Blastocystosis
Encyclopedia
Blastocystosis refers to a medical condition caused by infection with Blastocystis
. Blastocystis is a protozoal, single-celled parasite that inhabits the gastrointestinal tracts of humans and animals. Many different types of Blastocystis exist, and they can infect humans, farm animals, birds, rodents, amphibians, reptiles, fish, and even cockroaches.
At the time, it was common practice to identify all Blastocystis from humans as Blastocystis hominis, while Blastocystis from animals was identified differently (i.e. Blastocystis ratti from rats). Research performed since then has shown that the concept of Blastocystis hominis as a unique species of Blastocystis infecting humans is not supported by microbiological findings. Although one species group associated with primates was found, it was also discovered that humans can acquire infection from any one of nine species groups of Blastocystis which are also carried by cattle, pigs, rodents, chickens, pheasants, monkeys, dogs and other animals. Research has suggested that some types produce few or no symptoms, while others producing illness and intestinal inflammation. Researchers have suggested conflicting reports may be due to the practice of naming all Blastocystis from humans Blastocystis hominis and have proposed discontinuing the use of that term.
A standard naming system for Blastocystis organisms from humans and animals has been proposed which names Blastocystis isolates according to the genetic identity of the Blastocystis organism rather than the host. The naming system used identifies all isolates as Blastocystis sp. subtype nn where nn is a number from 1 to 9 indicating the species group of the Blastocystis organism. The identification of the species can not be performed with a microscope at this time, because the different species look alike. Identification requires equipment for genetic analysis that is common in microbiology laboratories, but not available to most physicians. Some new scientific papers have begun using the standard naming system.
The most commonly reported symptoms are:
Less commonly reported symptoms are:
A number of researchers have investigated the possibility that some species of Blastocystis are more virulent than others. An Italian researcher reported differences in the protein profiles of isolates associated with chronic and acute infection. A research team from Malaysia reported that isolates from symptomatic patients produced large amoeboid forms that were not present in isolates from asymptomatic patients. The development of a classification system for Blastocystis in 2007 produced a series of studies investigating this possibility.
The studies that followed generally found that there is no specific "pathogenic" or non-pathogenic species of Blastocystis. One study investigated the subtypes found in patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and chronic diarrhea, and found the subtypes in these diseases were similar (subtypes 2 and 3), and have also found in asymptomatic carriers. The researchers concluded that host factors, such as age and genetics, may play the dominant role in determining the symptoms seen in the disease.
:
The following reports have linked Blastocystis infection to inflammatory bowel disease
:
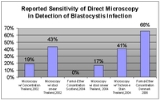
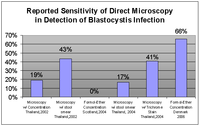 For identification of infection, the only method clinically available in most areas is the Ova and Parasite (O&P) exam, which identifies the presence of the organism by microscopic examination of a chemically preserved stool specimen. This method is sometimes called "Direct Microscopy". In the United States, pathologists are required to report the presence of Blastocystis when found during an O&P exam, so a special test does not have to be ordered. Direct Microscopy is inexpensive, as the same test can identify a variety of gastrointestinal infections, such as Giardia
For identification of infection, the only method clinically available in most areas is the Ova and Parasite (O&P) exam, which identifies the presence of the organism by microscopic examination of a chemically preserved stool specimen. This method is sometimes called "Direct Microscopy". In the United States, pathologists are required to report the presence of Blastocystis when found during an O&P exam, so a special test does not have to be ordered. Direct Microscopy is inexpensive, as the same test can identify a variety of gastrointestinal infections, such as Giardia
, Entamoeba histolytica
, Cryptosporidium
. However one laboratory director noted that pathologists using conventional microscopes failed to identify many Blastocystis infections, and indicated the necessity for special microscopic equipment for identification. The following table shows the sensitivity of Direct Microscopy in detecting Blastocystis when compared to stool culture, a more sensitive technique. Stool culture was considered by some researchers to be the most reliable technique, but a recent study found stool culture only detected 83% of individuals infected when compared to polymerase chain reaction
(PCR) testing.
Reasons given for the failure of Direct Microscopy include: (1) Variable Shedding: The quantity of Blastocystis organisms varies substantially from day to day in infected humans and animals; (2) Appearance: Some forms of Blastocystis resemble fat cells or white blood cells, making it difficult to distinguish the organism from other cells in the stool sample; (3) Large number of morphological forms: Blastocystis cells can assume a variety of shapes, some have been described in detail only recently, so it is possible that additional forms exist but have not been identified.
Several methods have been cited in literature for determination of the significance of the finding of Blastocystis:
Serum antibody testing: A 1993 research study performed by the NIH with United States patients suggested that it was possible to distinguish symptomatic and asymptomatic infection with Blastocystis using serum antibody testing. The study used blood samples to measure the patient's immune reaction to chemicals present on the surface of the Blastocystis cell. It found that patients diagnosed with symptomatic Blastocystis infection exhibited a much higher immune response than controls who had Blastocystis infection but no symptoms. The study was repeated in 2003 at Ain Shams University
in Egypt with Egyptian patients with equivalent results.
Fecal Antibody Testing: A 2003 study at Ain Shams University in Egypt indicated that patients symptomatically infected could be distinguished with a fecal antibody test. The study compared patients diagnosed with symptomatic Blastocystis infection to controls who had Blastocystis infection but no symptoms. In the group with symptoms, IgA antibodies to Blastocystis were detected in fecal specimens that were not present in the healthy control group.
Stool Culture: Culturing has been shown to be a more reliable method of identifying infection. In 2006, researchers reported the ability to distinguish between disease causing and non-disease causing isolates of Blastocystis using stool culture. Blastocystis cultured from patients who were sick and diagnosed with Blastocystis infection produced large, highly adhesive amoeboid forms in culture. These cells were absent in Blastocystis cultures from healthy controls. Subsequent genetic analysis showed the Blastocystis from healthy controls was genetically distinct from that found in patients with symptoms. Protozoal culture is unavailable in most countries due to the cost and lack of trained staff able to perform protozoal culture.
Genetic Analysis of isolates: Researchers have used techniques which allow the DNA of Blastocystis to be isolated from fecal specimens. This method has been reported to be more reliable at detecting Blastocystis in symptomatic patients than stool culture. This method also allows the species group of Blastocystis to be identified. Research is continuing into which species groups are associated with symptomatic (see Genetics and Symptoms) blastocystosis.
Immuno-Fluorescence (IFA) Stain: An IFA stain causes Blastocystis cells to glow when viewed under a microscope, making the diagnostic method more reliable. IFA stains are in use for Giardia
and Cryptosporidium
for both diagnostic purposes and water quality testing. A 1991 paper from the NIH described the laboratory development of one such stain. However, no company currently offers this stain commercially.
from an infected human or animal. Blastocystis infection can be spread from animals to humans, from humans to other humans, from humans to animals, and from animals to animals. Risk factors for infection have been reported as following:
Research studies have suggested the following items are not risk factors for contracting Blastocystis infection:
A 1999 in vitro from Pakistan study found 40% of isolates are resistant to common antiprotozoal drugs. A study of isolates from patients diagnosed with IBS found 40% of isolates resistant to Metronidazole
and 32% resistant to furazolidone
. Drugs reported in studies have included Metronidazole
, TMP-SMX
, Doxycycline
, Nitazoxanide
Iodoquinol and Paromomycin. Iodoquinol has been found to be less effective in practice and in-vitro. Miconazole
has been reported as an agent against Blastocystis growth in-vitro.
Physicians have described the successful use of a variety of discontinued antiprotozoals in treatment of Blastocystis infection. Emetine
was reported as successful in cases in early 20th century with British soldiers who contracted Blastocystis infection while serving in Egypt. In vitro testing showed emetine
was more effective than Metronidazole
or furazolidone
. Emetine is available in the United States through special arrangement with the Center for Disease Control. Clioquinol
(Entero-vioform) was noted as successful in treatment of Blastocystis infection but removed from the market following an adverse event in Japan. Stovarsol
and Narsenol, two arsenic-based antiprotozoals, were reported to be effective against the infection. Carbarsone was available as an anti-infective compound in the United States as late as 1991, and was suggested as a possible treatment. The reduction in the availability of antiprotozoal drugs has been noted as a complicating factor in treatment of other protozoal infections. For example, in Australia
, production of diloxanide furoate
ended in 2003, paromomycin is available under special access provisions, and the availability of iodoquinol is limited.
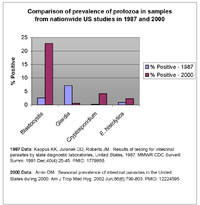
 Like other protozoal infections, the prevalence of Blastocystis infection varies depending on the area investigated and the population selected. A number of different species groups of Blastocystis infect humans, with some being reported to cause disease while others do not. To date surveys have not distinguished between different types of Blastocystis in humans so the significance of findings may be difficult to evaluate. Developing countries have been reported to have higher incidences, however recent studies suggest that symptomatic infection with Blastocystis may be prevalent in certain areas of industrialized countries as well:
Like other protozoal infections, the prevalence of Blastocystis infection varies depending on the area investigated and the population selected. A number of different species groups of Blastocystis infect humans, with some being reported to cause disease while others do not. To date surveys have not distinguished between different types of Blastocystis in humans so the significance of findings may be difficult to evaluate. Developing countries have been reported to have higher incidences, however recent studies suggest that symptomatic infection with Blastocystis may be prevalent in certain areas of industrialized countries as well:
Blastocystis
Blastocystis is a genus of single-celled protozoan parasites belonging to a group of organisms known as the Stramenopiles that includes algae, diatoms, and water molds...
. Blastocystis is a protozoal, single-celled parasite that inhabits the gastrointestinal tracts of humans and animals. Many different types of Blastocystis exist, and they can infect humans, farm animals, birds, rodents, amphibians, reptiles, fish, and even cockroaches.
Classification
Physicians have produced conflicting reports regarding whether Blastocystis causes disease in humans. These reports resulted in a brief debate in medical journals in the early 1990s between some physicians in the United States who believed that Blastocystis was harmless, and physicians in the United States and overseas who believed it could cause disease.At the time, it was common practice to identify all Blastocystis from humans as Blastocystis hominis, while Blastocystis from animals was identified differently (i.e. Blastocystis ratti from rats). Research performed since then has shown that the concept of Blastocystis hominis as a unique species of Blastocystis infecting humans is not supported by microbiological findings. Although one species group associated with primates was found, it was also discovered that humans can acquire infection from any one of nine species groups of Blastocystis which are also carried by cattle, pigs, rodents, chickens, pheasants, monkeys, dogs and other animals. Research has suggested that some types produce few or no symptoms, while others producing illness and intestinal inflammation. Researchers have suggested conflicting reports may be due to the practice of naming all Blastocystis from humans Blastocystis hominis and have proposed discontinuing the use of that term.
A standard naming system for Blastocystis organisms from humans and animals has been proposed which names Blastocystis isolates according to the genetic identity of the Blastocystis organism rather than the host. The naming system used identifies all isolates as Blastocystis sp. subtype nn where nn is a number from 1 to 9 indicating the species group of the Blastocystis organism. The identification of the species can not be performed with a microscope at this time, because the different species look alike. Identification requires equipment for genetic analysis that is common in microbiology laboratories, but not available to most physicians. Some new scientific papers have begun using the standard naming system.
Signs and symptoms
Researchers have published conflicting reports concerning whether Blastocystis causes symptoms in humans, with one of the earliest reports in 1916. The incidence of reports associated with symptoms began to increase in 1984, with physicians from Saudi Arabia reporting symptoms in humans and US physicians reporting symptoms in individuals with travel to less developed countries. A lively debate ensued in the early 1990s, with some physicians objecting to publication of reports that Blastocystis caused disease. Some researchers believe the debate has been resolved by finding of multiple species of Blastocystis that can infect humans, with some causing symptoms and others being harmless (see Genetics and Symptoms).The most commonly reported symptoms are:
- abdominal pain
- constipation
- diarrhea
- weight loss
- fatigue
- flatulence
Less commonly reported symptoms are:
- Skin Rash
- Headache, depression
- Arthritic symptoms and joint pain
- Intestinal inflammation
Variation in severity
Researchers have sought to develop models to understand the variety of symptoms seen in humans. Some patients do not have symptoms, while others report severe diarrhea and fatigue.A number of researchers have investigated the possibility that some species of Blastocystis are more virulent than others. An Italian researcher reported differences in the protein profiles of isolates associated with chronic and acute infection. A research team from Malaysia reported that isolates from symptomatic patients produced large amoeboid forms that were not present in isolates from asymptomatic patients. The development of a classification system for Blastocystis in 2007 produced a series of studies investigating this possibility.
The studies that followed generally found that there is no specific "pathogenic" or non-pathogenic species of Blastocystis. One study investigated the subtypes found in patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and chronic diarrhea, and found the subtypes in these diseases were similar (subtypes 2 and 3), and have also found in asymptomatic carriers. The researchers concluded that host factors, such as age and genetics, may play the dominant role in determining the symptoms seen in the disease.
Associations
The following reports have linked Blastocystis infection to Irritable bowel syndromeIrritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome is a diagnosis of exclusion. It is a functional bowel disorder characterized by chronic abdominal pain, discomfort, bloating, and alteration of bowel habits in the absence of any detectable organic cause. In some cases, the symptoms are relieved by bowel movements...
:
- A study of IBS patients in the Middle East found 46% were infected with Blastocystis vs. 7% of healthy controls.
- An additional study of IBS patients in the Middle East showed a "significantly increased" immune reaction in IBS patients to Blastocystis, even when the organism could not be identified in stool samples.
- A European study compared Blastocystis infection rates in IBS patients to those of healthy controls and found a statistically significant infection rate in IBS patients.
- Early reports from the US physicians in the 1980s suggested the presence of the organism was not relevant to the diagnostic process, and patients infected with Blastocystis could be diagnosed with IBS.
The following reports have linked Blastocystis infection to inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease
In medicine, inflammatory bowel disease is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine. The major types of IBD are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.-Classification:...
:
- A study using riboprinting identified specific types of Blastocystis as associated with inflammation.
- A case report described inflammatory bowel disease in conjunction with Blastocystis infection.
- Three research groups have reported experimental infection of mice with Blastocystis produces intestinal inflammation.
- An article in a non-peer reviewed medical journal noted that the increase in Blastocystis case reports coincided with reported increases in the prevalence of inflammatory bowel diseaseInflammatory bowel diseaseIn medicine, inflammatory bowel disease is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine. The major types of IBD are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.-Classification:...
from several European countries.
Clinically available
Diagnosis is performed by determining if the infection is present, and then making a decision as to whether the infection is responsible for the symptoms. Diagnostic methods in clinical use have been reported to be of poor quality and more reliable methods have been reported in research papers.
Giardia
Giardia is a genus of anaerobic flagellated protozoan parasites of the phylum Metamonada in the supergroup "Excavata" that colonise and reproduce in the small intestines of several vertebrates, causing giardiasis, commonly known as Beaver fever...
, Entamoeba histolytica
Entamoeba histolytica
Entamoeba histolytica is an anaerobic parasitic protozoan, part of the genus Entamoeba. Predominantly infecting humans and other primates, E. histolytica is estimated to infect about 50 million people worldwide...
, Cryptosporidium
Cryptosporidium
Cryptosporidium is a protozoan that can cause gastro-intestinal illness with diarrhea in humans.Cryptosporidium is the organism most commonly isolated in HIV positive patients presenting with diarrhea...
. However one laboratory director noted that pathologists using conventional microscopes failed to identify many Blastocystis infections, and indicated the necessity for special microscopic equipment for identification. The following table shows the sensitivity of Direct Microscopy in detecting Blastocystis when compared to stool culture, a more sensitive technique. Stool culture was considered by some researchers to be the most reliable technique, but a recent study found stool culture only detected 83% of individuals infected when compared to polymerase chain reaction
Polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction is a scientific technique in molecular biology to amplify a single or a few copies of a piece of DNA across several orders of magnitude, generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular DNA sequence....
(PCR) testing.
Reasons given for the failure of Direct Microscopy include: (1) Variable Shedding: The quantity of Blastocystis organisms varies substantially from day to day in infected humans and animals; (2) Appearance: Some forms of Blastocystis resemble fat cells or white blood cells, making it difficult to distinguish the organism from other cells in the stool sample; (3) Large number of morphological forms: Blastocystis cells can assume a variety of shapes, some have been described in detail only recently, so it is possible that additional forms exist but have not been identified.
Several methods have been cited in literature for determination of the significance of the finding of Blastocystis:
- Diagnosis only when large numbers of organism present: Some physicians consider Blastocystis infection to be a cause of illness only when large numbers are found in stool samples. Researchers have questioned this approach, noting that it is not used with any other protozoal infections, such as GiardiaGiardiaGiardia is a genus of anaerobic flagellated protozoan parasites of the phylum Metamonada in the supergroup "Excavata" that colonise and reproduce in the small intestines of several vertebrates, causing giardiasis, commonly known as Beaver fever...
or Entamoeba histolyticaEntamoeba histolyticaEntamoeba histolytica is an anaerobic parasitic protozoan, part of the genus Entamoeba. Predominantly infecting humans and other primates, E. histolytica is estimated to infect about 50 million people worldwide...
. Some researchers have reported no correlation between number of organisms present in stool samples and the level of symptoms. A study using polymerase chain reactionPolymerase chain reactionThe polymerase chain reaction is a scientific technique in molecular biology to amplify a single or a few copies of a piece of DNA across several orders of magnitude, generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular DNA sequence....
testing of stool samples suggested that symptomatic infection can exist even when sufficient quantities of the organism do not exist for identification through Direct Microscopy. - Diagnosis-by-exclusion: Some physicians diagnose Blastocystis infection by excluding all other causes, such as infection with other organisms, food intolerances, colon cancer, etc. This method can be time consuming and expensive, requiring many tests such as endoscopyEndoscopyEndoscopy means looking inside and typically refers to looking inside the body for medical reasons using an endoscope , an instrument used to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike most other medical imaging devices, endoscopes are inserted directly into the organ...
and colonoscopyColonoscopyColonoscopy is the endoscopic examination of the large bowel and the distal part of the small bowel with a CCD camera or a fiber optic camera on a flexible tube passed through the anus. It may provide a visual diagnosis and grants the opportunity for biopsy or removal of suspected...
. - Disregarding Blastocystis : In the early to mid 1990s, some US physicians suggested all findings of Blastocystis are insignificant. No recent publications expressing this opinion could be found.
Not clinically available
The following diagnostic methods are not routinely available to patients. Researchers have reported that they are more reliable at detecting infection, and in some cases can provide the physician with information to help determine whether Blastocystis infection is the cause of the patient's symptoms:Serum antibody testing: A 1993 research study performed by the NIH with United States patients suggested that it was possible to distinguish symptomatic and asymptomatic infection with Blastocystis using serum antibody testing. The study used blood samples to measure the patient's immune reaction to chemicals present on the surface of the Blastocystis cell. It found that patients diagnosed with symptomatic Blastocystis infection exhibited a much higher immune response than controls who had Blastocystis infection but no symptoms. The study was repeated in 2003 at Ain Shams University
Ain Shams University
Ain Shams University is an institute of higher education located in Cairo, Egypt. Founded in 1950, the university provides education at the undergraduate, graduate and post-graduate levels.-History:...
in Egypt with Egyptian patients with equivalent results.
Fecal Antibody Testing: A 2003 study at Ain Shams University in Egypt indicated that patients symptomatically infected could be distinguished with a fecal antibody test. The study compared patients diagnosed with symptomatic Blastocystis infection to controls who had Blastocystis infection but no symptoms. In the group with symptoms, IgA antibodies to Blastocystis were detected in fecal specimens that were not present in the healthy control group.
Stool Culture: Culturing has been shown to be a more reliable method of identifying infection. In 2006, researchers reported the ability to distinguish between disease causing and non-disease causing isolates of Blastocystis using stool culture. Blastocystis cultured from patients who were sick and diagnosed with Blastocystis infection produced large, highly adhesive amoeboid forms in culture. These cells were absent in Blastocystis cultures from healthy controls. Subsequent genetic analysis showed the Blastocystis from healthy controls was genetically distinct from that found in patients with symptoms. Protozoal culture is unavailable in most countries due to the cost and lack of trained staff able to perform protozoal culture.
Genetic Analysis of isolates: Researchers have used techniques which allow the DNA of Blastocystis to be isolated from fecal specimens. This method has been reported to be more reliable at detecting Blastocystis in symptomatic patients than stool culture. This method also allows the species group of Blastocystis to be identified. Research is continuing into which species groups are associated with symptomatic (see Genetics and Symptoms) blastocystosis.
Immuno-Fluorescence (IFA) Stain: An IFA stain causes Blastocystis cells to glow when viewed under a microscope, making the diagnostic method more reliable. IFA stains are in use for Giardia
Giardia
Giardia is a genus of anaerobic flagellated protozoan parasites of the phylum Metamonada in the supergroup "Excavata" that colonise and reproduce in the small intestines of several vertebrates, causing giardiasis, commonly known as Beaver fever...
and Cryptosporidium
Cryptosporidium
Cryptosporidium is a protozoan that can cause gastro-intestinal illness with diarrhea in humans.Cryptosporidium is the organism most commonly isolated in HIV positive patients presenting with diarrhea...
for both diagnostic purposes and water quality testing. A 1991 paper from the NIH described the laboratory development of one such stain. However, no company currently offers this stain commercially.
Transmission and risk factors
Humans contract Blastocystis infection by drinking water or eating food contaminated with fecesFeces
Feces, faeces, or fæces is a waste product from an animal's digestive tract expelled through the anus or cloaca during defecation.-Etymology:...
from an infected human or animal. Blastocystis infection can be spread from animals to humans, from humans to other humans, from humans to animals, and from animals to animals. Risk factors for infection have been reported as following:
- International travel: Travel to less developed countries has been cited in development of symptomatic Blastocystis infection. A 1986 study in the United States found that all individuals symptomatically infected with Blastocystis reported recent travel history to less developed countries. In the same study, all hospital employees working in New York who were screened for Blastocystis were found to have asymptomatic infections.
- Military service: Several studies have identified high rates of infection in military personnel. An early account described infection of British troops in Egypt in 1916 who recovered following treatment with emetineEmetineEmetine is a drug used as both an anti-protozoal and to induce vomiting. It is produced from the ipecac root.-Early emetine-based preparations:Early use of emetine was in the form of oral administration of the extract of ipecac root, or ipecacuanha...
. A 1990 study published in Military MedicineMilitary Medicine (journal)Military Medicine is the official monthly journal of the Association of Military Surgeons of the United States. Articles published in the journal are peer-reviewed scientific papers, case reports, and editorials. The journal also publishes letters to the editor and book reviews. The journal...
from Lackland AFB in Texas concluded symptomatic infection was more common in foreign nationals, children, and immunocompromised individuals. A 2002 study published in Military Medicine of army personnel in ThailandThailandThailand , officially the Kingdom of Thailand , formerly known as Siam , is a country located at the centre of the Indochina peninsula and Southeast Asia. It is bordered to the north by Burma and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the...
identified a 44% infection rate. Infection rates were highest in privates who had served the longest at the army base. A follow-up study found a significant correlation between infection and symptoms, and identified the most likely cause as contaminated water. A 2007 newspaper article suggested the infection rate of US military personnel returning from the Gulf War was 50%, quoting the head of Oregon State UniversityOregon State UniversityOregon State University is a coeducational, public research university located in Corvallis, Oregon, United States. The university offers undergraduate, graduate and doctoral degrees and a multitude of research opportunities. There are more than 200 academic degree programs offered through the...
's Biomedicine department.
- Consumption of Untreated Water (well water): Many studies have linked Blastocystis infection with contaminated drinking water. A 1993 study of children infected symptomatically with Blastocystis in Pittsburgh indicated that 75% of them had a history of drinking well water or travel in less developed countries. Two studies in Thailand linked Blastocystis infection in military personnel and families to drinking of unboiled and untreated water. A book published in 2006 noted that in an OregonOregonOregon is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is located on the Pacific coast, with Washington to the north, California to the south, Nevada on the southeast and Idaho to the east. The Columbia and Snake rivers delineate much of Oregon's northern and eastern...
community, infections are more common in winter months during heavy rains. A research study published in 1980 reported bacterial contamination of well water in the same community during heavy rainfall. A 2007 study from China specifically linked infection with Blastocystis sp. subtype 3 with drinking untreated water. Recreational contact with untreated water, for example though boating, has also been identified as a risk factor. Studies have shown that Blastocystis survives sewage treatment plants in both the United Kingdom and Malaysia. Blastocystis cysts have been shown to be resistant to chlorination as a treatment method and are among the most resistant cysts to ozone treatment.
- Contaminated Food: Contamination of leafy vegetables has been implicated as a potential source for transmission of Blastocystis infection, as well as other gastrointestinal protozoa. A Chinese study identified infection with Blastocystis sp. subtype 1 as specifically associated with eating foods grown in untreated water.
- Daycare facilities: A Canadian study identified an outbreak of Blastocystis associated with daycare attendance. Prior studies have identified outbreaks of similar protozoal infections in daycares.
- Geography: Infection rates vary geographically, and variants which produce symptoms may be less common in industrialized countries. For example, a low incidence of Blastocystis infection has been reported in Japan. And a study of individuals infected with Blastocystis in Japan found that many (43%, 23/54) carried Blastocystis sp. subtype 2, which was found to produce no symptoms in 93% (21/23) of patients studied, in contrast to other variants which were less common but produced symptoms in 50% of Japanese individuals. Studies in urban areas of industrialized countries have found Blastocystis infection associated with a low incidence of symptoms. In contrast, studies in developing countries generally show Blastocystis to be associated with symptoms. In the United States, a higher incidence of Blastocystis infection has been reported in California and West Coast states.
- Prevalence over Time: A 1989 study of the prevalence of Blastocystis in the United States found an infection rate of 2.6% in samples submitted from all 48 states. The study was part of the CDCCenters for Disease Control and PreventionThe Centers for Disease Control and Prevention are a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services headquartered in Druid Hills, unincorporated DeKalb County, Georgia, in Greater Atlanta...
's MMWR Report. A more recent study, in 2006, found an infection rate of 23% in samples submitted from all 48 states. However, the more recent study was performed by a private laboratory located in the Western US, and emphasized samples from Western states, which have previously been reported to have a higher infection rate.
Research studies have suggested the following items are not risk factors for contracting Blastocystis infection:
- Consumption of municipal water near water plant (not a risk factor): One study showed that municipal water was free of Blastocystis, even when drawn from a polluted source. However, samples taken far away from the treatment plant showed cysts. The researchers suggested that aging pipes may permit intrusion of contaminated water into the distribution system.
- Human-to-Human transmission among adults (not a risk factor): Some research suggests that direct human-to-human transmission is less common even in households and between married partners. One study showed different members of the same household carried different subtypes of Blastocystis.
Pathogeneses
Pathogenesis refers to the mechanism by which an organism causes disease. The following disease-causing mechanisms have been reported in studies of Blastocystis infection:- Barrier Disruption: In isolates from Blastocystis sp. subtype 4, study has demonstrated that Blastocystis has the ability to alter the arrangement of F-actin in intestinal epithelial cellsEpitheliumEpithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line the cavities and surfaces of structures throughout the body, and also form many glands. Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, selective...
. Actin filamentsActinActin is a globular, roughly 42-kDa moonlighting protein found in all eukaryotic cells where it may be present at concentrations of over 100 μM. It is also one of the most highly-conserved proteins, differing by no more than 20% in species as diverse as algae and humans...
are important in stabilizing tight junctions; they in turn stabilize the barrier, which is a layer of cells, between the intestinal epithelial cells and the intestinal content. The parasite causes the actin filaments to rearrange, and so compromising barrier function. This has been suggested to contribute to the diarrheal symptoms sometimes observed in Blastocystis patients.
- Invasiveness: Invasive infection has been reported in humans and animal studies.
- Immune Modulation: Blastocystis has been shown to provoke cells from the human colon to produce inflammatory cytokines Interleukin-8 and GM-CSF. Interleukin-8 plays a role in rheumatoid arthritis.
- Protease Secretion: Blastocystis secretes a proteaseProteaseA protease is any enzyme that conducts proteolysis, that is, begins protein catabolism by hydrolysis of the peptide bonds that link amino acids together in the polypeptide chain forming the protein....
that breaks up antibodies produced and secreted into the gastrointestinal tractGastrointestinal tractThe human gastrointestinal tract refers to the stomach and intestine, and sometimes to all the structures from the mouth to the anus. ....
lumen. These antibodies, known as immunoglobulin A (IgA)AntibodyAn antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin, is a large Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique part of the foreign target, termed an antigen...
, make up the immune defense systemImmune systemAn immune system is a system of biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease by identifying and killing pathogens and tumor cells. It detects a wide variety of agents, from viruses to parasitic worms, and needs to distinguish them from the organism's own...
of human by preventing the growth of harmful microorganisms in the body and by neutralizing toxinToxinA toxin is a poisonous substance produced within living cells or organisms; man-made substances created by artificial processes are thus excluded...
s secreted by these microorganisms. By breaking up the antibodies, it allows the persistence of Blastocystis in the human gut. Another more recent study has also shown and proposed that, in response to the proteases secreted by Blastocystis, the intestinal host cellsHost (biology)In biology, a host is an organism that harbors a parasite, or a mutual or commensal symbiont, typically providing nourishment and shelter. In botany, a host plant is one that supplies food resources and substrate for certain insects or other fauna...
would signal a series of events to be carried out, eventually leading to the self-destruction of the host cells – a phenomenon known as apoptosisApoptosisApoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
- Other secretory mechanism: A study of a different protozoan which produces similar symptoms, Entamoeba histolyticaEntamoeba histolyticaEntamoeba histolytica is an anaerobic parasitic protozoan, part of the genus Entamoeba. Predominantly infecting humans and other primates, E. histolytica is estimated to infect about 50 million people worldwide...
, found that organism secretes several neurologically active chemicals, such as serotoninSerotoninSerotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract, platelets, and in the central nervous system of animals including humans...
and Substance PSubstance PIn the field of neuroscience, substance P is a neuropeptide: an undecapeptide that functions as a neurotransmitter and as a neuromodulator. It belongs to the tachykinin neuropeptide family. Substance P and its closely related neuropeptide neurokinin A are produced from a polyprotein precursor...
. Serum levels of serotoninSerotoninSerotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract, platelets, and in the central nervous system of animals including humans...
have been found to be elevated in patients with Entamoeba histolyticaEntamoeba histolyticaEntamoeba histolytica is an anaerobic parasitic protozoan, part of the genus Entamoeba. Predominantly infecting humans and other primates, E. histolytica is estimated to infect about 50 million people worldwide...
. One paper noted the diffuse symptoms of Blastocystis infection correlate with serotoninSerotoninSerotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract, platelets, and in the central nervous system of animals including humans...
's role in the body, and suggested a similar mechanism may be present in Blastocystis infection.
Treatment
There is a lack of scientific study to support the efficacy of any particular treatment. An additional review published in 2009 made a similar conclusion, noting that because the diagnostics in use have been unreliable, it has been impossible to determine whether a drug has eradicated the infection, or just made the patient feel better. Historical reports, such as one from 1916, note difficulty associated with eradication of Blastocystis from patients, describing it as "an infection that is hard to get rid of."A 1999 in vitro from Pakistan study found 40% of isolates are resistant to common antiprotozoal drugs. A study of isolates from patients diagnosed with IBS found 40% of isolates resistant to Metronidazole
Metronidazole
Metronidazole is a nitroimidazole antibiotic medication used particularly for anaerobic bacteria and protozoa. Metronidazole is an antibiotic, amebicide, and antiprotozoal....
and 32% resistant to furazolidone
Furazolidone
Furazolidone is a nitrofuran antibacterial. It is marketed by Roberts Laboratories under the brand name Furoxone and by GlaxoSmithKline as Dependal-M.-Uses:It is used to treat diarrhoea and enteritis caused by bacteria or protozoan infections....
. Drugs reported in studies have included Metronidazole
Metronidazole
Metronidazole is a nitroimidazole antibiotic medication used particularly for anaerobic bacteria and protozoa. Metronidazole is an antibiotic, amebicide, and antiprotozoal....
, TMP-SMX
Co-trimoxazole
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole or co-trimoxazole is a sulfonamide antibiotic combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole, in the ratio of 1 to 5, used in the treatment of a variety of bacterial infections.The name co-trimoxazole is the British Approved Name, and has been marketed worldwide...
, Doxycycline
Doxycycline
Doxycycline INN is a member of the tetracycline antibiotics group, and is commonly used to treat a variety of infections. Doxycycline is a semisynthetic tetracycline invented and clinically developed in the early 1960s by Pfizer Inc. and marketed under the brand name Vibramycin. Vibramycin...
, Nitazoxanide
Nitazoxanide
Nitazoxanide, also known by the brand names Alinia and Annita is a synthetic nitrothiazolyl-salicylamide derivative and an antiprotozoal agent.Nitazoxanide is a light yellow...
Iodoquinol and Paromomycin. Iodoquinol has been found to be less effective in practice and in-vitro. Miconazole
Miconazole
Miconazole is an imidazole antifungal agent, developed by Janssen Pharmaceutica, commonly applied topically to the skin or to mucus membranes to cure fungal infections. It works by inhibiting the synthesis of ergosterol, a critical component of fungal cell membranes...
has been reported as an agent against Blastocystis growth in-vitro.
Physicians have described the successful use of a variety of discontinued antiprotozoals in treatment of Blastocystis infection. Emetine
Emetine
Emetine is a drug used as both an anti-protozoal and to induce vomiting. It is produced from the ipecac root.-Early emetine-based preparations:Early use of emetine was in the form of oral administration of the extract of ipecac root, or ipecacuanha...
was reported as successful in cases in early 20th century with British soldiers who contracted Blastocystis infection while serving in Egypt. In vitro testing showed emetine
Emetine
Emetine is a drug used as both an anti-protozoal and to induce vomiting. It is produced from the ipecac root.-Early emetine-based preparations:Early use of emetine was in the form of oral administration of the extract of ipecac root, or ipecacuanha...
was more effective than Metronidazole
Metronidazole
Metronidazole is a nitroimidazole antibiotic medication used particularly for anaerobic bacteria and protozoa. Metronidazole is an antibiotic, amebicide, and antiprotozoal....
or furazolidone
Furazolidone
Furazolidone is a nitrofuran antibacterial. It is marketed by Roberts Laboratories under the brand name Furoxone and by GlaxoSmithKline as Dependal-M.-Uses:It is used to treat diarrhoea and enteritis caused by bacteria or protozoan infections....
. Emetine is available in the United States through special arrangement with the Center for Disease Control. Clioquinol
Clioquinol
Clioquinol is an antifungal drug and antiprotozoal drug. It is neurotoxic in large doses. It is a member of a family of drugs called hydroxyquinolines which inhibit certain enzymes related to DNA replication...
(Entero-vioform) was noted as successful in treatment of Blastocystis infection but removed from the market following an adverse event in Japan. Stovarsol
Acetarsol
Acetarsol is an anti-infective.It was first discovered in 1921 at Pasteur Institute by Ernest Fourneau, and sold under the brand name Stovarsol . It has been given in suppositories.-References:...
and Narsenol, two arsenic-based antiprotozoals, were reported to be effective against the infection. Carbarsone was available as an anti-infective compound in the United States as late as 1991, and was suggested as a possible treatment. The reduction in the availability of antiprotozoal drugs has been noted as a complicating factor in treatment of other protozoal infections. For example, in Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
, production of diloxanide furoate
Diloxanide furoate
Diloxanide furoate is an anti-protozoal drug used in the treatment of Entamoeba histolytica and some other protozoal infections.-Safety and effectiveness:...
ended in 2003, paromomycin is available under special access provisions, and the availability of iodoquinol is limited.
Epidemiology


- A nation-wide study conducted by the CDCCenters for Disease Control and PreventionThe Centers for Disease Control and Prevention are a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services headquartered in Druid Hills, unincorporated DeKalb County, Georgia, in Greater Atlanta...
using data reported from 1987 found the prevalence Blastocystis infection in the United States to be 2.6%. The study indicated that Western states, such as California, reported a higher prevalence.
- A 2000 study by a private laboratory of stool samples from 48 states in the United States identified a prevalence of 23%. The study was conducted by a laboratory in Arizona and emphasized Western states which have previously been found to have higher rates of Blastocystis infection.
- A Canadian study of samples received in 2005 identified Blastocystis as the most prevalent protozoal infection identified.
- A study in Pakistan identified Blastocystis infection in 7% of the general population and 46% of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. The study used stool culture for identification.
In other animals
Experimental infection in immunocompetent and immunocompromised mice has produced intestinal inflammation, altered bowel habits, lethargy and death. Chronic diarrhea has been reported in non-human higher primates.Research
While many enteric protists are the subject of research, Blastocystis is unusual in that basic questions concerning how it should be diagnosed and treated and how it causes disease remain unsettled. The following groups have ongoing research programs directed at these questions:| Country | Organization | Year Established | Research focus | Research | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singapore | National University of Singapore National University of Singapore The National University of Singapore is Singapore's oldest university. It is the largest university in the country in terms of student enrollment and curriculum offered.... |
1991 | Co-culture, pathogenesis | Tan Singh |
|
| Malaysia | University of Malaya University of Malaya The University of Malaya is located on a campus near the centre of Kuala Lumpur, and is the oldest university in Malaysia. It was founded in 1905 as a public-funded tertiary institution... |
1996 | Ultrastructure, pathogenicity | Kumar | |
| United States | Blastocystis Research Foundation | 2006 | Phylogenetics, pathogenicity, treatment |
Article | |
| Denmark | Statens Serum Institut Statens Serum Institut Statens Serum Institut , or SSI for short, is a Danish sector research institute located on the island of Amager in Copenhagen. Its purpose is to combat and prevent infectious diseases, congenital disorders, and threats from weapon of mass destruction... |
2006 | Diagnostics | Stensvold |
See also
- BlastocystisBlastocystisBlastocystis is a genus of single-celled protozoan parasites belonging to a group of organisms known as the Stramenopiles that includes algae, diatoms, and water molds...
- List of parasites (human)
- History of emerging infectious diseasesHistory of emerging infectious diseasesThe discovery of disease-causing pathogens is an important activity in the field of medical science, as many viruses, bacteria, protozoa, fungi, helminthes and prions are identified as a confirmed or potential pathogen...

