
Beta Barium Borate
Encyclopedia
Beta barium borate
(β-barium borate, BBO or β-BaB2O4) is a crystal frequently used for frequency mixing and other nonlinear optics
applications. It has a wide transmission range, from approximately 200 nanometres to beyond 3 micrometres, and is used particularly for its transparency in the deep ultraviolet.
BBO has a trigonal crystal system
, belongs to crystallographic point group
3m, and belongs to the crystallographic space group
R3c. BBO has strong negative uniaxial birefringence
and can be phase-matched for type I (ooe) second harmonic generation
from 409.6 to 3500 nm. The temperature sensitivity of the indices of refraction is low, leading to an unusually large (55 °C) temperature phase-matching bandwidth. The crystal is mildly hygroscopic.
β-Barium borate differs from α-barium borate in the
positions of the barium ions within the crystal. Both phases are birefringent, however the α phase, which exists above 925 °C, possesses centric symmetry and thus does not have the same nonlinear properties as the β phase.
The nonlinear nature of BBO allows for the production of pairs of photons via spontaneous parametric down-conversion. This is an important resource for experimental quantum information
, particularly as a method of producing entangled photons
.
Barium borate
Barium borate, also called barium diborate, barium boron oxide, barium metaborate, or BBO is an inorganic compound, a borate of barium. It is available as a hydrate or dehydrated....
(β-barium borate, BBO or β-BaB2O4) is a crystal frequently used for frequency mixing and other nonlinear optics
Nonlinear optics
Nonlinear optics is the branch of optics that describes the behavior of light in nonlinear media, that is, media in which the dielectric polarization P responds nonlinearly to the electric field E of the light...
applications. It has a wide transmission range, from approximately 200 nanometres to beyond 3 micrometres, and is used particularly for its transparency in the deep ultraviolet.
BBO has a trigonal crystal system
Crystal system
In crystallography, the terms crystal system, crystal family, and lattice system each refer to one of several classes of space groups, lattices, point groups, or crystals...
, belongs to crystallographic point group
Crystallographic point group
In crystallography, a crystallographic point group is a set of symmetry operations, like rotations or reflections, that leave a central point fixed while moving other directions and faces of the crystal to the positions of features of the same kind...
3m, and belongs to the crystallographic space group
Space group
In mathematics and geometry, a space group is a symmetry group, usually for three dimensions, that divides space into discrete repeatable domains.In three dimensions, there are 219 unique types, or counted as 230 if chiral copies are considered distinct...
R3c. BBO has strong negative uniaxial birefringence
Birefringence
Birefringence, or double refraction, is the decomposition of a ray of light into two rays when it passes through certain anisotropic materials, such as crystals of calcite or boron nitride. The effect was first described by the Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who saw it in calcite...
and can be phase-matched for type I (ooe) second harmonic generation
Second harmonic generation
An optical frequency multiplier is a nonlinear optical device, in which photons interacting with a nonlinear material are effectively "combined" to form new photons with greater energy, and thus higher frequency...
from 409.6 to 3500 nm. The temperature sensitivity of the indices of refraction is low, leading to an unusually large (55 °C) temperature phase-matching bandwidth. The crystal is mildly hygroscopic.
β-Barium borate differs from α-barium borate in the
positions of the barium ions within the crystal. Both phases are birefringent, however the α phase, which exists above 925 °C, possesses centric symmetry and thus does not have the same nonlinear properties as the β phase.
The nonlinear nature of BBO allows for the production of pairs of photons via spontaneous parametric down-conversion. This is an important resource for experimental quantum information
Quantum information
In quantum mechanics, quantum information is physical information that is held in the "state" of a quantum system. The most popular unit of quantum information is the qubit, a two-level quantum system...
, particularly as a method of producing entangled photons
Photon entanglement
This brief explanation of photon entanglement is a supplement to the article Bohr-Einstein debates and is designed to help clarify the discussion of the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen argument in quantum theory which takes place in that article.-Entanglement:...
.
Physical properties
- Lattice parameters: a=b=1.253 nm, c=1.272 nm, Z=6
- Melting point: 1095±5 °C
- Phase transition temperature: 925±5 °C
- Mohs hardness: 4.5
- Density: 3.85 g/cm3
Optical properties
- Refractive index, 1064 nm:
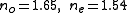
- Refractive index, 532 nm:
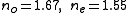
- Refractive index, 266 nm:
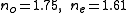
- Transparency range (> 0.5 cm−1): 198–2600 nm
- Thermo-optic coefficients:
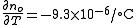

- Nonlinear optical coefficients:
- d22 = 2.3 pm/V
- d31 = -0.16 pm/V
- High damage threshold of 10 GW/cm2 for 100 ps pulse-width at 1064 nm.
Sellmeier equations (for λ in micrometres)
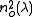 = 2.7359+0.01878/(λ2 - 0.01822)-0.01354 λ2
= 2.7359+0.01878/(λ2 - 0.01822)-0.01354 λ2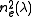 = 2.3753+0.01224/(λ2-0.01667)-0.01516 λ2
= 2.3753+0.01224/(λ2-0.01667)-0.01516 λ2

