pskov Lake system at the southeast corner of Ugandi, about southwest of...
, Livonians, Latgallians, Estonians
Estonians
Estonians are a Finnic people closely related to the Finns and inhabiting, primarily, the country of Estonia. They speak a Finnic language known as Estonian...
.
Events of the battle
The knights marched southward into Samogitia, raiding and plundering local settlements. The locals had only a few days to gather troops for defense. On the knights' northward return, however, they encountered a determined group of Samogitians at a river crossing. Unwilling to risk losing their horses in the swampland, the Holsteiners refused to fight on foot, forcing the knights to camp for the night. The next morning, on the day of Saint MauriceSaint Maurice
Saint Maurice was the leader of the legendary Roman Theban Legion in the 3rd century, and one of the favorite and most widely venerated saints of that group. He was the patron saint of several professions, locales, and kingdoms...
, the main pagan forces, likely led by Duke Vykintas
Vykintas
thumb|200 px|Monument to Duke Vykintas in TveraiVykintas was Duke of Samogitia and rival to future King of Lithuania Mindaugas. In 1236 he probably led Samogitian forces in the Battle of Saule against the Livonian Order...
, arrived at the camp. The Lithuanian light cavalry flung javelins at short range, which were highly effective against the unwieldy Livonian heavy cavalry. The swampy terrain was advantageous for lightly armed pagans. The slaughter of the Christian troops, including Volkwin, sowed the seeds of confusion in the Livonian ranks. The lightly armed native forces under the command of the Brothers soon fled from the battle. Those crusaders and knights who tried to flee to Riga were allegedly killed by the Semigallians
Semigallians
Semigallians were the Baltic tribe that lived in the southcentral part of contemporary Latvia and northern Lithuania...
.
Location
The exact location where the battle took place is unknown. The Chronicum Livoniae by Hermann de Wartberge mentioned that the battle was fought in terram Sauleorum. Traditionally, this was identified with ŠiauliaiŠiauliai
Šiauliai , is the fourth largest city in Lithuania, with a population of 133,900. It is the capital of Šiauliai County. Unofficially, the city is the capital of Northern Lithuania.-Names:...
in Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
or with the small town of Vecsaule near Bauska
Bauska
Bauska is a town in Bauska municipality, in the Zemgale region of southern Latvia. The town is situated at the confluence of the rivers Mūsa and Mēmele where they form the Lielupe River...
in what is today southern Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
. In 1965 the German historian Friedrich Benninghoven proposed Jauniūnai village in Joniškis district, Lithuania as the battle site. The theory gained some academic support and in 2010 the Lithuanian government sponsored construction of the memorial in Jauniūnai – a 29 metres (95.1 ft) tall sundial
Sundial
A sundial is a device that measures time by the position of the Sun. In common designs such as the horizontal sundial, the sun casts a shadow from its style onto a surface marked with lines indicating the hours of the day. The style is the time-telling edge of the gnomon, often a thin rod or a...
, a pond, and a park of oaks. The village of Pamūšis, situated some 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) east of Janiūnai on the Mūša River
Muşa River
The Muşa River is a tributary of the Bâsca Mică River in Romania.-References:* Administraţia Naţională Apelor Române - Cadastrul Apelor - Bucureşti* Institutul de Meteorologie şi Hidrologie - Rîurile României - Bucureşti 1971...
, also claims to be the location of the battle. Saule/Saulė means "the Sun" in both Latvian and Lithuanian.

