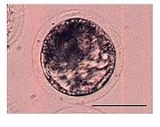
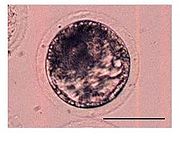
Blastocyst
Encyclopedia
- See also: BlastocystisBlastocystisBlastocystis is a genus of single-celled protozoan parasites belonging to a group of organisms known as the Stramenopiles that includes algae, diatoms, and water molds...
, a single-celled parasite.
The blastocyst is a structure formed in the early embryogenesis
Embryogenesis
Embryogenesis is the process by which the embryo is formed and develops, until it develops into a fetus.Embryogenesis starts with the fertilization of the ovum by sperm. The fertilized ovum is referred to as a zygote...
of mammal
Mammal
Mammals are members of a class of air-breathing vertebrate animals characterised by the possession of endothermy, hair, three middle ear bones, and mammary glands functional in mothers with young...
s, after the formation of the morula
Morula
A morula is an embryo at an early stage of embryonic development, consisting of cells in a solid ball contained within the zona pellucida....
. It is a specifically mammalian example of a blastula
Blastula
The blastula is a hollow sphere of cells formed during an early stage of embryonic development in animals . The blastula is created when the zygote undergoes the cell division process known as cleavage. The blastula is preceded by the morula and is followed by the gastrula in the developmental...
. It possesses an inner cell mass (ICM), or embryoblast
Inner cell mass
In early embryogenesis of most eutherian mammals, the inner cell mass is the mass of cells inside the primordial embryo that will eventually give rise to the definitive structures of the fetus...
, which subsequently forms the embryo
Embryo
An embryo is a multicellular diploid eukaryote in its earliest stage of development, from the time of first cell division until birth, hatching, or germination...
, and an outer layer of cells, or trophoblast
Trophoblast
Trophoblasts are cells forming the outer layer of a blastocyst, which provide nutrients to the embryo and develop into a large part of the placenta. They are formed during the first stage of pregnancy and are the first cells to differentiate from the fertilized egg...
, which later forms the placenta
Placenta
The placenta is an organ that connects the developing fetus to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake, waste elimination, and gas exchange via the mother's blood supply. "True" placentas are a defining characteristic of eutherian or "placental" mammals, but are also found in some snakes and...
. The trophoblast surrounds the inner cell mass and a fluid-filled blastocyst cavity known as the blastocoele
Blastocoele
A blastocoel or blastocele is the fluid-filled central region of a blastocyst...
or the blastocystic cavity. The human blastocyst comprises 70-100 cells
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
.
Blastocyst formation begins at day 5 after fertilization in humans, when the blastocoele opens up in the morula, a process known as hatching.
Parts of the blastocyst
The blastocyst consists of two primary cell types:- the inner cell massInner cell massIn early embryogenesis of most eutherian mammals, the inner cell mass is the mass of cells inside the primordial embryo that will eventually give rise to the definitive structures of the fetus...
, also known as the "embryoblast" (this part of the embryo is used in stem cell research) - the trophoblastTrophoblastTrophoblasts are cells forming the outer layer of a blastocyst, which provide nutrients to the embryo and develop into a large part of the placenta. They are formed during the first stage of pregnancy and are the first cells to differentiate from the fertilized egg...
, a layer of cells surrounding the inner cell mass and the blastocyst cavity (blastocoeleBlastocoeleA blastocoel or blastocele is the fluid-filled central region of a blastocyst...
)
The former is the source of embryonic stem cells and gives rise to all later structures of the adult organism. The latter combines with the maternal endometrium
Endometrium
-Function:The endometrium is the innermost glandular layer and functions as a lining for the uterus, preventing adhesions between the opposed walls of the myometrium, thereby maintaining the patency of the uterine cavity. During the menstrual cycle or estrous cycle, the endometrium grows to a...
to form the placenta
Placenta
The placenta is an organ that connects the developing fetus to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake, waste elimination, and gas exchange via the mother's blood supply. "True" placentas are a defining characteristic of eutherian or "placental" mammals, but are also found in some snakes and...
in eutherian mammals.
Formation of the blastocyst
The morulaMorula
A morula is an embryo at an early stage of embryonic development, consisting of cells in a solid ball contained within the zona pellucida....
is a solid ball of about 16 undifferentiated, spherical cells. As cell division continues in the morula, the blastomeres change their shape and tightly align themselves against each other. This is called compaction and is likely mediated by cell surface adhesion glycoproteins.

