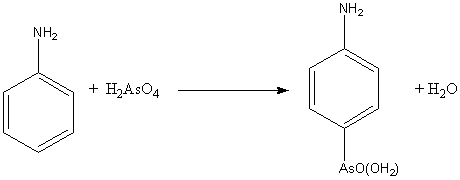
Bechamp reaction
Encyclopedia
In organic synthesis
, the Bechamp reaction is used for producing arsonic acids from activated aromatic rings such as aniline
. It was first described by A. J. Bechamp in 1863. The reaction is an electrophilic aromatic substitution
, using arsenic acid
as a reactant.
One example of an important arsonic acid is roxarsone. This is 4-hydroxy-3-nitrobenzenearsonic acid. It exhibits an anticoccidial action and promotes growth in animals.
Organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the construction of organic compounds via organic reactions. Organic molecules can often contain a higher level of complexity compared to purely inorganic compounds, so the synthesis of organic compounds has...
, the Bechamp reaction is used for producing arsonic acids from activated aromatic rings such as aniline
Aniline
Aniline, phenylamine or aminobenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H5NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the prototypical aromatic amine. Being a precursor to many industrial chemicals, its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane...
. It was first described by A. J. Bechamp in 1863. The reaction is an electrophilic aromatic substitution
Electrophilic aromatic substitution
Electrophilic aromatic substitution EAS is an organic reaction in which an atom, usually hydrogen, appended to an aromatic system is replaced by an electrophile...
, using arsenic acid
Arsenic acid
Arsenic acid is the chemical compound with the formula H3AsO4. More descriptively written as AsO3, this colorless acid is the arsenic analogue of phosphoric acid. Arsenate and phosphate salts behave very similarly. Arsenic acid as such has not been isolated, but only found in solution where it...
as a reactant.
One example of an important arsonic acid is roxarsone. This is 4-hydroxy-3-nitrobenzenearsonic acid. It exhibits an anticoccidial action and promotes growth in animals.


