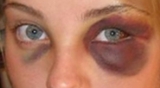
Blunt trauma
Encyclopedia
In medical
terminology, blunt trauma, blunt injury, non-penetrating trauma or blunt force trauma refers to a type of physical trauma
caused to a body part, either by impact, injury or physical attack; the latter usually being referred to as blunt force trauma. The term itself is used to refer to the precursory trauma, from which there is further development of more specific types of trauma, such as concussions, abrasions, lacerations, and/or bone fracturing
. Blunt trauma is contrasted with penetrating trauma
, in which an object such as a bullet enters the body.
or dashboard
, causing contusions
in less serious cases or rupturing of internal organs due to briefly increased intraluminal pressure in more serious cases where speed or forward force is greater.
Abdominal trauma caused by deceleration and impact shows a similar effect to trauma to any other part of the body; namely the rupturing or damage of free and relatively fixed objects, a classic example of such an injury would be a hepatic tear along the ligamentum teres followed with injuries to the renal arteries
.
As with most trauma, blunt abdominal trauma is often the cause of further injury, depending upon the severity of the accident. In the majority of cases, the liver
and spleen
(see Blunt splenic trauma
) are most severely affected, followed by damage to the small intestine
. Recent studies utilizing CT scanning have suggested that hepatic and other concomitant injuries may develop from blunt abdominal trauma.
In rare cases, BAT has been attributed to several medical techniques such as the Heimlich Maneuver, attempts at cardiopulmonary resuscitation, and manual thrusts to clear an airway. Although these are rare causes of blunt abdominal trauma, it is often thought that they are caused by applying unnecessary pressure when administering such techniques.
Among equestrians
with BAT, common causes include kicks from the horse and the horse falling on top of its rider.
".
Usually, in the case of examination, areas such as the head or those linked with the respiratory system
have a higher priority, and are examined before the abdomen, so as to administer, if necessary, medical treatments which will immediately limit the amount of progressive damage which could be caused from such injuries. The amount of time spent on diagnosing abdominal injury should be minimal, and expedited by using relatively quick methods of determining the extent of such injury, such as by identifying free intra-abdominal fluid through diagnostic peritoneal lavage (DPL)
before recommending a laparotomy
if the situation requires one.
. Most cases require IV therapy
along with other methods of stabilisation such as securing the airway or providing a respirator
.
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
terminology, blunt trauma, blunt injury, non-penetrating trauma or blunt force trauma refers to a type of physical trauma
Physical trauma
Trauma refers to "a body wound or shock produced by sudden physical injury, as from violence or accident." It can also be described as "a physical wound or injury, such as a fracture or blow." Major trauma can result in secondary complications such as circulatory shock, respiratory failure and death...
caused to a body part, either by impact, injury or physical attack; the latter usually being referred to as blunt force trauma. The term itself is used to refer to the precursory trauma, from which there is further development of more specific types of trauma, such as concussions, abrasions, lacerations, and/or bone fracturing
Bone fracture
A bone fracture is a medical condition in which there is a break in the continuity of the bone...
. Blunt trauma is contrasted with penetrating trauma
Penetrating trauma
Penetrating trauma is an injury that occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue of the body, creating an open wound. In blunt, or non-penetrating trauma, there may be an impact, but the skin is not necessarily broken. The penetrating object may remain in the tissues, come back out...
, in which an object such as a bullet enters the body.
Blunt abdominal trauma (BAT)
Blunt abdominal trauma is often referred to as the most common type of trauma, representing around 50 to 75 percent of blunt trauma. The majority of BAT is often attributed to car-to-car collisions, in which rapid deceleration often propels the driver forwards into the steering wheelSteering wheel
A steering wheel is a type of steering control in vehicles and vessels ....
or dashboard
Dashboard
A dashboard is a control panel placed in front of the driver of an automobile, housing instrumentation and controls for operation of the vehicle....
, causing contusions
Bruise
A bruise, also called a contusion, is a type of relatively minor hematoma of tissue in which capillaries and sometimes venules are damaged by trauma, allowing blood to seep into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Bruises can involve capillaries at the level of skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscle,...
in less serious cases or rupturing of internal organs due to briefly increased intraluminal pressure in more serious cases where speed or forward force is greater.
Abdominal trauma caused by deceleration and impact shows a similar effect to trauma to any other part of the body; namely the rupturing or damage of free and relatively fixed objects, a classic example of such an injury would be a hepatic tear along the ligamentum teres followed with injuries to the renal arteries
Renal artery
The renal arteries normally arise off the side of the abdominal aorta, immediately below the superior mesenteric artery, and supply the kidneys with blood. Each is directed across the crus of the diaphragm, so as to form nearly a right angle with the aorta....
.
As with most trauma, blunt abdominal trauma is often the cause of further injury, depending upon the severity of the accident. In the majority of cases, the liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
and spleen
Spleen
The spleen is an organ found in virtually all vertebrate animals with important roles in regard to red blood cells and the immune system. In humans, it is located in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen. It removes old red blood cells and holds a reserve of blood in case of hemorrhagic shock...
(see Blunt splenic trauma
Blunt splenic trauma
Blunt splenic trauma occurs when a significant impact to the spleen from some outside source damages or ruptures the spleen. Treatment varies depending on severity, but often consists of embolism or splenectomy. -Cause:...
) are most severely affected, followed by damage to the small intestine
Intestine
In human anatomy, the intestine is the segment of the alimentary canal extending from the pyloric sphincter of the stomach to the anus and, in humans and other mammals, consists of two segments, the small intestine and the large intestine...
. Recent studies utilizing CT scanning have suggested that hepatic and other concomitant injuries may develop from blunt abdominal trauma.
In rare cases, BAT has been attributed to several medical techniques such as the Heimlich Maneuver, attempts at cardiopulmonary resuscitation, and manual thrusts to clear an airway. Although these are rare causes of blunt abdominal trauma, it is often thought that they are caused by applying unnecessary pressure when administering such techniques.
Among equestrians
Equestrianism
Equestrianism more often known as riding, horseback riding or horse riding refers to the skill of riding, driving, or vaulting with horses...
with BAT, common causes include kicks from the horse and the horse falling on top of its rider.
Diagnosis
Although blunt trauma is a condition in itself, the main emphasis on the diagnosis of blunt trauma is to ascertain the cause of the accident, any further injury and its correlation with the medical, dietary, and physiological history of the patient gathered from various sources, such as family and friends, or previous physicians, in order to establish the most swift path to recovery. This method is given the mnemonic "SAMPLESAMPLE History
SAMPLE history is an mnemonic acronym to remember key questions for a person's assessment. The SAMPLE history is usually taken along with vital signs. It is used for alert people, but often much of this information can also be obtained from the family of an unresponsive person...
".
Usually, in the case of examination, areas such as the head or those linked with the respiratory system
Respiratory system
The respiratory system is the anatomical system of an organism that introduces respiratory gases to the interior and performs gas exchange. In humans and other mammals, the anatomical features of the respiratory system include airways, lungs, and the respiratory muscles...
have a higher priority, and are examined before the abdomen, so as to administer, if necessary, medical treatments which will immediately limit the amount of progressive damage which could be caused from such injuries. The amount of time spent on diagnosing abdominal injury should be minimal, and expedited by using relatively quick methods of determining the extent of such injury, such as by identifying free intra-abdominal fluid through diagnostic peritoneal lavage (DPL)
Diagnostic peritoneal lavage
Diagnostic peritoneal lavage is a procedure where, after application of local anesthesia, a vertical skin incision is made one third of the distance from the umbilicus to the pubic symphysis. The linea alba is divided and the peritoneum entered after it has been picked up to prevent bowel...
before recommending a laparotomy
Laparotomy
A laparotomy is a surgical procedure involving a large incision through the abdominal wall to gain access into the abdominal cavity. It is also known as coeliotomy.- Terminology :...
if the situation requires one.
Treatment
Whenever any blunt trauma is sustained to the body, it is normal to ensure first that there is no bleeding, internal or back injury, or breathing problems before administering any type of rehabilitative care to the patient. In cases of car accidents, or where a patient has had some form of accelerated impact, the likelihood is that there will be progressive damage to internal organs, as well as the fracturing of bones, both of which are dealt with by splinting fractures and controlling external hemorrhagingBleeding
Bleeding, technically known as hemorrhaging or haemorrhaging is the loss of blood or blood escape from the circulatory system...
. Most cases require IV therapy
Intravenous therapy
Intravenous therapy or IV therapy is the infusion of liquid substances directly into a vein. The word intravenous simply means "within a vein". Therapies administered intravenously are often called specialty pharmaceuticals...
along with other methods of stabilisation such as securing the airway or providing a respirator
Medical ventilator
A medical ventilator can be defined as any machine designed to mechanically move breatheable air into and out of the lungs, to provide the mechanism of breathing for a patient who is physically unable to breathe, or breathing insufficiently....
.
See also
- Blunt splenic traumaBlunt splenic traumaBlunt splenic trauma occurs when a significant impact to the spleen from some outside source damages or ruptures the spleen. Treatment varies depending on severity, but often consists of embolism or splenectomy. -Cause:...
- Blunt trauma personal protective equipmentBlunt trauma personal protective equipmentBlunt Trauma Personal Protective Equipment protects the wearer against injuries caused by blunt impacts. For law enforcement, corrections, military, and other personnel involved in emergency response operations, the protection against blunt impact threats can be a matter of life or death...
- Geriatric traumaGeriatric traumaGeriatric trauma refers to a traumatic injury that occurs to an elderly person. The three prevailing causes of traumatic death in the elderly are falls , traffic collisions and burns....
- Penetrating traumaPenetrating traumaPenetrating trauma is an injury that occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue of the body, creating an open wound. In blunt, or non-penetrating trauma, there may be an impact, but the skin is not necessarily broken. The penetrating object may remain in the tissues, come back out...
- Pediatric traumaPediatric traumaPediatric trauma refers to a traumatic injury that happens to an infant, child or adolescent.-Anatomic and physiologic differences in children:There are significant anatomical and physiological differences between children and adults...

