
Belt problem
Encyclopedia
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
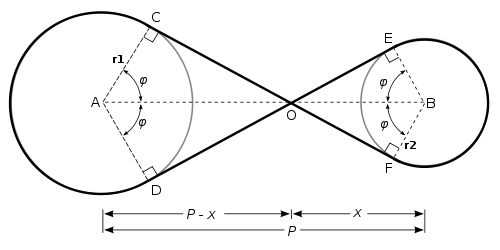
problem which requires finding the length of a crossed belt
Belt (mechanical)
A belt is a loop of flexible material used to link two or more rotating shafts mechanically. Belts may be used as a source of motion, to transmit power efficiently, or to track relative movement. Belts are looped over pulleys. In a two pulley system, the belt can either drive the pulleys in the...
that connects two circular pulley
Pulley
A pulley, also called a sheave or a drum, is a mechanism composed of a wheel on an axle or shaft that may have a groove between two flanges around its circumference. A rope, cable, belt, or chain usually runs over the wheel and inside the groove, if present...
s with radius
Radius
In classical geometry, a radius of a circle or sphere is any line segment from its center to its perimeter. By extension, the radius of a circle or sphere is the length of any such segment, which is half the diameter. If the object does not have an obvious center, the term may refer to its...
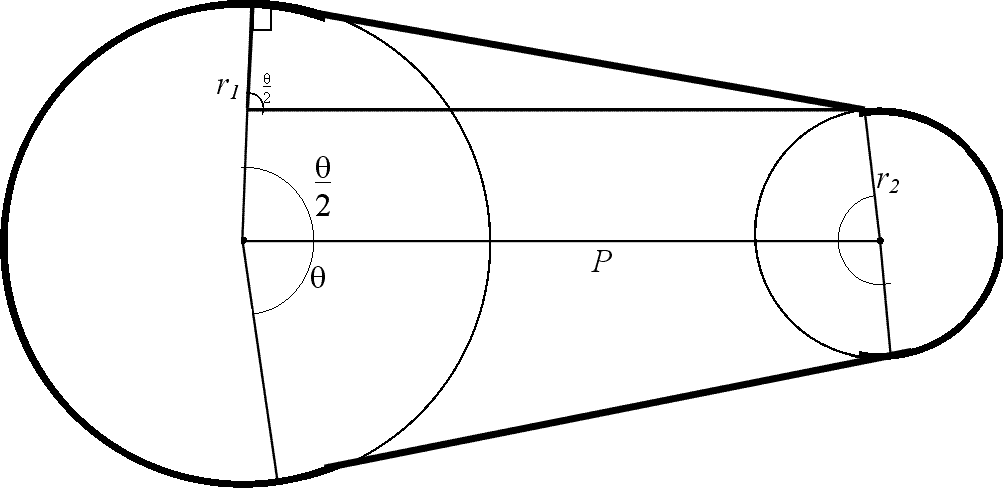
r1 and r2 whose centers are separated by a distance P (see diagram). The solution of the belt problem requires trigonometry
Trigonometry
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that studies triangles and the relationships between their sides and the angles between these sides. Trigonometry defines the trigonometric functions, which describe those relationships and have applicability to cyclical phenomena, such as waves...
and the concepts of the bitangent line
Bitangent
In mathematics, a bitangent to a curve C is a line L that touches C in two distinct points P and Q and that has the same direction to C at these points...
, the vertical angle, and congruent angles.
Solution
Clearly triangleTriangle
A triangle is one of the basic shapes of geometry: a polygon with three corners or vertices and three sides or edges which are line segments. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted ....
s ACO and ADO are congruent
Congruence (geometry)
In geometry, two figures are congruent if they have the same shape and size. This means that either object can be repositioned so as to coincide precisely with the other object...
right angled triangles, as are triangle
Triangle
A triangle is one of the basic shapes of geometry: a polygon with three corners or vertices and three sides or edges which are line segments. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted ....
s BEO and BFO. In addition, triangle
Triangle
A triangle is one of the basic shapes of geometry: a polygon with three corners or vertices and three sides or edges which are line segments. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted ....
s ACO and BEO are similar
Similarity (geometry)
Two geometrical objects are called similar if they both have the same shape. More precisely, either one is congruent to the result of a uniform scaling of the other...
. Therefore angle
Angle
In geometry, an angle is the figure formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint, called the vertex of the angle.Angles are usually presumed to be in a Euclidean plane with the circle taken for standard with regard to direction. In fact, an angle is frequently viewed as a measure of an circular arc...
s CAO, DAO, EBO and FBO are all equal. Denoting this angle
Angle
In geometry, an angle is the figure formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint, called the vertex of the angle.Angles are usually presumed to be in a Euclidean plane with the circle taken for standard with regard to direction. In fact, an angle is frequently viewed as a measure of an circular arc...
by
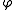 , the length of the belt is
, the length of the belt is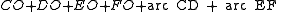
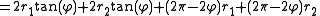
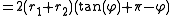
This uses the fact that the length of an arc
Arc (geometry)
In geometry, an arc is a closed segment of a differentiable curve in the two-dimensional plane; for example, a circular arc is a segment of the circumference of a circle...
= the radius
Radius
In classical geometry, a radius of a circle or sphere is any line segment from its center to its perimeter. By extension, the radius of a circle or sphere is the length of any such segment, which is half the diameter. If the object does not have an obvious center, the term may refer to its...
× the measure of the angle
Angle
In geometry, an angle is the figure formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint, called the vertex of the angle.Angles are usually presumed to be in a Euclidean plane with the circle taken for standard with regard to direction. In fact, an angle is frequently viewed as a measure of an circular arc...
facing the arc
Arc (geometry)
In geometry, an arc is a closed segment of a differentiable curve in the two-dimensional plane; for example, a circular arc is a segment of the circumference of a circle...
in radian
Radian
Radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius. The radian is the standard unit of angular measure, used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly a SI supplementary unit, but this category was abolished in 1995 and the radian is now considered a SI derived unit...
s.
To find
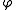 we see from the similarity
we see from the similaritySimilarity (geometry)
Two geometrical objects are called similar if they both have the same shape. More precisely, either one is congruent to the result of a uniform scaling of the other...
of triangle
Triangle
A triangle is one of the basic shapes of geometry: a polygon with three corners or vertices and three sides or edges which are line segments. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted ....
s ACO and BEO that
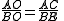
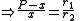
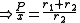
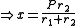
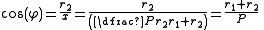
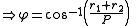
For fixed P the length of the belt depends only on the sum of the radius values r1 + r2, and not on their individual values.
Pulley problem
Pulley
A pulley, also called a sheave or a drum, is a mechanism composed of a wheel on an axle or shaft that may have a groove between two flanges around its circumference. A rope, cable, belt, or chain usually runs over the wheel and inside the groove, if present...
problem, as shown, is similar to the belt problem; however, the belt
Belt (mechanical)
A belt is a loop of flexible material used to link two or more rotating shafts mechanically. Belts may be used as a source of motion, to transmit power efficiently, or to track relative movement. Belts are looped over pulleys. In a two pulley system, the belt can either drive the pulleys in the...
does not cross itself. In the pulley problem the length of the belt is
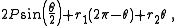
where
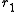 represents the radius of the larger pulley,
represents the radius of the larger pulley, 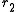 represents the radius of the smaller one, and:
represents the radius of the smaller one, and: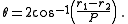
Applications
The belt problem is used in real life in the design of aeroplanes, bicycle gears, carČar
Čar is a village in the municipality of Bujanovac, Serbia. According to the 2002 census, the town has a population of 296 people.-References:...
s, and other items with pulley
Pulley
A pulley, also called a sheave or a drum, is a mechanism composed of a wheel on an axle or shaft that may have a groove between two flanges around its circumference. A rope, cable, belt, or chain usually runs over the wheel and inside the groove, if present...
s or belts
Belt (mechanical)
A belt is a loop of flexible material used to link two or more rotating shafts mechanically. Belts may be used as a source of motion, to transmit power efficiently, or to track relative movement. Belts are looped over pulleys. In a two pulley system, the belt can either drive the pulleys in the...
that cross each other as in the belt problem. The pulley problem is also used in the design of conveyor belt
Conveyor belt
A conveyor belt consists of two or more pulleys, with a continuous loop of material - the conveyor belt - that rotates about them. One or both of the pulleys are powered, moving the belt and the material on the belt forward. The powered pulley is called the drive pulley while the unpowered pulley...
s found in airport
Airport
An airport is a location where aircraft such as fixed-wing aircraft, helicopters, and blimps take off and land. Aircraft may be stored or maintained at an airport...
luggage
Luggage
Baggage is any number of bags, cases and containers which hold a traveller's articles during transit.Luggage is more or less the same concept as "baggage", but is normally used in relation to the personal luggage of a specific person or persons Baggage is any number of bags, cases and containers...
belts and automated factory
Factory
A factory or manufacturing plant is an industrial building where laborers manufacture goods or supervise machines processing one product into another. Most modern factories have large warehouses or warehouse-like facilities that contain heavy equipment used for assembly line production...
lines.

