
Bilge pump
Encyclopedia
A bilge pump is a water pump
used to remove bilge water. Since fuel can be present in the bilge, electric bilge pumps are designed to not cause sparks. Electric bilge pumps are often fitted with float switch
es which turn on the pump when the bilge fills to a set level. Since bilge
pumps can fail, use of a backup pump are often advised. The primary pump is normally located at the lowest point of the bilge, while the secondary pump would be located somewhat higher. This ensures that the secondary pump activates only when the primary pump is overwhelmed and keeps the secondary pump free of the debris in the bilge that tends to clog the primary pump.
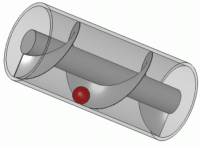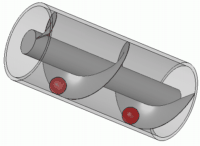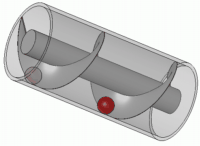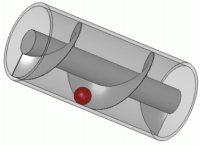
Ancient bilge 'force pumps' had a number of common uses. Depending on where the pump was located in the hull
of the ship, it could be used to suck in sea water into a live fish tank to preserve fish until the ship was docked and the fish ready to be sold. Another use of the force pump was to combat fires. Water would again be sucked in through the bottom of the hull, and then pumped onto the blaze. Yet another suggested use for a force pump was to dispel water from a ship. The pump would be placed near the bottom of the hull so as to suck water out of the ship. Force pumps were used on land as well. They could be used to bring water up from a well or to fill high placed tanks so that water could be pressure pumped from these tanks. These tanks were for household use and/or small scale irrigation. The force pump was portable and could therefore, as on ships, be used to fight fire.
Force pumps could be made of either wood or bronze. Based on ancient texts, it seems that bronze was the preferred material since it lasted longer and was more easily transported. Wood was easier to build, put together, and repair but was not as durable as bronze. Because these were high-value objects, few are found in shipwrecks; they were often recovered after the ship sank. Force pumps were fairly simple in their construction consisting of a cylinder, a piston, and a few valves. Water would fill the cylinder after which the piston would descend into the cylinder, causing the water to move to a higher placed pipe. The valve would close, locking the water into the higher pipe, and then propelling it in a jet stream.
 The Greek writer Athenaeus of Naucratis
The Greek writer Athenaeus of Naucratis
described how King Hieron II commissioned Archimedes to design a huge ship, the Syracusia
, which could be used for luxury travel, carrying supplies, and as a naval warship. The Syracusia is said to have been the largest ship built in classical antiquity. According to Athenaeus, it was capable of carrying 600 people and included garden decorations, a gymnasium
and a temple dedicated to the goddess Aphrodite
among its facilities. Since a ship of this size would leak a considerable amount of water through the hull, the Archimedes screw was purportedly developed in order to remove the bilge water. Archimedes' machine was a device with a revolving screw-shaped blade inside a cylinder. It was turned by hand, and could also be used to transfer water from a body of water into irrigation canals. The Archimedes screw is still in use today for pumping liquids and granulated solids such as coal and grain. The Archimedes screw described in Roman times by Vitruvius
may have been an improvement on a screw pump that was used to irrigate the Hanging Gardens of Babylon
, but this is disputed due to a lack of actual evidence.
Water Pump
Water Pump is one of the neighbourhoods of Gulberg Town in Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan. It is near main Water Pump that supplies fresh water to the city of Karachi....
used to remove bilge water. Since fuel can be present in the bilge, electric bilge pumps are designed to not cause sparks. Electric bilge pumps are often fitted with float switch
Float switch
A float switch is a device used to detect the level of liquid within a tank. The switch may be used in a pump, an indicator, an alarm, or other devices....
es which turn on the pump when the bilge fills to a set level. Since bilge
Bilge
The bilge is the lowest compartment on a ship where the two sides meet at the keel. The word was coined in 1513.-Bilge water:The word is sometimes also used to describe the water that collects in this compartment. Water that does not drain off the side of the deck drains down through the ship into...
pumps can fail, use of a backup pump are often advised. The primary pump is normally located at the lowest point of the bilge, while the secondary pump would be located somewhat higher. This ensures that the secondary pump activates only when the primary pump is overwhelmed and keeps the secondary pump free of the debris in the bilge that tends to clog the primary pump.
Ancient bilge 'force pumps' had a number of common uses. Depending on where the pump was located in the hull
Hull (watercraft)
A hull is the watertight body of a ship or boat. Above the hull is the superstructure and/or deckhouse, where present. The line where the hull meets the water surface is called the waterline.The structure of the hull varies depending on the vessel type...
of the ship, it could be used to suck in sea water into a live fish tank to preserve fish until the ship was docked and the fish ready to be sold. Another use of the force pump was to combat fires. Water would again be sucked in through the bottom of the hull, and then pumped onto the blaze. Yet another suggested use for a force pump was to dispel water from a ship. The pump would be placed near the bottom of the hull so as to suck water out of the ship. Force pumps were used on land as well. They could be used to bring water up from a well or to fill high placed tanks so that water could be pressure pumped from these tanks. These tanks were for household use and/or small scale irrigation. The force pump was portable and could therefore, as on ships, be used to fight fire.
Force pumps could be made of either wood or bronze. Based on ancient texts, it seems that bronze was the preferred material since it lasted longer and was more easily transported. Wood was easier to build, put together, and repair but was not as durable as bronze. Because these were high-value objects, few are found in shipwrecks; they were often recovered after the ship sank. Force pumps were fairly simple in their construction consisting of a cylinder, a piston, and a few valves. Water would fill the cylinder after which the piston would descend into the cylinder, causing the water to move to a higher placed pipe. The valve would close, locking the water into the higher pipe, and then propelling it in a jet stream.
Archimedes Screw

Athenaeus
Athenaeus , of Naucratis in Egypt, Greek rhetorician and grammarian, flourished about the end of the 2nd and beginning of the 3rd century AD...
described how King Hieron II commissioned Archimedes to design a huge ship, the Syracusia
Syracusia
Syracusia was a ancient Greek ship sometimes claimed to be the largest transport ship of antiquity. It only sailed once, from Syracuse in Sicily to Alexandria in the Ptolemaic Kingdom.-General characteristics:...
, which could be used for luxury travel, carrying supplies, and as a naval warship. The Syracusia is said to have been the largest ship built in classical antiquity. According to Athenaeus, it was capable of carrying 600 people and included garden decorations, a gymnasium
Gymnasium (ancient Greece)
The gymnasium in ancient Greece functioned as a training facility for competitors in public games. It was also a place for socializing and engaging in intellectual pursuits. The name comes from the Ancient Greek term gymnós meaning "naked". Athletes competed in the nude, a practice said to...
and a temple dedicated to the goddess Aphrodite
Aphrodite
Aphrodite is the Greek goddess of love, beauty, pleasure, and procreation.Her Roman equivalent is the goddess .Historically, her cult in Greece was imported from, or influenced by, the cult of Astarte in Phoenicia....
among its facilities. Since a ship of this size would leak a considerable amount of water through the hull, the Archimedes screw was purportedly developed in order to remove the bilge water. Archimedes' machine was a device with a revolving screw-shaped blade inside a cylinder. It was turned by hand, and could also be used to transfer water from a body of water into irrigation canals. The Archimedes screw is still in use today for pumping liquids and granulated solids such as coal and grain. The Archimedes screw described in Roman times by Vitruvius
Vitruvius
Marcus Vitruvius Pollio was a Roman writer, architect and engineer, active in the 1st century BC. He is best known as the author of the multi-volume work De Architectura ....
may have been an improvement on a screw pump that was used to irrigate the Hanging Gardens of Babylon
Hanging Gardens of Babylon
The Hanging Gardens of Babylon were considered to be one of the greatest Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, and the only one of the Wonders which may in fact have been legendary. They were purportedly built in the ancient city-state of Babylon, near present-day Al Hillah, Babil, in Iraq...
, but this is disputed due to a lack of actual evidence.

